Summary
Nitrendipine solution 5 mg·ml−1 in the dose of 5 mg was given orally to 20 patients with chronic renal failure and elevated diastolic blood pressure (≥110 mmHg), of whom 10 were on maintenance haemodialysis (endogenous creatinine clearance <5 ml·min−1) and 10 were at the predialysis stage (endogenous creatinine clearance 5–20 ml·min−1).
The aim of the study was to investigate the influence of kidney function and/or dialysis treatment on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of a solution of nitrendipine and to assess its antihypertensive efficacy.
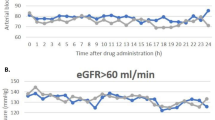
After 10 min there was a significant reduction in blood pressure from 188/113 to 173/100 (patients not dependent on dialysis) and from 197/112 to 161/94 mmHg (patients dependent on dialysis). The maximum fall in blood pressure (approximately 30%) was attained after 90 min in the dialysis patients and after 120 min in the non-dialysis group. Blood pressure increased again about 3 h after the administration of nitrendipine but it was still below baseline after 12 h. The terminal elimination half-life (4.1 h in the dialysis patients and 3.6 h in non-dialysis patients) was similar to that observed in patients with normal renal function. The pharmacokinetics of nitrendipine did not differ between the dialysis and non-dialysis groups. There was a correlation between plasma concentration and the blood pressure reduction. The maximum plasma concentration of nitrendipine was reached after 0.5 h (median) and did not differ between the two groups. The mean maximum plasma concentration was 14.8 μg·1−1 in the study population as a whole, with comparable means in the dialysis (17.3 μg·1−1) and non-dialysis (12.4 μg·1−1) groups.
The nitrendipine solution proved to be effective in lowering acutely elevated blood pressure in patients with advanced renal failure and renal hypertension, and was well tolerated. The pharmacokinetics was not affected by renal impairment or by dialysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan NM (1986) Renal parenchymal hypertension. In: Kaplan NM (ed). Clinical Hypertension. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 292–316
Reuler JB, Magarian GJ (1988) Hypertensive emergencies and urgencies: definition, recognition and management. J Gen Intern Med 3: 64–74
Karachalios GN, Donas G, Tsimiklis S, Statkakais V (1988) Treatment of hypertensive emergencies with nifedipine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 26: 351–355
Rahn KH (1989) How should we treat a hypertensive emergency? Am J Cardiol 63: 48c-50c
Stoepel K, Heise A, Kazda S (1981) Pharmacological studies of the antihypertensive effect of nitrendipine. Arzneimittelforschung/Drug Res 31: 2056–2061
Burris JF, Notargiacomo AV, Papademetriou V, Freis ED (1982) Acute and short-term effects of a new calcium antagonist in hypertension. Hypertension 4 [Suppl 2]: 32–35
Vlachakis ND, Vanov SK, Taylor RJ, Pun EFC (1984) Controlled comparison of nitrendipine and placebo in the treatment of hypertension. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München, pp 443–449
Deck K, Stoepel D, Leibowitz D, Taylor R, Vanov S (1984) Some aspects of the clinical pharmacology of nitrendipine. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München, pp 397–407
Rämsch KD, Sommer J (1984) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of nitrendipine. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München, pp 409–421
Wortmann A, Schmidt M, Bachmann K (1987) Antihypertensive Wirkung der Einmalgabe von Nitrendipin. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 76: 469–472
Esper RJ, Machado RA, Esper RC, Menna J (1987) Dose assessment and long-term effectiveness of nitrendipine in the treatment of mild and moderate hypertensive patients. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9 [Suppl 4]: 164–168
Grabensee B (1985) Therapie der hypertensiven Krise. Dtsch Med Wochenschrift 45: 1738–1740
Mikus G, Eichelbaum M (1987) Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, metabolism, and hemodynamic effects of the calcium channel antagonist nitrendipine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9 [Suppl 4]: 140–141
Aronoff GR (1987) Pharmacokinetics of nitrendipine in patients with renal failure: comparison to normal subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 10 [Suppl 10]: 974–976
Mikus G, Mast V, Fischer C, Machleidt C, Kuhlmann U, Eichelbaum M (1991) Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, metabolism and acute and chronic antihypertensive effects of nitrendipine in patients with chronic renal failure and moderate to severe hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 31: 313–322
Rämsch KD, Graefe KH, Scherling D, Sommer J, Ziegler R (1986) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of calcium-blocking agents nifedipine, nitrendipine and nimodipine. Am J Nephrol 6 [Suppl 1]: 73–80
Kindler J, Planz G, Giani G, Clasen W, Homburg A, Kierdorf H (1987) Comparison of nitrendipine and dihydralazine in a triple combination therapy in moderate and severe arterial hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9 [Suppl 4]: 256–262
Baumelou A, Bentchikou A, Vray M, Jourdan J, Eugene M (1987) Nitrendipine in patients with renal disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9 [Suppl 4]: 174–177
Bortel vL, Böhm R, Mooy J, Schiffers P, Rahn KH (1989) Pharmacokinetics of nitrendipine in the terminal renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36: 467–471
Ankermann T, Osterkamp U, Santos SR, Kirch W (1989) Elimination and haemodynamic effects of nitrendipine in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36: 433–437
Späh F, Grosser KD (1988) Treatment of hypertensive urgencies and emergencies with nitrendipine, nifedipine and clonidine: effect on blood pressure and heart rate. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 12 [Suppl 4]: 154–156
Kleinbloesem CH, Brummelen van P, Woittiez AJ, Faber H, Breimer DD (1986) Influence of hemodialysis on the pharmacokinetics and hemodynamic effects of nifedipine during continuous intravenous infusion. Clin Pharmacokinet 11: 316–322
Bogaert MG, Rosseel MT, Joos R, Boelaert J (1984) Plasma concentrations of nifedipine in patients with renal failure. Arzneimittelforschung/Drug Res 36: 307–308
Hansson L, Andren L, Orö L, Ryman T (1984) The antihypertensive effects and pharmacokinetics of nitrendipine in patients with essential hypertension. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München, pp 423–433
Kleinbloesem CH, Brummelen vP, Faber H, Danhof M, Vermeulen NPE, Breimer DD (1984) Variability in nifedipine pharmacokinetics and dynamics: a new oxidation polymorphism in man. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 3721–3724
Krol GJ, Lettieri JT, Mazzu AL, Burkholder DE, Birkett JP, Taylor RJ, Bon C (1987) Bioequivalence of different nitrendipine tablet dosage formulations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9 [Suppl 4]: 129–135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kierdorf, H., Müller, A., Blanke, P.M. et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of oral nitrendipine solution in hypertensive patients with advanced renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45, 129–134 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315493
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315493