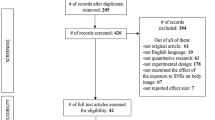
Abstract
A group of physically active women (n=112) and men (n=88) of a broad range of ages were compared on a number of variables related to body image, weight and diet concerns, and degree of exercise participation. Interrelationships between these measures were also examined. Results indicated that men and women were equally dissatisfied with their current weight. Although most women wanted to lose weight, the men were evenly divided between those who wanted to lose and those who wanted to gain. Women, however, were more dissatisfied with their bodies and placed greater importance on their appearance as an influence on their feelings of well-being. Although there were no sex differences in degree of physical activity, women were more likely than men to exercise to try and lose weight. Of interest was the finding that age was not related to body focus or body dissatisfaction for either sex. For women and older men, the degree to which they exercised was not associated with any of the body image variables. A very different pattern of relationships was found for young men. Greater body satisfaction was associated with increases in exercise participation and with increased body focus, a variable that was also associated with increased levels of exercise. The profile of results is considered in the context of social influences such as health promotion and sex roles — factors that have likely affected current attitudes to physical appearance and physical attractiveness among both sexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belloc, N. B., & Breslow, L. (1972). Relationship of physical health status and health practices. Preventative Medicine, 1, 409–421.
Breslow, L., & Enstrom, J. E. (1980). Persistence of health habits and their relationship to mortality. Preventative Medicine, 9, 469–483.
Canada Fitness Survey. (1982). Canada's fitness: Preliminary findings of the 1981 survey. Canadian Federal Ministry of Fitness and Amateur Sport, Ottawa, Canada.
Davis, C., Fox, J., Cowles, M. P., Hastings, P., & Schwass, K. (1990). The functional role of exercise in the development of weight and diet concerns in women. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 34, 563–574.
Dolan, B. M., Birtchnell, S. A., & Lacey, J. H. (1987). Body image distortion in non-eating disordered women and men. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 31, 513–520.
Drewnowski, A., & Yee, D. K. (1987). Men and body image: Are males satisfied with their body weight? Psychosomatic Medicine, 49, 626–634.
Durnin, J. V. G. A., & Passmore, R. (1967). Energy, work and leisure. London: Heinemann.
Durnin, J. V. G. A., & Womersley, J. (1974). Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: Measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. British Journal of Nutrition, 32, 77–96.
Fallon, A. E., & Rozin, P. (1985). Sex differences in perceptions of desirable body shape. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 94, 102–105.
Garner, D. M., Garfinkel, P. E., Schwartz, D., & Thompson, M. (1980). Cultural expectations of thinness in women. Psychological Reports, 47, 483–491.
Garner, D. M., Rockert, W., Olmsted, M. P., Johnson, C., & Coscina, D. V. (1985). Psychological principles in the treatment of bulimia and anorexia nervosa. In D. M. Garner & P. E. Garfinkel (Eds.), Handbook for psychotherapy for anorexia nervosa and bulimia. New York: The Guilford Press.
Gray, S. H. (1977). Social aspects of body image: Perceptions of normalcy of weight and affect of college undergraduates. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 45, 1035–1040.
Health and Welfare Canada. (1988). Promoting healthy weights: A discussion paper. Health Services and Promotion Branch of Health and Welfare.
International Conference on Exercise, Fitness, and Health Consensus Statement. (1989). Canadian Journal of Sport Sciences, Supplement 2.
Katz, J. L. (1986). Long-distance running, anorexia nervosa, and bulimia: A report of two cases. Comparative Psychiatry, 27, 74–78.
McCann, I. L., & Holmes, D. S. (1984). Influence of aerobic exercise on depression. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46, 1142–1147.
Mintz, L. B., & Betz, N. E. (1986). Sex differences in the nature, realism, and correlates of body image. Sex Roles, 15, 185–195.
Mishkind, M. E., Rodin, J., Silberstein, L. R., & Striegel-Moore, R. H. (1986). The embodiment of masculinity. American Behavioral Scientist, 29, 545–562.
Myers, A. M., Zivian, M. T., Kirkland, S., & Zager, L. (1985). Body images: Cohort and age differences across the life span. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Canadian Psychological Association, Halifax.
Pasman, L., & Thompson, J. K. (1988). Body image and eating disturbance in obligatory runners, obligatory weightlifters, and sedentary individuals. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 7, 759–769.
Powers, P. D., & Erikson, M. T. (1986). Body-image in women and its relationship to self-image and body satisfaction. The Journal of Obesity and Weight Regulation, 5, 37–50.
Rodin, J., Silberstein, L. R., & Striegel-Moore, R. H. (1985). Women and weight: A normative discontent. In T. B. Sonderegger (Ed.), Nebraska Symposium on Motivation: Vol. 32, Psychology and gender. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Silberstein, L. R., Striegel-Moore, R. H., Timko, C., & Rodin, J. (1988). Behavioral and psychological implications of body dissatisfaction: Do men and women differ? Sex Roles, 19, 219–232.
Silverstein, B., Perdue, L., Peterson, B., & Kelly, E. (1986). The role of the mass media in promoting a thin standard of bodily attractiveness for women. Sex Roles, 14, 519–532.
Silverstein, B., Peterson, B., & Perdue, L. (1986). Some correlates of the thin standard of bodily attractiveness in women. The International Journal of Eating Disorders, 5, 145–159.
Warren, B. J., Stanton, A. L., & Blessing, D. L. (1990). Disordered eating patterns in competitive female athletes. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 9, 565–569.
Zellner, D. A., Harner, D. E., & Adler, R. L. (1989). Effects of eating abnormalities and gender on perceptions of desirable body shape. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 98, 93–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, C., Cowles, M. Body image and exercise: A study of relationships and comparisons between physically active men and women. Sex Roles 25, 33–44 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289315
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289315