Summary
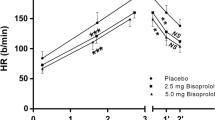
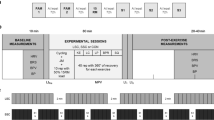
In 15 healthy, not specifically trained volunteers (age: 26.6±2.7 years) single equipotent doses of a selective β1-blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) (200 mg Epanolol-Visacor; V) and of a selective β1-blocker without ISA (100 mg Metoprolol; M) were compared with placebo (P) with respect to their influence upon physical performance capacity and metabolism in a random, double blind, cross-over experimental setting. The subjects underwent three step by step incremental treadmill tests and three treadmill endurance tests until volitional exhaustion. Maximum running speed and maximum oxygen uptake were used as measures of maximum performance capacity. Running speed and oxygen uptake related to individual anaerobic threshold, and running time and running distance in the endurance tests were used as measures of endurance capacity. Both maximum and endurance performances were reduced significantly by β-blockade. No relevant differences were discerned between V and M. The uniform reduction in exercise heart rate with both β-blockers demonstrated the application of equipotent doses. At rest, heart rate was significantly higher under V than under M. Carbohydrate metabolism was unaffected, both βblockers showing equal inhibition of lipolysis during exercise. We conclude that intrinsic sympathomimetic activity has no influence upon physical performance and metabolism during selective β1-blockade.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhras F, Smyth P, Jefferies S, Jackson G (1985) “Visacor”, a new once daily cardioselective beta-blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity for stable angina (abstract). Cardiovasc Pharmacother, International Symposium, Geneva, April 22–25
Borg GAV (1973) Perceived exertion: a note on “history” and methods. Med Sci Sports 5:90–93
Carlsson E, Fellenius E, Lundborg P, Svensson E (1978) β-adrenoceptor blockers, plasma-potassium, and exercise. Lancet II:424–425
Clausen T, Flatman JA (1980) β2-adrenoceptors mediate the stimulating effect of adrenaline on active electrogenic NAK transport in rat soleus muscle. Br J Pharmacol 68:749–755
Fellenius E (1983) Muscle fatigue and beta-blockers — a review. Int J Sports Med 4:1–8
Franz IW, Lohmann FW (1979) Der Einfluß einer chronischen sog. kardioselektiven und nicht kardioselektiven Beta-Rezeptoren-Blockade auf den Blutdruck, die Sauerstoffaufnahme und den Kohlenhydratstoffwechsel. Z Kardiol 68:503–509
Frisk-Holmberg M, Jorfeld L, Juhlin-Dannfelt A (1981) Metabolic effects in muscle during antihypertensive therapy with beta1- and beta1/beta2-adrenoceptor blockers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 30:611–618
Kaiser P, Hylander B, Eliasson K, Kaijser L (1985) Effect of beta1-selective and nonselective beta blockade on blood pressure relative to physical performance in men with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 55:79D-84D
Keul J, Linnet N, Eschenbruch E (1968) The photometric autotitration of free fatty acids. Z Klin Chem Biochem 6:394–398
Kindermann W, Scheerer W, Salas-Fraire O, Biro G, Wölfing A (1984) Verhalten der körperlichen Leistungsfähigkeit und des Metabolismus unter akuter Beta1- und Beta1/2-Blockade. Z Kardiol 73:380–387
Kullmer T, Kindermann W (1985) Physical performance and serum potassium under chronic beta-blockade. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:350–354
Lohmann FW (1981) Die Beeinflussung des Stoffwechsels durch Beta-Rezeptoren-Blocker. Klin Wochenschr 59:49–57
Lundborg P, Åström H, Bengtsson C, Fellenius E, von Schenk H, Svensson L, Smith U (1981) Effect of betablockade on exercise performance and metabolism. Clin Sci 61:229–305
Norris SC, Harry JD, Smith HJ, Morton P, Cook SKK (1985) Does ISA alter subjective awareness of beta-adrenoceptor blockade? Proc Br Pharmacol Soc C6:249
Pringle TH, O'Connor PC, McNeill AJ, Riddell JG, Shanks RG (1985) Beta-adrenoceptor blocking activity and cardioselectivity in man of ICI 141,292. Br J Clin Pharmacol 19:137–138
Schnabel A, Kindermann W, Salas-Fraire O, Cassens J, Steinkraus V (1983) Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on supramaximal exercise capacity. Int J Sports Med 4:278–281
Smith HJ, Halliday SF, Carl DCN, Stribling D (1983) Effects of selective (beta1- and beta2) and nonselective beta adrenoceptor antagonists on the cardiovascular and metabolic responses to isoproterenol: comparison with ICI 141,292. Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:211–215
Stegmann H, Kindermann W, Schnabel A (1981) Lactate kinetics and individual anaerobic threshold. Int J Sports Med 2:160–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kullmer, T., Kindermann, W. & Singer, M. Effects on physical performance of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) during selective β1-blockade. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 292–298 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690895
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690895