Summary
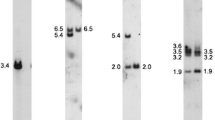
The liver enzyme tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT; EC 2.6.1.5) catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the catabolic pathway of tyrosine. Deficiency in TAT enzyme activity underlies the autosomally inherited disorder tyrosinemia II (Richner-Hanhart syndrome). Using a human TAT cDNA clone as hybridization probe, we have determined the chromosomal location of the TAT structural gene by Southern blot analysis of DNAs from a series of human x rodent somatic cell hybrids. The results assign the TAT gene to human chromosome 16.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson SM, Pispa JP (1982) Purification and properties of human liver tyrosine aminotransferase. Clin Chim Acta 125:117–123
Buist NRM, Kennaway NG, Fellmann JH (1985) Tyrosinemia type II: hepatic cytosol tyrosine aminotransferase deficiency (the “Richner-Hanhart syndrome”). In: Bickel H, Wachtel U (eds) Inherited diseases of amino acid metabolism. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, pp 203–235
Chandra T, Stackhouse R, Kidd VJ, Woo SLC (1983) Isolation and sequence characterization of a cDNA clone of human antithrombin III. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:1845–1848
Cheung P, Kao FT, Law ML, Jones C, Puck TT, Chan L (1984) Localization of the structural gene for human apolipoprotein A-I on the long arm of human chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:508–511
Cox DR, Gedde-Dahl T Jr (1985) Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 13, 14, 15 and 16., In: Human Gene Mapping 8. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:206–241
Glücksohn-Waelsch S (1979) Genetic control of morphogenetic and biochemical differentiation: lethal albino deletions in the mouse. Cell 16:225–237
Goldsmith LA (1983) Tyrosinemia and related disorders. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Frederickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 287–299
Granner DK, Hargrove JL (1983) Regulation of the synthesis of tyrosine aminotransferase: the relationship to mRNATAT. Mol Cell Biochem 53/54:113–128
Greengard O (1970) The developmental formation of enzymes in rat liver. In: Litwack G (ed) Biochemical actions of hormones, vol 1. Academic Press, New York London, pp 53–87
Inui K, Kao FT, Fujibavashi S, Jones C, Morse HG, Law ML, Wenger DA (1985) The gene coding for a sphingolipid activator protein, SAP-1, is on human chromosome 10. Hum Genet 69: 197–200
Kao FT, Morse HG, Law ML, Lidsky A, Chandra T, Woo SLC (1984) Genetic mapping of the structural gene for antithrombin III to human chromosome 1. Human Genet 67:34–36
Labarca C, Paigen K (1980) A simple, rapid and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem 102:344–352
Lalley PA, McKusick VA, (1985) Report of the committee on comparative mapping. In. Human Gene Mapping 8. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:536–566
Melton DA, Krieg PA, Rebagliati MR, Maniatis T, Zinn K, Green MR (1984) Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7035–7056
Morse HG, Patterson D, Jones C (1982) Giemsa-11 technique: applications in basic research. Mammalian Chromosome Newslett 23:127–133
Müller G, Scherer G, Zentgraf H, Ruppert S, Herrmann B, Lehrach H, Schütz G (1985) Isolation, characterization and chromosomal mapping of the mouse tyrosine aminotransferase gene. J Mol Biol 184:367–373
Ohisalo JJ, Laskowska-Klita T, Andersson SM (1982) Development of tyrosine aminotransferase and p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase activities in fetal and neonatal human liver. J Clin Invest 70:198–200
Räihä NCR, Schwartz A (1973) Enzyme induction in human fetal liver in organ culture. Enzyme 15:330–339
Scherer G, Schmid W, Strange CM, Röwekamp W, Schütz G (1982) Isolation of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine aminotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:7205–7208
Shinomiya T, Scherer G, Schmid W, Zentgraf H, Schütz G (1984) Isolation and characterization of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1346–1350
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natt, E., Kao, FT., Rettenmeier, R. et al. Assignment of the human tyrosine aminotransferase gene to chromosome 16. Hum Genet 72, 225–228 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291882
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291882