Abstract
Male guinea pigs were exposed continuously to 5°C for 2–18 weeks (BW=239–1074 g) or to an ambientPO2=80 mm Hg for 2–14 weeks (BW=244–965g). Control guinea pigs were kept at 22°C and an average ambientPO2 of 133 mm Hg.
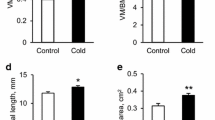
The right and the left ventricular free walls were separated from the septum and weighed (RVW and LVW). Myoglobin concentrations [Mb] of the right and the left ventricles were measured. In all animals, total heart weights (THW), RVW and LVW were linearly related to BW. In the control animals, ventricular [Mb] increased with BW for 2–3 weeks after birth but remained unchanged thereafter. In the 5°C animals, after 4 weeks of exposure, [Mb] in the right and the left ventricles was significantly higher than that of the controls. THW also was significantly higher in the 5°C animals. Furthermore, this cold-induced cardiac hypertrophy was due to both right and left ventricular hypertrophy. In hypoxia-acclimated animals, after 14 weeks of exposure toPO2=80 mm Hg, the [Mb] of the RV was significantly higher than that of the controls, whereas there was no significant difference between the [Mb] of the LV of the control and hypoxic animals. THW was significantly higher in the hypoxic guinea pigs than in the controls or the 5°C animals. The hypoxia-induced cardiac hypertrophy was due to a marked right ventricular hypertrophy while LVW was significantly lower in the hypoxic animals than in the controls
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, A. F., Jensen, R.: Gross cardiac changes in cattle with high mountain (Brisket) disease and in experimental cattle maintained at high altitude. Am. J. Vet. Res.20, 680–689 (1959)
Beznák, M.: The behaviour of the weight of the heart and the blood pressure of albino rats under different conditions. J. Physiol.124, 44–63 (1954)
Booth, N. H., Maaske, C. A., Nielsen, T. W.: Ventricular weight ratios of normal swine and from swine with pulmonic stenosis. J. Appl. Physiol.21, 1256–1260 (1966)
Burton, R. R., Smith, A. H.: Effect of polycythemia and chronic hypoxia on heart mass in the chicken. J. Appl. Physiol.22, 782–785 (1967)
Butler, P. J.: The effects of progressive hypoxia on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems of the chicken. J. Physiol.191, 309–324 (1967)
Chauca, D., Bligh, J.: An additive effect of cold exposure and hypoxia on pulmonary artery pressure in sheep. Res. Vet. Sci.21, 123–124 (1976)
Criscuolo, D., Clark, R. T., Mefferd, R. B.: Effect of low and high iron supplementation on hypoxic rats. Am. J. Physiol.180, 215–218 (1955)
Cueva, S., Sillau, H., Valenzuela, A., Ploog, H.: High altitude induced pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure in broiler chickens. Res. Vet. Sci.16, 370–374 (1974)
Dawson, C. A., Nadel, E. R., Horvath, S. M.: Cardiac output in the cold-stressed swimming rat. Am. J. Physiol.214, 320–325 (1968)
Hart, J. S.: Comparative physiology of thermoregulation. Vol. 2. New York, New York: Academic Press 1971
Hartley, L. H., Alexander, J. K., Modelski, M., Grover, R. F.: Subnormal cardiac output at rest and during exercise in residents at 3,100 m altitude. J. Appl. Physiol.23, 839–848 (1967)
Heroux, O., Gridgeman, N. T.: The effect of cold-acclimation on the size of organs and tissue of the rat, with special reference to modes of expression of results. Can J. Biochem. Physiol.36, 209–216 (1958)
Hultgren, H. N., Marticorena, E., Miller, H.: Right ventricular hypertrophy in animals at high altitude. J. Appl. Physiol.18, 913–918 (1963)
Hurtado, A., Rotta, A., Merino, C., Pons, J.: Studies of myohemoglobin at high altitudes. Am. J. Med. Sci.194, 708–713 (1937)
Jansky, L., Hart, J. S.: Cardiac output and organ blood flow in warm-and cold-acclimated rats exposed to cold. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.46, 653–659 (1968)
Lechner, A. J.: Respiratory adaptations in burrowing pocket gophers from sea level and high altitude. J. Appl. Physiol.41, 168–173 (1976)
Lechner, A. J., Salvato, V. L., Banchero, N.: Hematology in guinea pigs acclimated to hypoxia during growth. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. (in press 1980)
Lin, Y.-C., Dawson, C. A., Horvath, S. M.: The expression of cardiac output in the albino rat,Rattus rattus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.33, 901–909 (1970)
McGrath, J. J.: Acclimation response of pigeons to simulated high altitude. J. Appl. Physiol.31, 274–276 (1971)
Morrison, P., Rosenmann, M., Sealander, J. A.: Seasonal variation of myoglobin in the northern red-back vole. Am. J. Physiol.211, 1305–1308 (1966)
Popovic, V., Kent, K., Mojovic, N., Mojovic, B., Hart, J. S.: Effect of exercise and cold on cardiac output in warm-and cold-acclimated rats. Fed. Proc.28, 1138–1142 (1969)
Reynafarje, B.: Simplified method for the determination of myoglobin. J. Lab. Clin. Med.61, 138–145 (1963)
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G.: Statistical Methods. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press 1967
Steffen, J. M., Roberts, J. C.: Temperature acclimation in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus): Biochemical and organ weight changes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.58B, 237–242 (1977)
Tappan, D. V., Reynafarje, B.: Tissue pigment manifestations of adaptation to high altitudes. Am. J. Physiol.190, 99–103 (1957)
Tucker, C. F., James, W. E., Berry, M. A., Johnstone, C. J., Grover, R. F.: Depressed myocardial function in the goat at high altitude. J. Appl. Physiol.41, 356–361 (1976)
Turek, Z., Ringnalda, B. E. M., Graudtner, M., Kreuzer, F.: Myoglobin distribution in the heart of growing rats exposed to a simulated altitude of 3,500 m in their youth or born in the low pressure chamber. Pflügers Arch.340, 1–10 (1973)
Valdivia, E.: Right ventricular hypertrophy in guinea pigs exposed to simulated high altitude. Circ. Res.5, 612–616 (1957)
Weathers, W. W., Snyder, G. K.: Functional acclimation of Japanese quail to simulated altitude. J. Comp. Physiol.93, 127–137 (1974)
Whipple, G. H.: The hemoglobin of striated muscle I. Variations due to age and exercise. Am. J. Physiol.76, 693–707 (1926)
Will, H. D., McMurty, I. F., Reeves, J. T., Grover, R. F.: Cold-induced pulmonary hypertension in cattle. J. Appl. Physiol.45, 469–473 (1978)
Wittenberg, J. B.: Myoglobin-facilitated oxygen diffusion: role of myoglobin in oxygen entry into muscle. Physiol. Rev50, 559–636 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Bui, M., Banchero, N. Effects of chronic exposure to cold or hypoxia on ventricular weights and ventricular myoglobin concentrations in guinea pigs during growth. Pflugers Arch. 385, 155–160 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588696
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588696