Abstract
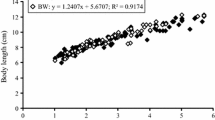
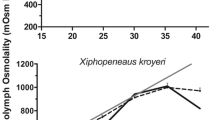
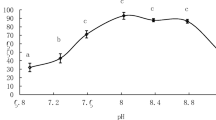
In Penaeus japonicus, the tolerance to ammonia increased with the development from nauplius to late juvenile. The 48-h LC50 of ammonia in nauplii (III–V), 96-h LC50 in zoeae (I–III), mysis (I–III), post-larvae (PL1) and late juveniles (10.4±1.1 g) were respectively 5.0, 6.1 to 8.1, 9.4 to 10.9, 15.5 and 52.7 mg Nl-1 (0.5, 0.6 to 0.7, 0.9, 1.3 and 3.1 mg NH3−Nl-1). In a chronic experiment (20 d), the LC50 in post-larvae (PL1) was 19.1 (1.4) at 96 h and 16.2 mg Nl-1 (1.3 mg NH3−Nl-1) at 480 h. Osmoregulatory capacity (OC) was calculated as the osmotic gradient between the hemolymph and the external medium at given salinities. The effects of ammonia on OC, Na+ and Cl- regulation and gill Na+−K+ ATPase activity in late juveniles were examined in fullstrength seawater, SW (1050 mosm kg-1, 36‰ S) and in dilute SW (450 mosm kg-1, 15%.), after 48 or 96 h exposure to various concentrations of ammonia. Ambient ammonia disrupted both hypo- and hyper-osmoregulation; decreased OC resulted from impaired Na+ and Cl- regulation. Gill Na+−K+ ATPase activity increased in SW and was not affected in dilute SW. The decrease of OC was ammonia-dose-dependent. The threshold ammonia concentrations affecting hypo-OC and hyper-OC were, respectively, 16 (1.3) and 32 mg Nl-1 (2.3 NH3−Nl-1) for a 48 h exposure; these concentrations were lower than the 48-h LC50 value, 65.3 mg Nl-1 (3.5 NH3−Nl-1). The time course of exposure to sublethal ammonia (48 mg Nl-1) demonstrated that the effect on osmoregulation was time-dependent. This effect was also temporary, and the exposed shrimps recovered control OC values after removal of excessive ambient ammonia. The possibility of using OC as an indicator of physiological condition in osmoregulating crustaceans and the acting mode of ammonia on osmotic and ionic regulation are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasbaster, J. S., Lloyd, R. (eds.) (1982). Water quality criteria for freshwater fish. Butterworths. London
Allan, G. L., Maguire, G. B., Hopkins, S. J. (1990). Acute and chronic toxicity of ammonia to juvenile Metapenaeus macleayi and Penaeus monodon and the influence of low dissolved-oxygen levels. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 91: 265–280
Aminot, A. (1983). Dosage de l'azote ammoniacal. In: Aminot, A., Chaussepied, M. (eds.). Manuel des analyses chimiques en milieu marin. Centre National pour l'Exploitation des Océans, Paris, p. 107–118
Armstrong, D. A., Buchanan, D. V., Mallon, M. H., Caldwell, R: S., Millemann, R. E. (1976). Toxicity of the insecticide methoxychlor to the Dungeness crab Cancer magister. Mar. Biol. 38: 239–252
Armstrong, D. A., Chippendale, D., Knight, A. W., Colt, J. E. (1978). Interaction of ionized and unionized ammonia on shortterm survival and growth of prawn larvae, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 154: 15–31
Bourguet, J.-P., Exbrayat, J.-M. (1976) A propos de la régulation ionigue du sodium et du chlore dans l'hémolymphe de Panoeus japonicus (Bate). C. r. hebd Seanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 283 (D): 59–61
Caldwell, R. S. (1974). Osmotic and ionic regulation in decapod Crustacea exposed to methoxychlor. In: Vernberg, F. J., Vernberg, W. B. (eds.) Pollution and physiology of marine organisms. Academic Press, New York, p. 197–223
Cameron, J. N. (1986). Responses to reversed NH3 and NH +4 gradients in a teleost (Ictalurus punctatus), an elasmobranch (Raja erinacea), and a crustacean (Callinectes sapidus): evidence for NH +4 /H+ exchange in the teleost and the elasmobranch. J. exp. Zool. 239: 183–195
Castille, F. L., Jr., Lawrence, A. L. (1981). A comparison of the capabilities of juvenile and adulte Penaeus setiferus and Penaeus stylirostris to regulate the osmotic, sodium, and chloride concentrations in the hemolymph. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 68(A): 677–680
Charmantier, G. (1987). L'osmorégulation chez les crevettes penaeidae (Crustacea, Decapoda). Océanis 13 (Fasc. 2): 179–196
Charmantier, G., Bouaricha, N., Charmantier-Daures, M., Thuet, P., Trilles, J.-P. (1989). Salinity tolerance and osmoregulatory capacity as indicator of the physiological state of penaeid shrimps. Spec. Publs eur. Aquat. cult. Soc. 10: 65–66
Charmantier, G., Trilles, J.-P. (1973). La pression osmotique de l'hémolymphe de Sphaeroma serratum (crustacé, isopode): variation en fonction de la salinité et de la sénescence. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 276 (D): 69–72
Charmantier-Daures, M., Thuet, P., Charmantier, G., Trilles, J.-P. (1988). Tolérance à la salinité et osmorégulation chez les postlarves de Penaeus japonicus et P. chinensis. Effet de la température. Aquat. living Resour. (Nantes) 1: 267–276
Chen, J. C., Lin, P. C., Lei, S. C. (1990). Toxicities of ammonia and nitrite to Penaeus monodon adolescents. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 89: 127–137
Chin, T. S., Chen, J. C. (1987). Acute toxicity of ammonia to larvae of the tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 66: 247–253
Colt, J. E., Armstrong, D. A. (1981). Nitrogen toxicity to crustaceans, fish and mollucs. In: Allen, L. J., Kinney, E. C. (eds.) Proceedings of the Bio-Engineering Symposium for Fish Culture. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, p. 34–47
Drach, P., Tchernigovtzeff, C. (1967). Sur la méthode de détermination des states d'intermue et son application générale aux crustacés. Vie Milieu 18(A): 595–610
Evans, D. H. (1977). Further evidence for Na+/NH +4 exchange in marine teleost fish. J. exp. Biol. 70: 213–220
Evans, D. H., Cameron, J. N. (1986). Gill ammonia transport. J. exp. Zool. 239: 17–23
Finney, D. J. (1962). Probit analysis: a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. Cambridge University Press, London
Franson, M. A. H. (ed.). (1981) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste-water. 15th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Hubert, J. J. (1980). Bioassay. Kendall Hunt Publishing Co., Toronto, Ontario
Hudinaga, M. (1942). Reproduction, development and rearing of Penaeus japonicus Bate. Japan. J. Zool. 10: 305–353
Inman, C. B. E., Lockwood, A. P. M. (1977). Some effects of methylmercury and lindane on sodium regulation in the amphipod Gammarus duebeni during changes in the salinity of its medium. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 58(C): 67–75
Ivanovici, A. M., Wiebe, W. J. (1981). Towards a working definition of “stress”: a review and critique. In: Barrett, G. W., Rosenberg, R. (eds.) Stress effects on natural ecosystems. Wiley-Interscience, Chichester, p. 13–27
Iwata, J., Shigueno, K. (1980). Osmotic concentration of hemolymph in various growth stages of Penaeus japonicus. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 46: p. 1547
Jayasankar, P., Muthu, M. S. (1983). Toxicity of ammonia to the larvae of Penaeus indicus H. Milne Edwards. Indian J. Fish. 30: 1–12
Kinne, O. (1976). Cultivation of marine organisms: water quality management and technology. In: Kinne, O. (ed.) Marine ecology. Vol. III, Part 1. Cultivation. Wiley-Interscience, Chichester, p. 79–300
Kinter, W. B., Merkens, L. W., Janicki, R. H., Guarino, A. M. (1972). Studies on the mechanism of toxicity of DDT and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): disruption of osmoregulation in marine fish. Envir. Hlth Perspectives 1: 169–173
Kormanik, G. A., Cameron, J. N. (1981). Ammonia excretion in animals that breath water: a review. Mar. Biol. Lett. 2: 11–23
Lloyd, D., Orr, L. D. (1969). The diuretic response by rainbow trout to sub-lethal concentrations of ammonia. Wat. Res. 3: 335–344
Lock, R. A. C., Cruijsen, P. M. J. M., Van Overbeeke, A. P. (1981). Effects of mercuric chloride and methylmercuric chloride on the osmoregulatory function of the gills in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 68(C): 151–159
Lucu, C., Devescovi, M., Siebers, D. (1989). Do amiloride and ouabain affect ammonia fluxes in perfused Carcinus gill epithelia? J. exp. Zool. 249: 1–5
McLusky, D. S., Hagerman, L., Mitchell, P. (1982). Effect of salinity acclimation on osmoregulation in Crangon crangon and Praunus flexuosus. Ophelia 21: 89–100
Neufeld, G. J., Pritchard, J. B. (1979). Osmoregulation and gill Na+−K+ ATPase in the rock crab, Cancer irroratus: response to DDT. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62(C): 165–172
Parry, G. (1960). Excretion. In: Waterman, T. H. (ed.) The physiology of Crustacea. Vol. 1. Metabolism and growth. Academic Press, New York, p. 341–366
Péqueux, A., Gilles, R., Marshall, W. S. (1988). NaCl transport in gills and related structures. In: Greger, R, (ed.) Advances in comparative and environmental physiology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 1–73
Piper, J. M., Lowell, S. J. (1981). One-step molybdate method for rapid determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of protein. Analyt. Biochem. 117: 70–75
Potts, W. T. W., Parry, G. (1964). Osmotic and ionic regulation in animals. Pergamon Press, London
Rainbow, P. S. (1990). Heavy metal levels in marine invertebrates. In: Furness, R. W., Rainbow, P. S. (eds.) Heavy metals in the marine environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, p. 67–79
Renfro, J. L., Schmidt-Nielsen, B., Miller, D., Benos, D., Allen, J. (1974). Methyl mercury and inorganic mercury: uptake, distribution and effect on osmoregulatory mechanisms in fishes. In: Vernberg, F. J., Vernberg, W. B. (eds.) Pollution and physiology of marine organisms. Academic Press, New York, p. 101–122
Rorive, G., Gilles, R. (1979). Intracellular inorganic osmotic effectors. In: Gilles, R. (ed.) Mechanisms of osmoregulation in animals, maintenance of cell volume. John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 83–110
Smith, P. K., Krohn, R. I., Herman Son, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Gartner, F. H., Provenzano, M. D., Fujimoto, E. K., Goeke, N. M., Olson, B. J., Klenk, D. C. (1985). Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Analyt. Biochem. 150: 76–85
Spaargaren, D. H. (1990). The effect of environmental ammonia concentrations on the ion-exchange of shore crabs, Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 97C (1): 87–91
Spotte, S. (1979). Fish and invertebrate culture: water management in closed systems. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Sprague, J. B. (1971). Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish. III. Sublethal effects and “safe” concentration. Wat. Res. 5: 245–266
Tarazona, J. V., Muñoz, M. J., Ortiz, J. A., Nuñez, M. O., Camargo, J. A. (1987). Fish mortality due to acute ammonia exposure. Aquacult. Fish. Mgmt 18: 167–172
Towle, D. W. (1984). Regulatory functions of Na+−K+ ATPase in marine and estuarine animals. In: Péqueux, A., Gilles, R., Bolis, L. (eds.) Osmoregulation in estuarine and marine animals, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 157–170
Towle, D. W. (1990). Sodium transport systems in gills. In: Kinne, R. K. H. (ed.) Comparative physiology. Vol. VII. Comparative aspects of sodium cotrasport systems. Basel, Karger, p. 241–263
Trussel, R. P. (1972). The percent unionized ammonia in aqueous solutions at different pH levels and temperature. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29: 1505–1507
Whitfield, M. (1978). The hydrolysis of ammonium ions in sea water — an experimental confirmation of predicted constants at one atmosphere pressure. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 58: 781–787
Wickins, J. F. (1976). The tolerance of warm-water prawns to recirculated water. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 9: 19–37
Young-Lai, W. W., Charmantier-Daures, M., Charmantier, G. (1991). Effect of ammonia on survival and osmoregulation in different life stages of the lobster Homarus americanus. Mar. Biol. 110: 293–300
Zaugg, W. S. (1982). A simplified preparation for adenosine triphosphatase determination in gill tissue. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 39: 215–217
Zitko, V. (1982). Letcur, the lethality curve program. Tech. Rep. Fish. aquat. Sciences Can. 1134: 1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Commnicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HP., Thuet, P., Trilles, J.P. et al. Effects of ammonia on survival and osmoregulation of various development stages of the shrimp Penaeus japonicus . Marine Biology 117, 591–598 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349770
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349770