Summary
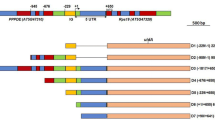
In mung bean (Vigna radiata, formerly Phaseolus aureus) one length heterogeneity in the intergenic spacer (IGS) of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is due to a variable number of 175-bp subrepeats. This spacer region downstream of the 25S rRNA coding region was characterized by seuquencing the 2.4 kb EcoRI/HindIII fragment of a 10.5 kb mung bean rDNA repeat. Within the 175-bp repetitive elements a sequence was detected showing strong similarity to the T2/T3-box (GACTTGC) found in Xenopus rDNA and involved in termination and enhancing transcription. In mung bean this sequence partly forms the stem of a possible stem-loop structure at the 3′ end of each subrepeat. Nuclease mapping of transcription termination sites (TTS) results in two signals, 65 bp and 315 bp downstream of the 3′ end of the 25S rRNA coding region. The longer transcript terminates 20 bp downstream of the stem-loop structure at the end of the first 175-bp subrepeat. A spacer model is proposed which allows “readthrough enhancement”. No cross-hybridization was observed between the 180-bp subrepeats in pea (Pisum sativum) rDNA and the mung bean 175-bp subrepeat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Moran LB, Gustafson JP (1986) The structure of DNA from the rye (Secale cereale) NOR R1 locus and its behaviour in wheat backgrounds. Can J Genet Cytol 28:673–685
Bonven BJ, Gocke E, Westergaard O (1987) A high affinity topoisomerase I binding sequence is clustered at DNase I hypersensitive sites in Tetrahymena r chromatin. Cell 41:541–555
Courvey AJ, Wang JC (1988) Influence of DNA sequence and supercoiling on the process of cruciform formation. J Mol Biol 202:35–43
Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Grellet F, Panabieres F, Ananiev ED, Delseny M (1988) Structural and transcriptional characterization of the external spacer of a ribosomal RNA nuclear gene from a higher plant. Eur J Biochem 172:767–776
Deltour R, Mosen H (1987) Proposals for the macromolecular organization of the higher plant nucleolonema. Biol Cell 60:75–86
Furlong JC, Forbes J, Robertson M, Maden BEH (1983) The external transcribed spacer and precoding region of Xenopus borealis rDNA: comparison with the corresponding region of Xenopus laevis rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 11:8183–8196
Futcher B (1988) Supercoiling and transcription, or vice versa? Trends Genet 4:271–272
Ganal M, Torres R, Hemleben V (1988) Complex structure of the ribosomal DNA spacer of Cucumis sativus (cucumber). Mol Gen Genet 212:548–554
Gerbi S (1986) Evolution of ribosomal DNA. In: MacIntyre R (ed) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Plenum, New York, p 419
Gerstner J, Schiebel K, von Waldburg G, Hemleben V (1988) Complex organization of the length heterogenous 5′ external spacer of mung bean ribosomal DNA. Genome 30:723–733
Grummt I, Maier U, Öhrlein A, Hassouna N, Bachellerie J (1985) Transcription of a mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3′ end of the 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3′spacer. Cell 43:801–810
Grummt I, Rosenbauer H, Niedermeyer H, Maier U, Öhrlein A (1986a) A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell 45:837–846
Grummt I, Kuhn A, Bartsch I, Rosenbauer H (1986b) A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell 47:901–911
Hemleben V, Ganal M, Gerstner J, Schiebel K, Torres RA (1988) Organization and length heterogeneity of plant ribosomal RNA genes. In: Kahl G (ed) Architecture of eukaryotic genes. VCH, Weinheim, p 371
Henderson S, Sollner-Webb B (1986) A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promotor of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell 47:891–900
Jordan G (1987) At the heart of the nucleolus. Nature 329:489–490
Jorgensen RA, Cuellar RE, Thompson WF, Kavanagh TA (1987) Structure and variation in ribosomal RNA genes of pea. Plant Mol Biol 8:3–12
Kato A, Yakura K, Tanifuji S (1985) Repeated DNA sequences found in the large spacer of Vicia faba rDNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 825:411–415
Kempers-Veenstra AE, Oliemans J, Offenberg H, Dekker AF, Piper PW, Planta RJ, Klootwijk J (1986) 3′-end formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J 5:2703–2710
Labhart P, Reeder RH (1986) Characterization of three sites of RNA 3′end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell 45:431–443
Lassner M, Dvorak J (1986) Preferential homogenization between adjacent and alternate subrepeats in wheat rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res 14:5499–5512
Lassner M, Anderson O, Dvorak J (1987) Hypervariation associated with a 12-nucleotide direct repeat and inferences on intergenomic homogenization of ribosomal RNA gene spacers based on the DNA sequence of a clone from the wheat Nor-D3 locus. Genome 29:770–781
Long E, Dawid I (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 49:727–764
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Martini G, Flavell RB (1985) The control of nucleolus volume in wheat, a genetic study of three developmental stages. Heredity 54:111–149
Martini G, O'Dell M, Flavell RB (1982) Partial inactivation of wheat nucleolus organisers by the nucleolus organiser chromosomes from Aegilops umbellulata. Chromosoma 84:687–700
Mitchelson K, Moss T (1987) The enhancement of ribosomal transcription by the recycling of RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res 15:9577–9596
Moss T (1983) A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature 302:223–228
Muller M, Pfund W, Metha V, Trask D (1985) Eucaryotic type I topoisomerase is enriched in the nucleolus and catalytically active on ribosomal DNA. EMBO J 4:1237–1243
Murtif VL, Rae PMM (1985) In vivo transcription of rDNA spacers in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3221–3240
Ness PJ, Koller T, Thoma F (1988) Topoisomerase I cleavage sites identified and mapped in the chromatin of Dictyostelium ribosomal RNA genes. J Mol Biol 200:127–130
Polans NO, Weeden NF, Thompson WF (1986) Distribution, inheritance and linkage relationships of ribosomal DNA spacer length variants in pea. Theor Appl Genet 72:289–295
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1987) Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. Plant Mol Biol 9:509–520
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1988) Recombination in Escherichia coli between cloned ribosomal RNA intergenic spacers from Vicia faba: A model for the generation of ribosomal RNA gene heterogeneity in plants. Plant Sci 55:27–31
Rogers SO, Honda S, Bendich AJ (1986) Variation in the ribosomal RNA genes among individuals of Vicia faba. Plant Mol Biol 6:339–345
Smith HC, Rothblum LI (1987) Ribosomal DNA sequences attached to the nuclear matrix. Biochem Genet 25:863–879
Taira T, Kato A, Tanifuji S (1988) Difference between two major size classes of carrot rDNA repeating units is due to reiteration of sequences of about 460 bp in the large spacer. Mol Gen Genet 213:170–174
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Iida Y, Sugiura M (1985) The complete sequence of rice 25S rRNA gene. Gene 37:225–259
Tautz D, Dover GA (1986) Transcription of the tandem array of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster does not terminate at any fixed point. EMBO J 5:1267–1273
Toloczyki C, Feix G (1986) Occurrence of 9 homologous repeat units in the external spacer region of a nuclear maize rRNA gene unit. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4969–4985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. G.Herrmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schiebel, K., von Waldburg, G., Gerstner, J. et al. Termination of transcription of ribosomal RNA genes of mung bean occurs within a 175 bp repetitive element of the spacer region. Molec Gen Genet 218, 302–307 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331282
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331282