Abstract
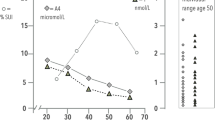
Sixty postmenopausal women suffering from genuine stress incontinence were recruited into a double-blind study comparing the effects of oral and intravaginal estrogens and placebo, alone and in combination with the alpha-adrenoreceptor stimulant drug phenyl-propanolamine (PPA). Side effects were more common with orally administered estrogen, whereas symptomatic improvements were greater than the vaginal route. Plasma estrone and estradiol were both elevated more when estrogen was given by the oral (x 3–4) than vaginal (x 2) route, although the estradiol/estrone ratio was lower with oral therapy; the biochemical alterations increased with increasing chronological age and menopausal age, and were slightly enhanced by the concurrent administration of PPA. Diurnal and nocturnal urinary frequency were both reduced to a greater extent with vaginal than oral estrogen treatment, and more when used with PPA. Stress incontinence was improved subjectively in all treatment groups, although objective improvement was maximal in those treated with vaginal estrogen plus PPA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith P. Age changes in the female urethra.Br J Urol 1972; 42: 667–676
van Keep P, Lauritzen C.Aging and Oestrogens, Basel Karger, 1973
Hilton P. Urethral pressure measurement by microtransducer: observations on themethodology, the pathophysiology of genuine stress incontinence, and the effects of its treatment in the female [MD Thesis]. Newcastle upon Tyne: University of Newcastle upon Tyne, 1981
Caine M, Raz S. The role of female hormones in stress incontinence. In: Proceedings of the 16th Congress of the International Society of Urologists. Amsterdam. 1973: 30
Walter S, Wolf H, Barlebo H, Kaalund-Jensen H. Urinary incontinence in post-menopausal women treated with oestrogens: a double-blind clinical trial.Urol Int 1970; 33: 135–143
Wilson PD, Faragher B, Butler B, Bu'Lock D, Robinson EL, Brown ADG. Treatment with oral piperazine sulphate for genuine stress incontinence in post-menopausal women.Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1987; 94:568–574
Rud T. The effects of oestrogens and gestagens on the urethral pressure profile in urinary continent and stress incontinent women.Acta Obstet Gynecol. Scand. 1980; 59: 265–270
Hilton P, Stanton SL. The use of intravaginal oestrogen cream in genuine stress incontinence.Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1983; 90: 940–944
Tanagho EA, Meyers FH, Smith D. Urethral resistance: its components and implications. I. Smooth muscle component.Invest Urol 1969; 7: 136–149
Donker PJ, Ivanovici F, Noach EL. Analysis of the urethral pressure profile by means of electromyography and the administration of drugs.Br J Urol 1972; 40: 180–193
Ek A, Alm P, Andersson K-E, Persson CGA. Adrenergic and cholinergic nerves of the human urethra and urinary bladder. A histochemical study.Acta Physiol Scand 1977; 90: 345–352
Gosling JA, Dixon J, Lendon RG. The autonomic innervation of the human male and female bladder neck and proximal urethra.J. Urol 1977; 118:302–305
Stewart BH, Banowsky LHW, Montague DK. Stress incontinence: conservative therapy with sympatomimetic drugs.J. Urol 1976; 115:558–559
Montague DK, Stewart BH. Urethral pressure profiles before and after Ornade administration in patients with stress urinary incontinence.J. Urol 1979; 122: 198–199
Hilton P, Stanton SL, The use of midodrine in genuine stress incontinence. In: Proceedings of the XIIth annual meeting of the International Continence Society, Leiden, Netherlands. 1982; 23–24
Hilton P, Stanton SL. Urethral pressure measurement by microtransducer: the results in normal women and in those with genuine stress incontinence.Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1983; 90: 919–934
Mayne CJ, Hilton P. The short pad-test: standardisation of method and a comparison with the one hour test.Neurourol Urodyn 1988; 7: 443–446
Abrams P, Blaivas JG, Stanton SL, Andersen JT. Standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function.Neurourol Urodyn 1988; 7: 403–427
Schreiter F, Fuchs P, Stockamp K. Estrogenic sensitivity of alphareceptors in the urethra musculature.Urol Int 1976; 31: 13–19
Ford SP, Reynolds LP, Farley DB, Bhatnagar RK, van Orden DE. Interaction of ovarian steroids and periarterial alpha1-adrenergic receptors in altering uterine blood flow during the estrous cycle of gilts.Am J. Obstet Gynecol 1984; 150: 480–484
Ek A, Andersson K-E, Gullberg B, Ulmsten U. Effects of oestradiol and combined norephedrin and oestradiol treatment on female stress incontinence.Zentralbe Gynakol 1980; 102: 839–844
Beisland HO, Fossberg E, Moer A, Sander S. Urethral sphinteric insufficiency in post-menopausal females: treatment with phenylpropanolamine and estriol separately and in combination.Urol Int 1984; 39: 211–216
Kiesswetter H, Hennrich F, Englisch M. Clinical and urodynamic assessment of pharmacologic therapy of stress incontinence.Urol Int 1983; 38: 58–63
Ryan KJ, Engel LL. The interconversion of oestrone and oestradiol by human tissue slices.Endrocinology 1953; 52: 287–291
Rigg LA, Hermann H, Yen SC. Absorption of estrogens from vaginal creams.N. Engl J Med 1978; 298: 195–197
Englund DE, Johansson EDB. Plasma levels of oestrone, oestradiol and gonadotrophins in postmenopausal women after oral and vaginal administration of conjugated equine oestrogens (Premarin),Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1978; 85: 957–964
Whitehead MI, Minardi J, Kitchen Y, Sharples MJ. Systematic absorption of estrogen from Premarin vaginal cream. In: Cooke ID, ed. The role of estrogen/progrestogen in the management of the menopause. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1978: 63–75
Paterson MEL, Wade-Evans T, Sturdee DW, Thom MH, Studd JW. Endometrial disease after treatment with oetrogens and progesterones in the climacteric.Br Med J 1980; 822–824
Thom MH, White PJ, Williams RM, Sturdee DW, Paterson MEL, Wade-Evans T, Studd JWW. Prevention and treatment of endometrical pathology in climacteric women receiving oestrogen therapy. Lancet II: 455–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilton, P., Tweddell, A.L. & Mayne, C. Oral and intravaginal estrogens alone and in combination with alpha-adrenergic stimulation in genuine stress incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 1, 80–86 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00600027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00600027