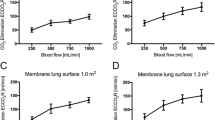
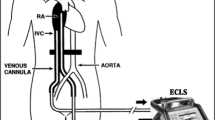
Summary
Extracorporeal CO2-removal promises to be an efficient alternative to the conservative treatment of advanced lung diseases. Extracorporeal CO2-removal is achieved in a veno-venous bypass in combination with low frequency ventilation. Positive clinical results in the treatment of adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are encouraging. In order to prove the applicability of this method to different kinds of respiratory insufficiency, physiological studies using animal models are necessary. We report here on experiments with dogs and sheep undergoing a veno-venous bypass employing a CO2-eliminator. The experimental results are compared with theoretical values which predict the important relationships between blood flow rate of the extracorporeal circulation (ECC), the CO2-elimination capacity of the CO2-eliminator and the low ventilation rate (down to apnea for 5 h) of the natural lung. It was shown that the blood gas data as well as acid base status could be maintained within physiological ranges:
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns DM, Spragg R, Moser KM (1983) The effect of venous CO2 unloading on the pattern of ventilatory output. In: Whipp BJ, Wiberg DM (eds) Modelling and control of breathing. Elsevier Science Publishing Co. Inc, New York, pp 282–289
Gattinoni L, Kolobow T, Tomlinson T, Iapichino G, Samaja M, White D, Pierce J (1978) Low frequency positive pressure ventilation with extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal: An experimental study. Anaesth Analg 57:470–477
Gattinoni L, Kolobow T, Agostoni A, Damia G, Pelizzola A, Rossi GP, Langer M, Sola R, Citterio R, Pesenti A, Fox U, Uziel L (1979) Clinical application of low frequency positive pressure ventilation with extracorporeal CO2-removal on the treatment of adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Int J Artificial Organs 2:282–283
Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Rossi GP, Vesconi S, Fox U, Kolobow T, Agostoni A, Pelizzola A, Langer M, Uziel L, Longoni F, Damia G (1980) Treatment of actue respiratory failure with low frequency positive pressure ventilation and extracorporeal removal of CO2. Lancet 11:292–294
Hecker JF (1983) The sheep as an experimental animal. Academic Press, London, pp 34–48
Kolobow T, Gattinoni L, Tomlinson T, Pierce JE (1978) An alternative to breathing. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 75:261–266
Lester A, Mottaghy K, Mussler K (183) Ein Monitoring-System zur Anzeige und überwachung von Vitalparametern und anderen Me\werten wÄhrend extrakorporaler Zirkulation. Biomed Techn 28:29
Phillipson EA, Duffin J, Cooper JD (1981) Critical dependence of respiratory rhythmicity on metabolic CO2 load. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 50:45–54
Roughton FJW (1964) In: Fenn WO, Rahn H (eds) Handbook of Physiology. American Physiology Society, Washington DC
Sandmann H (1982) Die klinische Eignung von Kapillarblut für die Blutgas- und SÄure-Basen-Diagnostik am wachen und narkotisierten Hund. Inaugural-Dissertation Justus-Liebig-UniversitÄt Gie\en
Shors EC, Huszcuzuk A, Wassermann K, Whipp BJ (1983) Effects of spinal-cord section and altered lung CO2 flow on the exercise hyperpnea in the dog. In: Whipp BJ, Wiberg DM (eds) Modelling and control of breathing. Elsevier Science Publishing Co. Inc., New York, pp 274–284
Zapol WM, Qvist J (1976) Artificial lungs for acute respiratory failure. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Reported in part at the 4th International Symposium on Aktuelle Probleme der Notfallmedizin und Intensivtherapie, Münster, 1983
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mottaghy, K., Bey, R., Oedekoven, B. et al. Extracorporeal CO2-removal: pulmonary and extracorporeal equilibria in dogs and sheep. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 54, 546–553 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422967
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422967