Summary
Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALC), a physiological component of the L-carnitine family, has been proposed for treating Alzheimer's disease in pharmacological doses. As this condition requires prolonged therapy, its kinetics has been examined after a multiple dose regimen, involving different routes of administration, in 11 patients suffering from Senile Dementia of Alzheimer Type.
The study design comprised a 3-day basal observation period, sham treatment with repeated blood sampling; treatment with 30 mg·kg−1 i.v. given twice for 10 days (plasma kinetics was studied on the 7th day), and 50 days of 2.0 g/day p.o. given in three daily doses. Total acid soluble L-carnitine, L-carnitine and acetyl-L-carnitine in plasma and CSF were evaluated using an enantioselective radioenzyme assay. Short chain L-carnitine esters were calculated as the difference between total and free-L-carnitine.
The plasma concentrations of individual components of the L-carnitine family did not change during the three days of the basal period, nor were they affected during the sham therapy period.
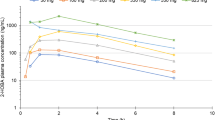
Following the i.v. bolus injections, the plasma concentrations showed a biphasic curve, with average t1/2 of 0.073 h and 1.73 h, respectively.
At the end of oral treatment, plasma acetyl-L-carnitine and L-carnitine short chain esters were significantly higher than during the run-in phase.
The CSF concentrations paralleled those in plasma, suggesting that ALC easily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
It is concluded that i.v. and oral administration of multiple doses of ALC can increase its plasma and CSF concentration in patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelucci L, Patacchioli FR, Tagliatela G et al (1986) Brain glucocorticoid receptor and adrenocortical activity are sensitive markers of senescence-retarding treatments in the rat. In: Biggio G, Spano PF, Toffano G et al (eds) Modulation of central and peripheral transmitter function. Fidia Research Series, Symposia in Neuroscience. Padova, Liviana Press Berlin, Springer, 3: 338–343
Angelucci L, Ramacci MT, Amenta F et al (1988) Acetyl-L-carnitine in the rat's hippocampus aging. Morphological, endocrine and behavioural correlates. In: Gorio A, Perez Polo JR, De Velis J et al (eds) Neural Development and regeneration. NATO ASI Series. Springer, Berlin, H22: 57–66
Calvani M, Carta A (1991) Clues to the mechanism of action of acetyl-L-carnitine in the central nervous system. Dementia 2: 1–6
Cucinotta D, Passeri M, Ventura S et al (1988) Multicenter clinical placebo-controlled study with acetyl-L-carnitine in the treatment of mildly demented elderly patients. Drug Dev Res 14: 213–216
Falchetto S, Kato G, Provini L (1971) The action of carnitines in cortical neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 49: 1–7
Fariello RG, Ferraro TN, Golden GT et al (1988) Systemic acetyl-L-carnitine normalizes pituitary-adrenocortical hyperactivity in pathological ageing brain. Med Sci Res 16: 291–292
Fritz JB (1963) Carnitine and its role in fatty acids metabolism. Adv Lipid Res 1: 285–334
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics, 2ed. Dekker, New York
Hiersemenzel R, Dietrich B, Hermann WM (1988) Therapeutic and EEG-effects of acetyl-L-carnitine in elderly outpatients with mild to moderate cognitive decline. Results of two double-blind placebo-controlled studies. In: Agnoli A, Cahn J, Lassen N et al (eds) Senile dementias. 2nd Int Symp J Libbey, Paris, pp 427–431
Hosein EA, Both SJ, Gasoi I et al (1966) Neuromuscular blocking activity and other pharmacological properties of various carnitine derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 156: 565–572
Kelly JG, Hunt S, Doyle GD et al (1990) Pharmacokinetics of oral acetyl-L-carnitine in renal impairment. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38: 309–312
Kirk RE (1982) Experimental design. Procedures for behavioural sciences. Brooks-Cole, Publ Co, 2nd Edition
Marzo A, Arrigoni Martelli E, Cardace G et al (1988) Pharmacokinetics of acetyl-L-carnitine after i.v. administration in healthy volunteers and dogs. Troisième Journées Mediterranéennes de Pharmacocinétique. Cap D'Adge: 19–21
Marzo A, Arrigoni Martelli E, Urso R et al (1989) Metabolism and disposition of intravenously administered acetyl-L-carnitine in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 37: 59–63
Marzo A, Cardace G, Monti N et al (1990) Chromatographic and non chromatographic assay of L-carnitine family components. J Chromatogr 527: 247–258
McKhann, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Nappi G, Martignoni E, Sinforiani E et al (1988) Acetyl-L-carnitine normalizes pituitary-adrenocortical hyperactivity in pathological ageing brain. Med Sci Res 16: 291–292
Onofri M, Bodis-Wollner I, Pola P et al (1983) Central cholinergic effects of levo-acetylcarnitine. Drugs Exp Clin Res 9: 161–169
Parnetti L, Gaiti A, Mecocci P et al (1990) Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on serum levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone and its clinical effect in patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer Type. Dementia 1: 165–168
Perez Polo JR, Werrbach-Perez K, Ramacci MT et al (1988) Role of nerve growth factors in neurological disease. In: Agnoli A, Cahn J, Lassen N et al (eds) Senile dementias. 2nd. International Symposium. Libbey, Paris, pp 15–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parnetti, L., Gaiti, A., Mecocci, P. et al. Pharmacokinetics of IV and oral acetyl-L-carnitine in a multiple dose regimen in patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42, 89–93 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314926
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314926