Abstract
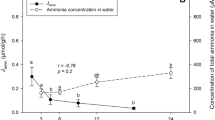
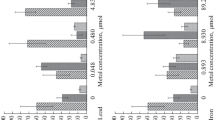
Hemolymph acid-base balance and ion concentrations were measured in shore crabs, Carcinus maenas (L.), kept in fullstrength sea water (≈33‰ S) and exposed to sublethal (0.5 mg l-1) and lethal (1 and 2 mg l-1) levels of copper in water. The study was conducted throughout the year 1987 on crabs collected near Arcachon (France). Whatever the dose, waterborne copper induced metabolic acidosis without marked changes of hemolymph ion concentrations. At the sublethal copper level, the acidosis was non-lactic and partly compensated by transitory hypocapnia. Complete recovery was observed within 20 d. At intermediate and lethal copper levels, this primary acidosis was later reinforced by hypercapnia and accumulation of lactic acid, indicating that restriction of respiratory gas exchange is the probable cause of death. A steep increase in the hemolymph calcium concentration before death suggests buffering of the acidosis by calcium-carbonate stores from the exoskeleton.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anderson, D. H., Robinson, R. J. (1946). Rapid electrometric determination of the alkalinity of seawater. Ind. Engng Chem. analyt. Edn 18: 767–769
Astrup, P. (1956). A simple electrometric technique for the determination of carbon dioxide tension in blood and plasma, total content of carbon dioxide in plasma, and bicarbonate content in “separated” plasma at a fixed carbon dioxide tension (40 mm Hg). Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 8: 33–43
Baker, J. T. P. (1969). Histological and electron microscopical observations on copper poisoning in the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26: 2785–2793
Bjerregaard, P., Vislie, T. (1986). Effect of copper on ion-and osmoregulation in the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Mar. Biol. 91: 69–76
Cardeilhac, P. T., Simpson, C. F., Lovelock, R. L., Yosha, S. F., Calderwood, H. W., Gudat, J. C. (1979). Failure of osmoregulation with apparent potassium intoxication in marine teleosts: a primary effect of copper. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 17: 231–239
Culberson, C., Pytkowicz, R. M., Hawley, J. E. (1970). Sewater alkalinity determination by the pH method. J. mar. Res. 28: 15–21
Dejours, P., Armand, J. (1980). Hemolymph acid-base balance of the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus as a function of the oxygenation and acid-base balance of the ambient water. Respir. Physiol. 41: 1–11
Depledge, M. H. (1984). Disruption of circulatory and respiratory activity in shore crabs [Carcinus maenas (L.)] exposed to heavy metal pollution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol 78C: 445–459
Hughes, G. M., Adeney, R. J. (1977). The effecs of zinc on the cardiac and ventilatory rhythms of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri, Richardson) and their responses to environmental hypoxia. Wat. Res. 11: 1069–1077
Jensen, F. B., Weber, R. E. (1987). Internal hypoxia-hypercapnia in tench exposed to aluminium in acid water: effects on blood gas transport, acid-base status and electrolyte composition in arterial blood. J. exp. Biol. 127: 427–442
McKim, J. M., Christensen, G. M., Hunt, E. P. (1970). Changes in the blood of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) after short-term and long-term exposure to copper. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 27: 1883–1889
Lauren, D. J., McDonald, D. G. (1985). Effects of copper on branchial ionoregulation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. comp. Physiol. (Sect. B) 155: 635–644
Lewis, S. D., Lewis, W. M. (1971). The effect of zinc and copper on the osmolality of blood serum of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus Rafinesque, and golden shiner, Notemigonus crysoleucas Mitchill. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 4: 639–643
Lorz, H. W., McPherson, B. P. (1976). Effects of copper or zinc in fresh water on the adaptation to sea water and ATPase activity, and the effects of copper on migratory disposition of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 33: 2023–2030
Olson, K. R., Fromm, P. O., Frantz, W. L. (1973). Ultrastructural changes of rainbow trout gills exposed to methyl mercury or mercuric chloride. Fedn Proc. Fedn Am. Socs exp. Biol. 32: p. 261
Skidmore, J. F., Tovell, P. W. A. (1972). Toxic effects of zinc sulphate on the gills of rainbow trout. Wat. Res. 6: 217–230
Spry, D. J., Wood, C. M. (1985). Ion flux rates, acid-base status, and blood gases in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri, exposed to toxic zinc in natural soft water. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 42: 1332–1341
Stagg, R. M., Shuttleworth, T. J. (1982a). The accumulation of copper in Platichthys flesus L. and its effects on plasma electrolyte concentrations. J. Fish Biol. 20: 491–500
Stagg, R. M., Shuttleworth, T. J. (1982b). The effects of copper on ionic regulation by the gills of the seawater-adapted flounder (Platichthys flesus L.). J. comp. Physiol. (Sect. B) 149: 83–90
Thurberg, F. P., Dawson, M. A., Collier, R. S. (1973). Effects of copper and cadmium on osmoregulation and oxygen consumption in two species of estuarine crabs. Mar. Biol. 23: 171–175
Truchot, J. P. (1976). Carbon dioxide combining properties of the blood of the shore crab Carcinus maenas (L.): carbon dioxide solubility coefficient and carbonic acid dissociation constants. J. exp. Biol. 64: 45–57
Zanders, I. P. (1980). Regulation of blood ions in Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65A: 97–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boitel, F., Truchot, J.P. Effects of sublethal and lethal copper levels on hemolymph acid-base balance and ion concentrations in the shore crab Carcinus maenas kept in undiluted sea water. Mar. Biol. 103, 495–501 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399581
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399581