Summary
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from 105 patients was analyzed by radio-immunoassay for the presence of material cross-reactive with peptide 89–169 of bovine myelin basic protein (BP).
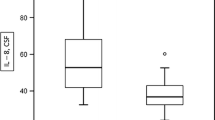
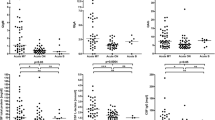
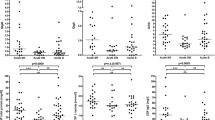
In a group of 72 multiple sclerosis patients, 52 showed higher BP content than the control group, i.e. more than 2 ng/ml CSF. Increased BP or BP fragments could be detected in CSF from almost all patients who recently (within 2 weeks) had had an acute episode, or after deterioration in the progressive form of the disease. Fifteen to 30 days after the onset of exacerbation or in a stable period, BP content decreases and in the slowly progressive form was in the range of the control group with one exception.
BP content was also elevated in the CSF of patients with other neurological diseases. The presence of BP in the CSF from patients with isolated retrobulbar neuritis is of particular interest. Thus the presence of material cross-reactive with BP fragment 89–169 is not specific for multiple sclerosis, but is a useful parameter in diagnosis and evaluation of MS.
Zusammenfassung
Mit Hilfe eines Radioimmunoassays wurde der Liquor von 105 Patienten auf Substanzen untersucht, die mit dem Fragment 89–169 des bovinen basischen Myelinproteins (BP) kreuzreagieren. Von 72 Patienten mit Multipler Sklerose hatten 52 einen höheren BP-Gehalt im Liquor als die Kontrollgruppe, d.h. mehr als 2 ng/ml. Dies war bei fast all jenen Patienten der Fall, bei denen der Liquor innerhalb von 2 Wochen nach einem akuten Schub bzw. zum Zeitpunkt einer deutlichen Verschlechterung des Zustandes bei der chronisch-progredienten Form gewonnen wurde. Der BP-Gehalt des Liquors nimmt zwischen dem 15. und 30. Tag nach Schubbeginn deutlich ab. In der schleichenden progredienten Form wurde mit einer Ausnahme kein erhöhter BP-Gehalt gefunden.
Das basische Myelinprotein ist aber auch im Liquor von Patienten mit anderen neurologischen Erkrankungen zu finden. Hervorzuheben ist das Auftreten von BP im Liquor von Patienten mit Retrobulbär-neuritis.
Der Nachweis von mit Bruchstück 89–169 kreuzreagierenden Substanzen im Liquor ist infolgedessen zwar nicht spezifisch für die Multiple Sklerose, ist aber ein wertvoller Parameter in der Diagnose und Einschätzung der MS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alling C, Karlsson B, Vällfors B (1980) Increase in myelin basic protein in CSF after brain surgery. J Neurol 223:225–230
Alvord EC, Hruby S, Sires L (1979) Degradation of myelin basic protein by cerebrospinal fluid: preservation of antigenic determinants under physiological conditions. Ann Neurol 6:474–482
Bashir R, Whitaker JN (1980) Molecular features of immunoreactive myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid of persons with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 7:50–57
Benuck M, Marks N, Hashim G (1975) Metabolic instability of myelin proteins. Breakdowns of basic protein induced by brain cathepsin D. Eur J Biochem 52:615–621
Carson JH, Barbarese E, Braun PE, McPherson TA (1978) Components in multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid that are detected by radioimmunoassay for myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 75:1976–1978
Cohen SR, McKhann GM, Guarnieri M (1975) A radioimmunoassay for myelin basic protein and its use for quantitative measurements. J Neurochem 25:371–376
Cohen SR, Brune MJ, Herndon RM, McKhann GM (1978) Cerebrospinal fluid myelin basic protein and multiple sclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 100:513–519
Cuzner ML, Davison AN, Rudge P (1978) Proteolytic enzyme activity of blood leukocytes and cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 4:337–344
Day ED, Pitts OM (1974) Radioimmunoassay of myelin basic protein in sodium sulfate. Immunochemistry 11:651–659
Deibler GE, Martenson RE, Kies MW (1972) Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem 2:139–165
Gutstein HS, Cohen SR (1978) Spinal fluid differences in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Science 199:301–303
Hunter WM, Greenwood FC (1962) Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature, Lond 194:495
Marks N, Benuck M, Hashim G (1974) Hydrolysis of myelin basic protein with brain acid proteinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 56:68–74
Martenson RE, Kramer AJ, Deibler GE (1975) Large peptides of bovine and guinea pig myelin basic proteins produced by limited peptic hydrolysis. Biochemistry 14:1067–1073
McPherson TA, Gilpin A, Seland TP (1972) Radioimmunoassay of CSF for encephalitogenic basic protein: a diagnostic test for MS? Can Med Assoc J 107:856–859
Norton WT (1972) Myelin. In: Albers RW, Siegel GJ, Katzmann RT, et al (eds) Basic neurochemistry. Little Brown and Company, Boston, pp 365–386
Ohta M, Matsubara F, Konishi T, Nishitani H (1980) Radioimmunoassay of myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid and its clinical application to patients with neurological diseases. Life Sciences 27:1069–1074
Palfreyman JW, Thomas GT, Ratcliffe JG (1977) Radioimmunoassay of human myelin basic protein in biological fluids and tissue extract. Biochem Soc Trans 5:1422–1424
Palfreyman JW, Thomas GT, Ratcliffe JG (1978) Radioimmunoassay of human myelin basic protein in tissue extract, cerebrospinal fluid and serum and its clinical application to patients with head injury. Clin Chim Acta 82:259–270
Prange H, Kohlschütter A, Ritter G (1980) Basisches Myelinprotein im Liquor cerebrospinalis bei Neurosyphilis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 105:1119–1121
Schmid G, Thomas G, Hempel K, Grüninger W (1974) Radioimmunological determination of myelin basic protein (MBP) and MBP-antibodies. Eur Neurol 12:173–185
Whitaker JN (1977) Myelin encephalitogenic protein fragments in cerebrospinal fluid of persons with multiple sclerosis. Neurology (Minneap) 27:911–920
Whitaker JN, Chou C-HJ, Chou FC-H, Kibler RF (1975) Antigenic determinants of bovine myelin encephalitogenic protein recognized by rabbit antibody to myelin encephalitogenic protein. J Biol Chem 250:9106–9111
Whitaker JN, Lisak RP, Bashir RM, Fitch OH, Seyer JM, Krance R, Lawrence JA, Ch'ien LT, O'Sullivan P (1980) Immunoreactive myelin basic protein in the cerebrospinal fluid in neurological disorders. Ann Neurol 7:58–64
Whitaker JN, Bashir RM, Chou C-HJ, Kibler RF (1980) Antigenic features of myelin basic protein-like material in cerebrospinal fluid. J Immunol 124:1148–1153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biber, A., Englert, D., Dommasch, D. et al. Myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. J Neurol 225, 231–236 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313295
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313295