Summary
Felodipine, a selective arteriolar dilator, was given to 13 hypertensive patients to assess its hypotensive effects and duration of action. Nine patients were treated with 5 mg three times a day and 4 with 10 mg three times a day.
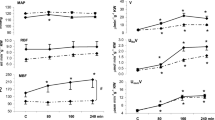
Mean blood pressures fell with both treatment regimens: 5 mg placebo 170/103 mmHg; 5 mg felodipine 148/91 mmHg; 10 mg placebo 154/93 mmHg; 10 mg felodipine 137/82 mmHg.
Heart rates increased as blood pressures fell with both treatments. However, in the patients given 5 mg three times a day this effect was less noticeable after successive doses.
Plasma concentrations of noradrenaline, both resting and tilted, increased after felodipine. There was a negative correlation between the fall in blood pressure and the increase in noradrenaline, suggesting that those patients with good baroreceptor reflexes were better able to counteract the effects of vasodilatation.
Four of the nine patients treated with 5 mg felodipine three times a day experienced mild and transient adverse effects. Of the four patients treated with 10 mg three times a day, three experienced moderate to severe headache, and for this reason recruitment into this group was stopped.
Felodipine at a divided daily dose of 15 mg effectively lowered blood pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahnoff M (1984) Determination of felodipine in plasma by gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Pharm Biomed Analysis 2: 519–526
Aoki K, Yoshida T, Kato S, Tazumi K, Sato I, Takikawa K, Hotta K (1976) Hypotensive action and increased plasma renin activity by Ca++ antagonist (nifedipine) in hypertensive patients. Jpn Heart J 17: 479–484
Been M, Macfarlane PW, Hillis WS (1985) Electrophysiological effects of felodipine. Drugs 29 [Suppl 2]: 76–80
Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG, Kauffman MP, Dangel A (1981) Operational sensitivity and acute resetting of aortic baroreceptors in dogs. Circ Res 48: 676–684
Culling W, Ruttley MSM, Sheridan DJ (1984) Acute haemodynamic effects of felodipine during beta-blockade in patients with coronary artery disease. Br Heart J 52: 431–434
Da Prada M, Zurcher G (1976) Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma on tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the fentomole range. Life Sci 19: 1161–1174
Davis JO, Freeman (1976) Mechanism regulating renin release. Physiol Rev 56: 1–56
Doward PK, Andresen MC, Burke SL, Oliver JR, Komer PI (1982) Rapid resetting of the aortic baroreceptors in the rabbit and its complications for short term and longer term reflex control. Cir Res 50: 428–439
Elmfeldt D, Hedner T (1983) Felodipine — a new vasodilator in addition to beta-receptor blockade in hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25: 571–575
Elmfeldt D, Hedner T (1985) Antihypertensive effects of felodipine compared with placebo. Drugs 29 [Suppl 2]: 109–116
Erne P, Bolli P, Bertel O, Hulthen UL, Kiowski W, Muller FD, Buhler FR (1983) Factors influencing the hypotensive effects of calcium antagonists. Hypertension 5 [Suppl II]: II-97
Gould BA, Mann S, Kieso H, Bala Subramanian V, Raftery EB (1982) The 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure profile with verapamil. Circulation 65: 22–27
Hallback-Nordlander M, Thalen P (1983) Differentiated resetting of vagal and sympathetic component of baroreflex control in SHR — effect of antihypertensive therapy with felodipine. J Hypertension 1 [Suppl 2]: 217–219
Johnsson G, Murray RG, Tweddel A, Hutton I (1983) Haemodynamic effects of a new vasodilator drug, felodipine, in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24: 49–53
Jones RI, Hornung RS, Sonecha T, Raftery EB (1983) The effect of a new calcium channel blocker nicardipine on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure and the pressor response to isometric and dynamic exercise. J Hypertension 1: 85–90
Lederballe-Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E, Christensen NJ, Kornerup HJ, Pedersen EB (1979) Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15: 235–240
Ljung B (1985) Vascular selectivity of felodipine. Drugs 29 [Suppl 2]: 46–58
McLeay RAB, Stallard TJ, Watson RDS, Littler WA (1983) The effect of nifedipine on arterial pressure and reflex cardiac control. Circulation 67: 1084–1090
Raemsch KD, Sommer J (1983) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nifedipine. Hypertension 5 [Suppl II, No 4]: II-18–II-24
Waite MA (1973) Measurement of concentration of angiotensin I in human blood by radioimmunoassay. Clin Sci Mol Med 45: 51–64
Watson RDS, Stallard TJ, Flinn RM, Littler WA (1980) Factors determining direct arterial pressure and its variability in hypertensive man. Hypertension 2: 333–341
Young MA, Watson RDS, Littler WA (1984) Baroreflex setting and sensitivity after acute and chronic nicardipine therapy. Clin Sci 66: 233–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mace, P.J.E., Stallard, T.J. & Littler, W.A. Felodipine in hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29, 383–389 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613449
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613449