Abstract
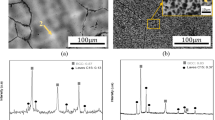
The oxide formed over polished iron-carbon alloys at 300°C and in a 100 Torr dry oxygen atmosphere was primarily due to the oxidation of the ferrite phase, but a thin protective oxide film (∼ 150 Å) was formed on the carbide phase. The protective nature was attributed to the existence of a kinetic barrier of CO and CO2 at the carbide-oxide interface. The initial oxide film formed on the carbide phase comprised many small, randomly oriented crystallites; approximately 70 Å in size, of γ-Fe2O3. This film then underwent a grain growth process via a strain-induced grain boundary migration accompanied by a phase transformation from γ-Fe2O3 to α-Fe2O3. This transformation produced a tensile stress in the oxide film which was later relieved by the generation of cracks along the newly grown grain boundaries. These cracks exposed fresh carbide surface, released the gas barrier at the carbide-oxide interface, and provided rapid diffusional paths for further oxidation. As a result, the oxide film (α-Fe2O3) was reduced to Fe3O4 and raised ridges appeared at the crack sites. Once the cracks were healed, the film again became protective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. W. Webb, J. T. Norton, and C. Wagner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 103, 112 (1956).
C. Wagner,Z. Phys. Chem. (B)22, 181 (1933).
R. W. Stewart and I. B. Cutler,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 50, 176 (1967).
J. Freel and A. K. Galwey,Trans. Faraday Soc. 63, 404 (1967).
R. B. Runk and H. J. Kim,Oxidation of Metals 2 (3), 285 (1970).
K. Hauffe,Oxidation of Metals (Plenum Press, New York, 1965).
P. A. Beck,Phil. Mag. Supplement 3, 245 (1954).
P. A. Beck and P. R. Sperry,J. Appl. Phys. 21, 150 (1950).
P. A. Beck,Metal Interfaces (American Society for Metals, Cleveland, 1955), p. 208.
W. E. Boggs, R. H. Kachik, and G. E. Pellissier,J. Electrochem. Soc. 112, 539 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by grant number DA-18-035-98(A) from the Chemical Research Laboratory, Edgewood Arsenal, Department of the Army. This paper is based on work performed as part of a thesis submitted by H. J. Kim to Lehigh University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree in Metallurgy and Materials Science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.J., Runk, R.B. The characterization of the thin oxide film formed over Fe3C at 300°C. Oxid Met 2, 307–318 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614623
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614623