Summary
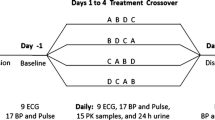
A double-blind randomised cross-over study was performed on 12 subjects suffering from reversible airway obstruction (asthma) to determine the relative bronchodilator effects of oral pseudoephedrine 60 mg, pseudoephedrine 180 mg, ephedrine 25 mg and matched placebo. Spirometry was used to measure vital capacity and forced expired volume in 1 s, and whole body plethysmography was used to measure specific airway conductance. Measurements were recorded before each drug was given, and 1 h and 2 h after each drug. Reversibility of the airway obstruction on each day of the study was demonstrated by significant improvements in all parameters of lung function in response to 400 µg of isoprenaline inhaled after the 2-h measurement. No significant bronchodilator effect could be shown following the ingestion of pseudoephedrine 60 mg or 180 mg. Only a week bronchodilator effect was demonstrated after ephedrine 25 mg in that the percentage change in vital capacity at 2 h after ephedrine was greater than that following either dose of pseudoephedrine or the placebo. It is concluded that oral pseudoephedrine in single doses of 60 mg or 180 mg has no significant bronchodilator action in man, and that a single dose of up to 180 mg pseudoephedrine does not cause tachycardia or hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Hospital Formulary (1976). Section 12:12-Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride NF
Drew CDM, Knight GT, Hughes DTD, Bush M (1978) Comparison of the effects of D-(-)-ephedrine and (-(+)-pseudoephedrine on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6:221–115
Empey DW, Young GA, Letley E, John GC, Smith P, McDonnell KA, Bagg LR, Hughes DTD (1980) Dose-response study of the nasal decongestant and cardiovascular effects of pseudoephedrine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 9:351–358
Martindale W (1977) The extra pharmacopoeia, 27th ed, pp 30–31. Wade A (ed). The Pharmaceutical Press
Permutt S (1978) What should we measure to evaluate bronchodilator drug response? Chest 73 [Suppl 6]:944–947
Silver HM, Okasaki Y (1963) The effects of pseudoephedrine in bronchospastic subjects. Curr Ther Res 5:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laitinen, L.A., Empey, D.W., Bye, C. et al. A comparison of the bronchodilator action of pseudoephedrine and ephedrine in patients with reversible airway obstruction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23, 107–109 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545963