Summary
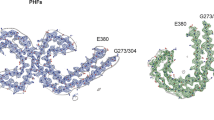
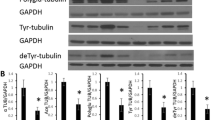
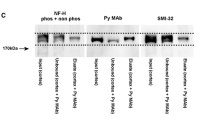
We have developed monoclonal antibodies that detect normal microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) epitopes in routinely fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. The somatodendritic distribution of MAP2 in bovine and human nervous tissue was confirmed with several of these antibodies. Furthermore, some of these antibodies immunohistochemically labeled certain pathological structures in Alzheimer brain, especially neurites in senile plaques. Electron microscopic observations, however, indicate that these MAP2 epitopes are not located in the Alzheimer paired helical filaments themselves, but in amorphous granular structures coexistent with them. While the pathological nature of these structures is undetermined, they may represent artefactual modifications of normal cytoskeletal components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan VJ, Kreis TE (1986) A microtubule-binding protein associated with membranes of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 103:2229–2239
Anderton BH, Breinburg D, Downes MJ, Green PJ, Tomlinson BE, Ulrich J, Wood JN, Kahn J (1982) Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature 298:84–86
Behrouz N, Defossez A, Delacourte A, Hublau P, Mazzuca M (1989) An antiserum to the N-terminal subsequence of the Alzheimer amyloid Beta protein does not react with neurofibrillary tangles. J Gerontol 44:B156-B159
Bernhardt R, Matus A (1984) Light and electron microscopic studies of the distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat brain: a difference between dendritic and axonal cytoskeletons. J Comp Neurol 226:203–221
Brion JP, Couck AM, Passareiro E, Flament-Durand J (1985) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease: an immunohis-tochemical study. J Submicrosc Cytol 17:89–96
Brion JP, Passareiro E, Nunez J, Flament-Durand J (1985) Mise en évidence immunologique de la protéine Tau au niveau des lésions de dégénérescence neurofibrillaire de la maladie d'Alzheimer. Arch Biol 95:229–235
Brion JP, Hanger DP, Bruce MT, Couck AM, Flament-Durand J, Anderton BH (1991) Tau in Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles: N- and C-terminal regions are differentially associated with paired helical filaments and the location of a putative abnormal phosphorylation site. Biochem J 273:127–133
Caceres A, Payne MR, Binder LI, Steward O (1983) Immunocytochemical localization of actin and microtubule-associated protein MAP2 in dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:1738–1742
Dammerman M, Yen SH, Shafit-Zagardo B (1989) Sequence of a human MAP2 region sharing epitopes with Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neurosci Res 24:487–495
Drubin D, Kirschner M (1986) Purification of Tau protein from brain. Methods Enzymol 134:156–159
Dustin P, Flament-Durand J, Vandermot G (1979) Aspects ultrastructuraux du vieillissement cérébral. Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg 134:369–383
Flynn G, Joly JC, Purich DL (1987) The 28.000 Mr microtubule-binding domain of microtubule-associated protein 2 also contains a neurofilament binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 148:1453–1459
Gheuens J, Cras P, Perry G, Boons J, Ceuterick C, Lübke U, Mercken M, Tabaton M, Vandermeeren M, Mulvihill P, Siedlak S, Van Heuverswijn H, Martin JJ (1991) Demonstration of a novel neurofilament-associated antigen in the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer and related diseases. Brain Res 558:43–52
Gilbert SP, Sloboda RD (1986) Identification of a MAP2-like ATP-binding protein associated with axoplasmic vesicles that translocate on isolated microtubules. J Cell Biol 103:947–956
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA (1989) Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein Tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 3:519–526
Gray EG, Paula-Barbosa M, Roher A (1987) Alzheimer's disease: paired helical filaments and cytomembranes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 13:91–110
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986) Microtubule-associated protein Tau a component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem 261:6084–6089
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, George L, Tung YC, Kim KS, Wisniewski HM (1989) Amyloid protein and neurofibrillary tangles coexist in the same neuron in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2853–2857
Guiroy DC, Miyazaki M, Multhaup G, Fischer P, Garruto RM, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Simms G, Gibbs CJ Jr, Gajdusek DC (1987) Amyloid of neurofibrillary tangles of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia and Alzheimer disease share identical amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2073–2077
Hasegawa M, Arai T, Ihara Y (1990) Immunochemical evidence that fragments of phosphorylated MAP5 (MAP1B) are bound to neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 4:909–918
Hirokawa N, Bloom GS, Vallee RB (1985) Cytoskeletal architecture and immunocytochemical localization of microtubule-associated proteins in regions of axons associated with rapid axonal transport: the β,β′-iminodipropionitrile-intoxicated axon as a model system. J Cell Biol 101:227–239
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Kondo J, Honda T, Mori H, Hamada Y, Miura R, Ogawara M, Ihara Y (1988) The carboxyl third of Tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron 1:827–834
Kosik KS, Duffy LK, Dowling MM, Abraham CR, McCluskey A, Selkoe DJ (1984) Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7941–7945
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubule-associated protein Tau is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4044–4048
Kosik KS, Orecchio LD, Bakalis S, Duffy L, Neve RL (1988) Partial sequence of MAP2 in the region of a shared epitope with Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neurochem 51:587–598
Kosik KS, Orecchio LD, Binder LI, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY, Lee G (1988) Epitopes that span the Tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron 1:817–825
Kziesak-Reding H, Dickson DW, Davies P, Yen SH (1987) Recognition of Tau epitopes by anti-neurofilament antibodies that bind to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3410–3414
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lewis SA, Wang D, Cowan NJ (1988) Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 shares a microtubule-binding motif with Tau protein. Science 242:936–939
Lewis SA, Ivanov IE, Lee GH, Cowan NJ (1989) Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and Tau. Nature 342:498–505
Linden M, Nelson BD, Leterrier JF (1989) The specific binding of the microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) to the outer membrane of rat mitochondria. Biochem J 261:167–173
Masters CL, Multhaup G, Simms G, Pottgiesser J, Martins RN, Beyreuther K (1985) Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J 4:2757–2763
Mercken M, Vandermeeren M, Six J, Lübke U, Boons J, Vandevoorde A, Gheuens J (1991) Affinity purification of human Tau proteins and the construction of a sensitive sandwich ELISA for human Tau detection. J Neurochem (in press)
Miller CJ, Brion JP, Calvert R, Chin TK, Eagles PAM, Downes MJ, Flament-Durand J, Haugh M, Kahn J, Probst A, Ulrich J, Anderton BH (1986) Alzheimer's paired helical filaments share epitopes with neurofilament side arms. EMBO J 5:269–276
Mori H, Kondo J, Ihara Y (1987) Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science 235:1641–1644
Nukina N, Ihara Y (1983) Immunocytochemical study on senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease II: abnormal dendrites in senile plaques as revealed by anti-microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) immunostaining. Proc Jpn Acad 59B:288–292
Nukina N, Kosik KS, Selkoe DJ (1987) Recognition of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by monoclonal neurofilament antibodies is due to crossreaction with Tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3415–3419
Perry G, Friedman R, Shaw G, Chau V (1987) Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3033–3036
Rosemblatt M, Fellous A, Mazie JC, Delacourte A, Defossez A (1989) Alzheimer's disease: microtubule-associated proteins 2 (MAP 2) are not components of paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett 252:91–94
Sattilaro RF, Dentler WL, LeCluyse EL(1981) Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) and the organization of actin filaments in vitro. J Cell Biol 90:467–473
Sattilano RF (1986) Interaction of microtubule-associated protein 2 with actin filaments. Biochemistry 25:2003–2009
Selkoe DJ, Podlisny MB, Gronbeck A, Mammen A, Kosik KS (1990) Molecular relation of amyloid filaments and paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Adv Neurol 51:171–179
Sims KB, Crandall JE, Kosik KS, Williams RS (1988) Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2) immunoreactivity in human fetal neocortex. Brain Res 449:192–200
Steiner B, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Gustke N, Meyer HE, Schmidt B, Mieskes G, Söling HD, Drechsel D, Kirshner MW, Goedert M, Mandelkow E (1990) Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein Tau: identification of the site for Ca2+ calmodulin dependent kinase and relationship with Tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer tangles. EMBO J 9:3539–3544
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH Jr, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in the identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Trojanowski JQ, Schuck T, Schmidt ML, Lee VMY (1989) Distribution of phosphate-independent MAP2 epitopes revealed with monoclonal antibodies in microwave-denatured human nervous system tissues. J Neurosci Methods 29:171–180
Vallee RB (1986) A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol 92:435–442
Wiche G, Briones E, Hirt H, Krepler R, Artlieb U, Denk H (1983) Differential distribution of microtubule-associated proteins MAP1 and MAP2 in neurons of rat brain and association of MAP1 with microtubules of neuroblastoma cells (clone N2A). EMBO J 2:1915–1920
Wischik CM, Novak M, Thögersen HC, Edwards PC, Runswick MJ, Jakes R, Walker JE, Milstein C, Roth M, Klug A (1988) Isolation of a fragment of Tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4506–4510
Wood JG, Mirra SS, Pollock NJ, Binder LI (1986) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein Tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4040–4043
Yen SH, Dickson DW, Crowe A, Butler M, Shelanski ML (1987) Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles contain unique epitopes and epitopes in common with the heat-stable microtubule-associated proteins Tau and MAP2. Am J Pathol 126:81–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Six, J., Lübke, U., Mercken, M. et al. Specific monoclonal antibodies against normal microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) epitopes present in Alzheimer pathological structures do not recognize paired helical filaments. Acta Neuropathol 83, 179–189 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308477
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308477