Summary
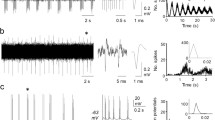
Compound action potentials evoked by electrical stimulation in the brainstem of anaesthetized, paralyzed cats and rabbits were recorded distally in the carotid sinus nerve. The latencies of the components of the responses were indicative of fibres with conduction velocities between 0.5 and 32 m/s. These include both myelinated and unmyelinated fibres. Using histological reconstructions of the ‘responsive sites’, the termination of the primary afferent fibres of the sinus nerve within the medulla was mapped.
In both cat and rabbit these responsive sites were restricted to thedorsomedial medulla in the vicinity of the NTS 0–3 mm rostral to the obex. Although in the cat the fast conducting myelinated fibres (conduction velocities >12.5 m/s) were discretely localized to the ventrolateral area of the NTS, the slower conducting myelinated and unmyelinated fibres were found more diffusely, spreading into areas dorsal and medial to the NTS. In the rabbit the terminals of all types of fibre were mainly confined to the NTS although some C fibres appeared to be grouped in the juxta-alar region. Responses were never evoked from the medial reticular formation or nucleus ambiguus in either cats or rabbits.
The organization of the sinus nerve input to the medulla is discussed in the light of these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, A. L.: The brain stem of the cat. Madison: University Wisconsin Press 1968
Biscoe, T. J., Sampson, S. R.: Rhythmical and non-rhythmical spontaneous activity recorded from the central cut end of the sinus nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.)196, 327–338 (1968)
Biscoe, T. J., Sampson, S. R.: Field potentials evoked in the brainstem of the cat by stimulation of the carotid sinus, glossopharyngeal, aortic and superior laryngeal nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.)209, 341–358 (1970a)
Biscoe, T. J., Sampson, S. R.: Responses of cells in the brainstem of the cat to stimulation of the sinus, glossopharyngeal, aortic and superior laryngeal nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.)209, 359–373 (1970b)
Borison, H. L., Brizzee K. R.: Morphology of emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone in cat medulla oblongata. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)77, 38–42 (1951)
Brizzee, K. R., Neal, L. M.: A re-evaluation of the cellular morphology of the area postrema in view of recent evidence for a chemoreceptor function. J. comp. Neurol.100, 41–62 (1954)
Cammermeyer, J.: Is the area postrema a neuro-vegetative nucleus? Acta anat. (Basel)2, 294–320 (1947)
Clemente, C. D., Breeman, V. L. van: Nerve fibres in the area postrema of cat, rabbit, guinea pig and rat. Anat. Rec.123, 65–80 (1955)
Cottle, M. K.: Degeneration studies of primary afferents of IXth and Xth cranial nerves in the cat. J. comp. Neurol.122, 329–343 (1964)
Crill, W. E., Reis, D. J.: Distribution of carotid sinus and depressor nerves in the cat brain stem. Amer. J. Physiol.214, 269–276 (1968)
Culberson, J. L., Kimmel, D. L.: Central distribution of primary afferent fibres of the glossopharyngeal and vagal nerves in the opossum Didelphis viginiana. Brain Res.44, 325–335 (1972)
Davies, R. O., Edwards, M. W.: Distribution of carotid body chemoreceptor afferents in the medulla of the cat. Brain Res.64, 451–454 (1973)
De Groat, W. C., Lalley, P. M.: Reflex sympathetic firing in response to electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve in the cat. Brain Res.80, 17–40 (1974)
Douglas, W. W., Ritchie, J. M.: Cardiovascular reflexes produced by electrical excitation of non-medullated afferents in the vagus, carotid sinus and aortic nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.)134, 167–178 (1956)
Douglas, W. W., Schaumann, W.: A study of depressor and pressor components of the cat's carotid sinus and aortic nerves using electrical stimuli of different intensities and frequencies. J. Physiol. (Lond.)132, 173–186 (1956)
Douglas, W. W., Ritchie, J. M., Schaumann, W.: Depressor reflexes from medullated and non-medullated fibres in the rabbit's aortic nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.)132, 187–198 (1956)
Erlanger, J., Gasser, H. S.: Electrical signs of nervous activity. Philadelphia: Univ. Pennsylvania Press 1937
Eyzaguirre, C., Uchizono, K.: Observations on the fibre content of nerves reaching the carotid body of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)159, 268–281 (1961)
Fidone, S. J., Sato A.: A study of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor A and C-fibres in the cat carotid nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.)205, 527–548 (1969)
Fussey I. F., Kidd, C., Whitwam, J. G.: Activity evoked in the brain stem by stimulation of C fibres in the cervical vagus nerve of the dog. Brain Res.49, 436–440 (1973)
Gabriel, M., Seller, H.: Interaction of baroreceptor afferents from carotid sinus and aorta at the nucleus tractus solitarii. Pflügers Arch.318, 7–20 (1970)
Heymans, C., Neil, E.: Reflexogenic areas of the cardiovascular system. London: Churchill 1958
Homma, S., Miura, M., Reis, D. J.: Intracellular recording from paramedian reticular neurones monosynaptically excited by stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve. Brain Res.18, 185–188 (1970)
Humphrey, D. R.: Neuronal activity in the medulla oblongata of cat evoked by stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve. In: Baroreceptors and Hypertension (P. Kezdi, ed.). Oxford: Pergamon 1967
Jankowska, E., Roberts, W. J.: An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)222, 597–622 (1972)
Kerr, F. W. L.: Facial, vagal and glossopharyngeal nerves in the cat. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)6, 264–281 (1962)
Kimmel, D. L., Kimmel, C. B.: Spinal distribution of glossopharyngeal and vagal afferent nerve fibers in the cat, rat and guinea pig. Anat. Rec.148, 299–300 (1964)
King, L. S.: Cellular morphology in the area postrema. J. comp. Neurol.66, 1–22 (1937).
Kötter, V., Zerbst, E., Schulze, A.: Untersuchungen zur Bahnung und Konvergenz pressorreceptorischer Afferenzen mit Hilfe der Konditions-Testreiztechnik. Pflügers Arch.320, 210–232 (1970)
Kumada, M., Nakajima, H.: Field potentials evoked in rabbit brain stem by stimulation of the aortic nerve. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 575–582 (1972)
Lipski, J., McAllen, R. M., Spyer, K. M.: The sinus nerve and baroreceptor input to the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)251, 61–78 (1975)
Lipski, J., McAllen, R. M., Spyer, K. M.: The carotid chemoreceptor input to the inspiratory neurones of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. J. Physiol. (Lond.)258, 115–116P (1976)
Little, R., Wennergren, G., Öberg B.: Aspects of the central integration of arterial baroreceptor and cardiac ventricular receptor reflexes in the cat. Acta physiol. scand.93, 85–96 (1975)
McAllen, R. M.: Projections of the carotid sinus baroreceptors to the medulla of the cat. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Birmingham 1973
McAllen, R. M., Spyer, K. M.: ‘Baroreceptor’ neurones in the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)222, 68–69P (1972)
McAllen, R. M., Spyer K. M.: The location of cardiac vagal preganglionic motoneurones in the medulla of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)258, 187–204 (1976)
Meessen, H., Olszewski, J.: A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the rhombencephalon of the rabbit. Basel: Karger 1949
Merrill, E. G.: Finding a respiratory function for the medullary respiratory neurons. pp. 451–486 in Essays on the Nervous System (R. Bellairs and E. G. Gray, eds.). Oxford: Clarendon Press 1974
Merrill, E. G., Aisnworth, A.: Glass-coated platinum-plated tungsten microelectrodes. Med. Biol. Eng.10, 662–672 (1972)
Mitchell, R. A., Herbert, D. A.: The effect of carbon dioxide on the membrane potential of medullary respiratory neurones. Brain Res.75, 345–349 (1974)
Miura, M., Reis, D. J.: Electrophysiological evidence that the carotid sinus nerve fibers terminate in the bulbar reticular formation. Brain Res.9, 394–397 (1968)
Miura, M., Reis D. J.: Termination and secondary projections of carotid sinus nerve in the cat brain stem. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 142–153 (1969)
Miura, M., Reis, D. J.: The role of solitary and paramedian reticular nuclei in mediating cardiovascular reflex responses from carotid baro- and chemoreceptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.)223, 525–548 (1972)
Neil, E., O'Regan, R. G.: Effects of sinus and aortic nerve efferents on arterial chemoreceptor function. J. Physiol. (Lond.)200, 69–71 (1969)
Niechaj, A., Dyba, S.: Conditioning of depressor responses evoked by stimulation of aortic nerve in the rabbit. Arch. intern. Physiol. Biochem.82, 663–668 (1974)
Ranson, S. W., Billingsley, P. R.: Vasomotor reactions from stimulation of the floor of the fourth ventricle. Studies in vasomotor reflex arcs; III. Amer. J. Physiol.41, 85–90 (1916)
Rhoton, A. L., O'Leary, J. L., Ferguson, J. P.: The trigeminal, facial, vagal and glossopharyngeal nerves in the monkey. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)14, 530–540 (1966)
Sampson, S. R., Mills, E.: Effects of sympathetic stimulation on discharges of carotid sinus baroreceptors. Amer. J. Physiol.218, 1650–1653 (1970)
Schwaber, J., Schneiderman, N.: Aortic nerve-activated cardio-inhibitory neurons and interneurons. Amer. J. Physiol.229, 783–789 (1975)
Seller, H., Illert, M.: The localization of the first synapse in the carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex pathway and its alteration of the afferent input. Pflügers Arch.306, 1–19 (1969)
Spyer, K. M.: Organisation of baroreceptor pathways in the brainstem. Brain Res.87, 221–226 (1975)
Spyer, K. M., Wolstencroft, J. H.: Problems of the afferent input to the paramedian reticular nucleus, and the central connections of the sinus nerve. Brain Res.26, 411–414 (1971)
Torvik, A.: Afferent connections to the sensory trigeminal nuclei, the nucleus of the solitary tract and adjacent structures. J. comp. Neurol.106, 51–141 (1956)
Wilson, J. T.: On the anatomy of the calamus region in the human bulb; with an account of a hitherto undescribed ‘nucleus postremus’. J. Anat. Physiol.40, 210–241, 357–386 (1906)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordan, D., Spyer, K.M. Studies on the termination of sinus nerve afferents. Pflugers Arch. 369, 65–73 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580812
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00580812