Abstract
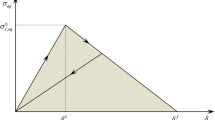
A limited study has been made of the effect of layer and bond strengths on the longitudinal tensile failure mode of an all beryllium laminate comprising a ductile (∼ 5% elongation), high purity substrate and an adhering, brittle (<1%), layer. It is proposed that the overall ductility is related to the extent of delamination at the interface which, in turn, is determined by the ratio (R) of bond strength to layer strength. When R is 0.23 extensive delamination along the gauge length is obtained resulting in maximum ductility, but at R=0.41 little separation occurs and the elongation is reduced almost to the minimum, namely that of the brittle layer. A simple calculation indicates that for the material used in this work, the influence on ductility of this mode of failure in the brittle condition may begin to be reduced when the layer is <1/3 of the total composite thickness, when multipoint delamination may be anticipated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Cook and J. E. Gordon, Phil. Mag. 282 (A) (1964) 508.
C. A. Calow, AWRE, Aldermaston, private communication.
C. A. Calow, AWRE, Aldermaston. To be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beasley, D., Bunce, J.E.J. The influence of layer and bond strengths on the ductility of an all beryllium laminate. J Mater Sci 10, 443–452 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543689
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543689