Summary
The ATPase activity of actomyosin prepared from taenia coli muscle of guinea pig was found to increase upon adding rabbit skeletal heavy meromyosin (HMM) in the absence of Ca2+. SDS-gel electrophoresis of muscle homogenates did not reveal the presence of troponin. Ca2+-regulation in taenia coli muscle thus appears to be myosin-linked.
The glycerinated muscles which did not develop any tension in the presence of EGTA contracted after irrigation with rabbit skeletal myosin.
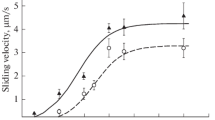
Skeletal HMM could also cause tension generation in strips of glycerinated taenia coli in the presence of EGTA. The tension developed by the muscles in the presence of Ca2+ was increased if HMM was added. The HMM-induced tension was associated with a marked increase in ATPase activity both in the presence and in the absence of Ca2+. No HMM-associated tension could be detected when inactivated HMM was employed or when MgATP was substituted with Mg-pyrophosphate or Mg-AMP-PNP.
The mechanical effect of HMM probably results from a mechanochemical interaction between the added HMM and muscle actin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma, N., Watanabe, S.: The major component of metin from rabbit skeletal and bovine cardiac muscle. J. biol. Chem.240, 2847–3851 (1965)
Bárány, M., Conover, T. E., Schlieselfeld, L. H., Gaetjens, E., Gaffart, M.: Relation of properties of isolated myosin to those of intact muscles of the sloth. Europ. J. Biochem.2, 156–164 (1967)
Bohr, D. F., Filo, R. S., Guthe, K. F.: Contractile proteins in vascular smooth muscle. Physiol. Rev., Suppl.5, 98–112 (1962)
Bremel, R. D.: Myosin linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. Nature (Lond.)252, 405–406 (1974)
Ebashi, S., Endo, M.: Calcium ions and muscle contraction. Progr. Biophys. molec. Biol.18, 123–183 (1968)
Filo, R. S., Bohr, D. F., Rüegg, J. C.: Glycerinated skeletal and smooth muscle: calcium and magnesium dependence. Science147, 1581–1583 (1965)
Gadasi, H., Oplatka, A., Lamed, R., Muhlrad, A.: A comparative study of muscle contraction and superprecipitation using trinitrophenylated myosin subfragments. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.58, 913–918 (1974)
Gordon, A. R., Siegman, M. J.: Mechanical properties of smooth muscle. I. Length-tension and force-velocity relation. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 1243–1249 (1971)
Ishikawa, H., Bischoff, R., Holtzer, H. C.: Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J. Cell Biol.43, 312–328 (1969)
Lamed, R., Oplatka, A.: Applications of immobilized ATP in the study of myosin. Biochemistry13, 3137–3142 (1974)
Lehman, W., Szent-Györgyi, A. G.: Regulation of muscular contraction. Distribution of actin control and myosin control in the animal kingdom. J. gen. Physiol.66, 1–30 (1975)
Lowey, S., Cohen, C.: Studies on the structure of myosin. J. molec. Biol.4, 293–308 (1962)
Lowey, S., Slayter, H. S., Weeds, A. G., Baker, H.: Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J. molec. Biol.42, 1–29 (1969)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Mrwa, U., Rüegg, J. C.: Myosin-linked calcium regulation in vascular smooth muscle. FEBS Letters60, 81–84 (1975)
Oplatka, A.: Some elementary aspects of mechanochemical coupling in actomyosinoid systems and their possible relevance to the platelet contractile system. Haemostasis4, 131–142 (1975)
Oplatka, A., Borejdo, J., Gadasi, H. P.: Tension development in stretched glycerinated muscle fibers and contractions of “ghost” myofibrils induced by irrigation with heavy meromyosin. FEBS Letters45, 55–58 (1974b)
Oplatka, A., Borejdo, J., Gadasi, H., Tirosh, R., Liron, N., Reisler, E.: Contraction of glycerinated muscle fibers, myofibrils and actin threads induced by water soluble myosin fragments. In: Proteins of contractile systems, Proc. FEBS Meetings, Vol. 31 (FEBS Meeting, Budapest, August 1974), pp. 41–46 Budapest: Akademiai Kiado 1975a
Oplatka, A., Gadasi, H., Borejdo, J.: The contraction of “ghost” myofibrils and glycerinated muscle fibers irrigated with heavy meromyosin subfragment-1. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.58, 905–912 (1974c)
Oplatka, A., Gadasi, H., Tirosh, R., Lamed Y., Muhlrad, A., Liron, N.: Demonstration of mechanochemical coupling in systems containing actin, ATP, and non-aggregating active myosin derivatives. J. Mechanochem. Cell Motil.2, 295–306 (1974a)
Pollard, T. D., Weihing, R. R.: Actin and myosin and cell movement. Biochemistry2, 1–65 (1974)
Schädler, M.: Proportionale Aktivierung von ATPase-Aktivität und Kontraktionsspannung durch Calciumionen in isolierten contractilen Strukturen verschiedener Muskelarten. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.296, 70–90 (1967)
Sobieszek, A., Bremel, R. D.: Preparation and properties of vertebrate smooth muscle myofibrils and actomyosin. Eur. J. Biochem.55, 49–60 (1975)
Sobieszek, A., Small, J. V.: Myosin-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. J. molec. Biol.102, 75–92 (1976)
Stracher, A., Chan, P. C.: Studies on the adenosinetriphosphate active center of myosin. In: Biochemistry of muscle contraction (J. Gergely, ed.), pp. 106–113. London: Churchill 1964
Weber, K., Osborn, M.: The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. biol. Chem.244, 4406–4412 (1969)
Weis-Fogh, T., Amos, W. B.: Evidence for new mechanism of cell motility. Nature (Lond.)236, 301–304 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a Katzir-Katchalsky fellowship (to J. B.) and by a grant from the Muscular Dystrophy Association of America (to A. O.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borejdo, J., Oplatka, A. Evidence for myosin-linked regulation in guinea pig taenia coli muscle. Pflugers Arch. 366, 177–184 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585875
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585875