Abstract
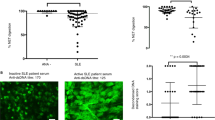
Recently it has been suggested that anti-dsDNA antibodies (Abs) promote tissue damage in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by cross-reactivity with highly negatively charged tissue components such as heparan sulphate (HS), the major glycosaminoglycan of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Other authors, however, support the theory of DNA-anti-dsDNA immune complex deposition in situ. To further elucidate the possible role of HS antibodies, we developed a new ELISA system with heparan sulphate bound to solid phase. SLE patients (n=40) showed a higher reactivity against HS (mean=28.4, SD=34.3) as compared to normal donors (n=28, mean=15.2, SD=6.3) and patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n=35, mean=14.3, SD=6.4). The addition of native dsDNA or HS to SLE sera was followed by a dose-dependent reduction in anti-HS reactivity. In contrast, in an anti-dsDNA ELISA, no reduction was observed when HS was added to SLE sera. An increase in reactivity was observed when SLE sera with and without a prior incubation with dsDNA were digested with DNAse I or II. After the purification of serum samples by protein A sepharose under dissociative conditions, seven out of eight SLE patients showed an increase in anti-HS reactivity. No correlation of the anti-HS Abs was found with organ involvement or other serological parameters. We concluded, that there is evidence for a direct anti-HS Ab reactivity in SLE sera. A part of these antibodies seems to show low avidity anti-dsDNA cross-reactivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koffler D, Schur PH, Kunke HG (1967) Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of SLE. J Exp Med 126:607–624
Stollar DB (1978) Nucleic acid antigens. In: Sela M (ed) The antigens, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–85
Tan EM, Schur PH, Carr RI, Kunkel HG (1966) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in serum of patients with SLE. J Clin Invest 45:1732–1740
Swaak AJG, SmeenkRJT (1985) Clinical differences between SLE patients in relation to the avidity of their anti-dsDNA. In: Peters M (ed) Protides of the biological fluids, vol 33. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 317–320
Bernstein RM, Hobbs RN, Lea DJ, Ward DJ, Hughes GRV (1985) Patterns of anti-histone antibody specificity in systemic rheumatic disease, primary sicca syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 28:285–289
Gripenberg M, Helve T, Kurki P (1985) Profiles of antibodies to histones, DNA and IgG in patients with systemic rheumatic diseases detemined by ELISA. J Rheumatol 12:934–941
Koffler D, Agnello V, Thoburn R, Kunkel HG (1971) SLE prototype of immune complex nephritis in man. J Exp Med [Suppl] 134:169–179
Eilat D (1985) Crossreactions of anti-DNA-Ab and the central dogma of lupus nephritis. Immunol Today 6:123–127
Faaber P, Capel PJA, Rijke GPM, Vier Winden G, v d Putte LBA, Koene RAP (1984) Crossreactivity of anti-DNA-antibodies with proteoglycans. Clin Exp Immunol 55:502–508
Faaber P, Rijke GMP, vd Putte LBA, Capel PJA, Berden JHM (1986) Crossreactivity of human and murine anti-DNA-antibodies with heparan sulphate, the major glycos-aminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest 77:1824–1830
Madaio MP, Carlson J, Cataldo J, Ucci A, Miglioreni P, Pankewycz O (1987) Murine monoclonal anti-DNA-antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol 138:2883–2890
Raz E, Brezis M, Rosenmann E, Eilat D (1989) Anti-DNA-antibodies bind directly to renal antigens and induce kidney dysfunction in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Immunol 142: 3076–3081
Sabbaga J, Peres LSR, Potocnjak P, Madaio MP (1989) A murine nephritogenic monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody binds directly to mouse laminin, the major non-collagenous protein component of the GBM. Eur J Immunol 19:137–144
Fraquhar MG, Courtoy PJ, Leukins MC, Kanwar YS (1982) Current knowledge of the functional architecture of the glomerular basement membrane. In: Kuehn K, Scoene H, Timpl R (eds) New trends in basement membrane research. Raven Press, New York, p 9
Groggel GC, Stevenson J, Hovingh P, Linker A, Border WA (1988) Changes in heparan sulphate correlate with increased glomerular permeability. Kidney Int 33:517–525
Kanwar YS, Jakubowski ML (1983) Distribution of sulphated GAG in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial matrix. Eur J Cell Biol 31:290–296
Termaat RM, Brinkman K, Nossent JC, Swaak AJG, Smeenk RJT, Berden JHM (1990) Anti-heparan-sulphate reactivity in sera from patients with SLE with renal or non-renal manifestations. Clin Exp Immunol 82:268–278
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield N, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of SLE. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Winkler T, Haenschel TA, Kalies J, Baenkler HW, Skwaril F, Kalden JR (1983) Constant isotype pattern of anti-DNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 72:434–439
Emlen W, Pisetski DS, Taylor RP (1986) Antibodies to DNA, a perspective. Arthritis Rheum 29:1417–1426
Lafter EM, Rauch J, Andrzejewski G, Stollar BD, Schwartz RS (1981) Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med 153: 897–909
Shoenfeld Y, Rauch J, Massicotte M, Stollar BD, Schwartz RS (1983) Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibody produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med 308:414–420
Smeenk RJT, Brinkman K, v d Brink HG, Westgeest AA (1988) Reaction patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA. J Immunol 140:3786–3792
Cotran RS, Reinke HG (1983) Anionic sites and the mechanisms of proteinuria. N Engl J Med 309:1050–1057
Aotsuka S, Okawa-Takatsuji M, Kinoshita M, Yokohari R (1988) Analysis of negatively charged dye-binding antibodies reactive with double stranded DNA and HS in serum from patients with rheumatic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 73:436–447
Fillit H, Shridhar PD, John DG, Valin C, Poon-King T, Zabriskie J (1985) Sera from patients with post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis contain antibodies to glomerular HS-PG. J Exp Med 161:277–289
Schmiedeke TJM, Stöckl FW, Weber R, Sugisaki Y, Batsford SR, Vogt A (1989) Histones have high affinity for the GBM. J Exp Med 169:1879–1894
Suzuki N, Harada T, Mizushima Y, Sakane T (1993) Possible pathogenetic role of cationic anti-DNA autoantibodies in the development of nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 151:1128–1136
Smeenk RJT, Lucassen WAM, Swaak TJG (1987) Is anti-cardiolipin activity a cross-reaction of anti-DNA or a separate entity. Arthritis Rheum 30:607–617
Brinkman K, Termaat RM d Jong J, v d Brink HG, Berden JHM, Smeenk RJT (1989) Crossreactive binding patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA are often caused by DNA/anti-DNA immune complexes. Res Immunol 140:595–612
Ehrenstein M, Longhurst C, Isenberg DA (1993) Production and analysis of IgG monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies from systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE) patients. Clin Exp Immunol 92:39–45
Hylkema MN, Lagemaat R van de, Kramers C, Swaak AJG, Berden JHM, Smeenk RJT (1993) Anti-heparan sulphate reactivity in relation to lupus nephritis. Second European Conference on SLE, Erlangen abstract no 26
Kramers C, Termaat RM, ter Borg EJ, Berden JH (1993) Higher anti-heparan sulphate reactivity during systemic lupus erythematosus disease exacerbations with renal manifestations, a long term prospective analysis. Clin Exp Immunol 93:34–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirner, K., Rascu, A., Nürnberg, W. et al. Evidence for direct anti-heparin-sulphate reactivity in sera of SLE patients. Rheumatol Int 14, 169–174 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00579703
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00579703