Abstract
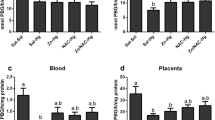
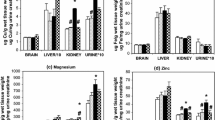
Mercuric mercury (Hg2+), like cadmium (Cd2+), interferes with the transport of certain essential metals to the conceptus in the pregnant Wistar rat and, at 48 h after the IV injection of a teratogenic dose (0.79 mg Hg2+/kg body weight) on day 12 of gestation, the foetal concentrations of Zn2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+, but not of Mg2+, are reduced significantly. Both Hg2+ and Cd2+, at teratogenic dose levels, inhibit the placental and foetal uptake of 65Zn2+ and 67Cu2+, but possibly by different mechanisms. In addition, the effects of Hg2+, at different times after dosing, on the uptake of these labelled tracers and of 59Fe3+, administered as 15-min pulses, do not parallel the changes in the placental and foetal concentrations and contents of the endogenous, stable metallic ions. The teratogenic dose of Hg2+ inhibits the placental and foetal uptake of L-[4,5-3H]-leucine, but not the incorporation of the labelled amino acid into foetal protein. In contrast, the corresponding dose of Cd2+ inhibits both leucine uptake and protein synthesis in the placenta and foetus. Similarly, Cd2+ inhibits the uptake of [2-14C]-thymidine and its incorporation into foetal DNA, whereas Hg2+ reduces the placental and foetal uptake, but has little or no effect on the utilization of the nucleoside. Since both Cd2+ and Hg2+ reduce the foetal uptake of 65Zn and the foetal concentration of Zn, but only Cd2+ interferes with DNA synthesis, it is unlikely that the inhibition of the metabolism of thymidine can be attributed to reduction in thymidine kinase activity in consequence of foetal Zn deficiency. It is concluded that the small amount of Cd2+ that is taken up by the foetus has a direct effect on the synthesis of DNA and protein, whereas Hg2+ primarily affects placental transport processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahokas RA, Dilts PV, La Haye EB (1980) Cadmium-induced fetal growth retardation: protective effect of excess dietary zinc. Am J Obstet Gynecol 136: 216–221
Baker E, Morgan EH (1968) The role of transferrin in placental iron transfer in the rabbit. Q J exp Physiol 54: 173–186
Baker E, Morgan EH (1970) Iron transfer across the perfused rabbit placenta. Life Sci 9: 765–772
Cerrati A, Franco PA, Garrone G, Puntrello C, Raggi I, Viola A (1984) Embryotoxic action induced by mercuric acetate in the rat. Arch Toxicol Suppl 7: 382
Danielsson BRG, Dencker L (1984) Effects of cadmium on the placental uptake and transport to the fetus of nutrients. Biol Res Pregnancy 5: 93–101
Danielsson BRG, Dencker L, Khayat A, Orsen I (1984) Fetotoxicity of inorganic mercury in the mouse: distribution and effects on nutrient uptake by placenta and fetus. Biol Res Pregnancy 5: 102–109
Dencker L (1976) Tissue localization of some teratogens at early and late gestation related to fetal effects. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 39 (Suppl.1): 5–25
Giles KW, Myers A (1965) An improved diphenylamine method for the estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Nature (Lond) 206: 93
Holt D, Webb M (1986) The toxicity and teratogenicity of mercuric mercury in the pregnant rat. Arch Toxicol 58: 243–248
Klein NW, Vogler MA, Chatot CL, Pierro LJ (1980) The use of cultured rat embryos to evaluate the teratogenic activity of serum: cadmium and cyclophosphamide. Teratology 21: 199–208
Larkin EC, Weintraub LR, Crosby WH (1970) Iron transport across rabbit allantoic placenta. Am J Physiol 218: 7–11
Martin PG, Hitchcock AB, King JF (1978) Cadmium toxicity in the pregnant rat. In: Mahlum DD, Sikov MR, Hackett PL, Andrew FD (eds), Developmental toxicology of energy related pollutants. Technical Information Center, US Dept. Energy, Washington, pp 586–599
Miller DS, Holliday CW (1982) HgCl2 inhibition of L-leucine transport in hamster placental slices. Environ Res 28: 32–38
Miller RK, Ng WW, Levin AA (1983) The placenta: relevance to toxicology. In: Clarkson TW, Nordberg GF, Sager PR (eds), Reproductive and developmental toxicity of metals. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 569–605
Murray MJ, Stein N (1971) Contribution of maternal rat iron stores to fetal iron in maternal iron deficiency and overload. J Nutr 101: 1583–1588
Record IR, Dreosti IE, Manuel SJ, Buckley RA (1982) Interactions of cadmium and zinc in cultured rat embryos. Life Sci 31: 2735–2743
Samarawickrama GP, Webb M (1981) The acute toxicity and teratogenicity of cadmium in the pregnant rat. J Appl Toxicol 1: 264–269
Sowa B, Steibert E (1985) Effect of oral cadmium administration to female rats during pregnancy on zinc, copper and iron content in placenta, foetal liver, kidney, intestine and brain. Arch Toxicol 56: 256–262
Thompson RH, Blanchflower WJ (1971) Wet ashing apparatus to prepare biological materials for atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Lab Practice 20: 859–861
Warner CW, Sadler TW, Tulis SA, Smith MK (1984) Zinc amelioration of cadmium-induced teratogenesis in vitro. Teratology 30: 47–53
Webb M (1983) Endogenous metal binding proteins in the control of zinc, copper, cadmium and mercury metabolism during prenatal and postnatal development. In: Clarkson TW, Nordberg GF, Sager PR (eds) Reproductive and developmental toxicity of metals, Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 655–674
Webb M, Samarawickrama GP (1981) Placental transport and embryonic utilization of essential metabolites in the rat at the teratogenic dose of cadmium. J Appl Toxicol 1: 270–277
Webster WS (1979) Iron deficiency and its role in cadmium-induced fetal growth retardation. J Nutr 109: 1640–1645
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holt, D., Webb, M. Comparison of some biochemical effects of teratogenic doses of mercuric mercury and cadmium in the pregnant rat. Arch Toxicol 58, 249–254 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297115
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297115