Summary
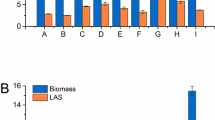
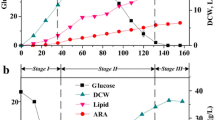
The film-submerged reactor (FSR) is a modified “Gorbach fermenter” (Gorbach 1969). Using this reactor at low rotation speed, good yeast growth was reached on n-alkanes. The biomass yield by Candida oleophila was more than 7 g/l from 1% alkanes in 48 h. Low aeration resulted in slow growth but high biomass yield, high aeration resulted in quick growth but lower yield. The optimal rotation frequency at tested conditions was 32 rpm. Alkane concentrations greater than 1% decreased the growth of C. oleophila. The influence of pH-regulation was not important, whereas the age of inoculum cultures showed significant influence on growth velocity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Faust U, Knecht R (1973) Kontinuierliche Fermentation zur mikrobiologischen Eiweißgewinnung. In: Dellweg H (Hrsg) 3. Symposium Technische Mikrobiologie. Versuchs- und Lehranstalt für Spiritusfabrikation und Fermentationstechnologie, Berlin, S 169–173
Gorbach G (1969) Die kontinuierliche Dünnschichtfermentation. Fette Seifen Anstrichmittel 71: 93–103
Kim YB, Rehm HJ (1982) Studies on a mixed culture of Candida parapsilosis and different bacilli on alkanes. II. Metabolites of C. parapsilosis and their utilization by Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 14: 112–119
Mimura A, Watanabe S, Takeda J (1971) Biochemical engineering analysis of hydrocarbon fermentation. III. Analysis of emulsification phenomena. J Ferment Technol 49: 225–271
Miura Y (1978) Mechanism of liquid hydrocarbon uptake by microorganisms and growth kinetics. Adv Biochem Eng 9:31–56
Moser A (1981) Bioprozeßtechnik. Berechnungsgrundlagen der Reaktionstechnik biokatalytischer Prozesse. Springer, Wien New York
Nakahara T, Erickson LE, Gutierrez JR (1977) Characteristics of hydrocarbon uptake in cultures with two liquid phases. Biotechnol Bioeng 19: 9–25
Phillips KL, Sallans HR, Spencer JFT (1961) Oxygen transfer in fermentation. A modified adsorption equation correlates oxygen transfer rate in unbaffled horizontal rotating fermentors. Ferment Res Eng 53:749–754
Sprenger B (1977) Einflüsse des Dispersionsgrades und der Zuluftmenge auf das Wachstum einer n-alkanverwertenden Hefe. Diplomarbeit Universität Münster, Fachbereich Biologie
Sprenger B, Rehm HJ (1983) Biomass production by Candida species from n-alkanes in a film-submerged reactor in comparison with known culture methods. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sprenger, B., Rehm, H.J. Biomass production by Candida oleophila from n-alkanes in a film-submerged reactor. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17, 265–268 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508018
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508018