Conclusions
-
1.
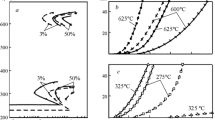
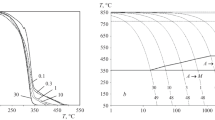
Plastic deformation by stretching accelerates and ensures the more complete intermediate transformation of austenite.
-
2.
The strengthening treatment, consisting of deformation of supercooled austenite in the initial stage of the intermediate transformation with subsequent completion of the transformation at the same temperature, makes it possible to increase the strength without a corresponding increase in hardness.
-
3.
This strengthening treatment is most effective in the temperature range of the intermediate transformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. M. Baranov, Metalloved. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., Nos. 4, 8 (1963).
Ya. S. Umanskii, B. N. Finkel'shtein, M. E. Blanter, S. T. Kishkin, N. S. Fastov, and S. S. Gorelik, Physical Metal Science [in Russian], Metallurgizdat (1956).
Additional information
Leningrad Mechanical Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 67–69, April, 1967.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baranov, S.M., Karatushin, S.I. Thermomechanical treatment of steel in the process of isothermal transformation of supercooled austenite. Met Sci Heat Treat 9, 317–319 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652977
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652977