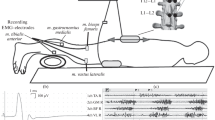
Summary
The present study examines the modulation of gastrocnemius-soleus (GS) monosynaptic reflexes as well as the intraspinal threshold changes of GS group I primary afferent terminals ending in the intermediate and motor nuclei during fictive locomotion in high decerebrate cats. The amplitude of the monosynaptic reflexes (MSR's) evoked in the medial gastrocnemius by stimulation of the lateral gastrocnemius nerve was increased during the extensor (E) phase, decreased during the flexion (F) phase of the step cycle and remainded transiently increased after spontaneous episodes of fictive stepping. The intraspinal threshold of populations and of single group Ia GS afferent fibers ending in the motor pool, as well as of single Ia and Ib fibers ending in the intermediate nucleus, showed a sustained reduction during the episodes of fictive locomotion with superimposed cyclic changes in phase with the step cycle. During fictive walking and trotting the reduction of the intraspinal threshold of both Ia and Ib fiber terminals was maximal during the middle or late portion of the F-phase. During fictive gallop elicited by stimulation of the superficial peroneus nerve, the decrease in the intraspinal threshold of the Ia afferent fibers occurred however in phase with the activity of the GS motoneurons. During episodes of fictive locomotion slow, sustained negative DC potential shifts lasting tents of seconds, reflecting an increase in the extracellular potassium concentration were recorded at the base of the dorsal horn and in the intermediate nucleus. The present findings support the existence of tonic and phasic depolarization of the intraspinal terminals of GS group Ia and Ib primary afferents during spontaneous fictive locomotion. It is suggested that accumulation of potassium ions in the extracellular space contributes mainly to the sustained depolarization of group I fibers. The phasic depolarization would be mostly due to the activation of specific sets of interneurons and may, in the case of Ia fibers, contribute to the cyclic modulation of the MRS elicited during fictive locomotion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akazawa K, Aldrige JW, Steeves JD, Stein RB (1982) Modulation of stretch reflexes during locomotion in the mesencephalic cat. J Physiol (Lond) 329: 553–567
Baev KV (1980) Polarization of primary afferent terminals in the lumbar spinal cord during fictitious locomotion. Neurophysiology (Kiev) 12: 305–311
Baev KV (1981) Retuning of segmental responses to peripheral stimulation in cats during fictitious locomotion. Neurophysiology (Kiev) 13: 206–212
Baev KV, Kostyuk PG (1982) Polarization of primary afferent terminals of lumbosacral cord elicited by the activity of spinal locomotor generator. Neuroscience 7: 1401–1409
Dubuc R, Cabelguen JM, Rossignol S (1985) Rhythmic antidromic discharges of single primary afferents recorded in cut dorsal root filaments during locomotion in the cat. Brain Res 359: 375–378
Dueñas SH, Rudomin P (1982) Excitability changes of intraspinal arborizations of Ia and Ib afferent fibers during fictive locomotion in the cat. Proc Mex Soc Physiol Sci 25: 99
Dueñas SH, Loeb GE, Marks WB (1985) Dorsal root reflex during locomotion in normal and decerebrate cats. Soc Neurosci 11: 1028
Dueñas SH, Loeb GE, Marks W (1986) Antidromic activity of primary afferents during locomotion in normal and decerebrate cats. Proc Mex Soc Physiol Sci 29: 234
Eidelberg E, Duenas SH, Rudomin P (1985) Excitability changes in ankle extensor group Ia and Ib afferents during spontaneous fictive locomotion. Soc Neurosci 11: 1028
Eccles JC, Kostyuk PG, Schmidt RF (1962) Central pathways responsible for depolarization of primary afferent fibers. J Physiol (Lond) 161: 258–281
Eccles R, Schmidt RF, Willis WD (1963) Depolarization of central terminals of group I afferents from muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 26: 1–27
Grillner S (1981) Control of locomotion in bipedes, tetrapods, and fish. In: Brooks VB (ed) American Physiological Society, Bethesda, Md. (Handbook of Physiology, SEC I. The nervous system, Vol II. Motor control, Part 2, pp 1179–1236)
Jiménez I, Rudomin P, Solodkin M, Vyklický L (1984) Specific and nonspecific mechanisms involved in generation of PAD of group Ia afferents in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 52: 921–940
Jankowska E, Lund S, Lundberg A (196) The effects of DOPA on the spinal cord. IV. Depolarization evoked in the central terminals of contralateral Ia afferents by volleys in the flexor reflex afferents. Acta Physiol Scand 68: 337–341
Kriz N, Sykova E, Ujec E, Vyklický L (1974) Changes of extracellular potassium concentration induced by neuronal activity in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 23: 1–15
Krnjević K, Morris ME (1975) Correlation between extracellular focal potentials and K+ potentials evoked by primary afferent activity. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 53: 921–922
Lothman EW, Somjen GG (1975) Extracellular potassium activity. Intracellular and extracellular potential responses in the spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 252: 115–136
Madrid J, Alvarado J, Dutton H, Rudomin P (1979) A method for the dynamic continuous estimation of excitability changes of single fiber terminals in the central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 11: 253–258
Mendell LM (1976) Properties and distribution of peripherally evoked presynaptic hyperpolarization in cat lumbar spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 336: 769–792
Orlovski GN (1972) Activity of vestibular neurons during locomotion. Brain Res 46: 85–98
Perret C, Cabelguen JM (1980) Main characteristics of the hindlimb locomotor cycle in the decorticate cat with special reference to bifunctional muscles. Brain Res 187: 333–352
Perret C (1983) Central generated pattern of motoneuron activity during locomotion in the cat. In: Roberts A, Roberts B (eds) Neural origin of rhythmic movements. Oxford University Press, Oxford Soc for Exp Biol Symp 37, pp 405–422
Richter DW, Camerer H, Sonnhof U (1978) Changes in extracellular potassium during the spontaneous activity of medullary respiratory neurones. Pflügers Arch 376: 139–149
Rudomin P, Núñez R, Madrid J, Burke RE (1974) Primary afferent hyperpolarization and presynaptic facilitation of Ia afferent terminals induced by large cutaneous fibres. J Neurophysiol 336: 769–792
Rudomin P, Engberg I, Jankowska E, Jiménez I (1980) Evidence of two different mechanisms involved in the generation of presynaptic fibers in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res 189: 256–261
Rudomin P, Jiménez I, Solodkin M, Dueñas S (1983) Sites of action of segmental and descending control of transmission on pathways mediating PAD of Ia and Ib afferent fibres in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 50: 743–769
Rudomin P, Solodkin M, Jiménez I (1985) Patterns of primary afferent depolarization and hyperpolarization of group Ia and Ib fibers produced by segmental and descending inputs. Soc Neurosci 15th Meeting, p 402
Rudomin P, Solodkin M, Jiménez I (1986) PAD and PAH response patterns of group Ia- and Ib-fibers to cutaneous and descending inputs in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 56: 987–1006
Schomburg ED, Roesler M, Meinck HM (1977) Phase dependent transmission in the excitatory propriospinal reflex pathways from forelimb afferents to lumbar motoneurones during fictive locomotion. Neurosci Lett 4: 249–259
Schomburg ED, Behrends HB (1978) The possibility of phase dependent monosynaptic and polysynaptic Ia excitation to homonymous motoneurons during fictive locomotion. Brain Res 143: 533–537
Shefchyk R, Stein RB, Jordan LM (1984) Synaptic transmission from muscle afferents during fictive locomotion in the mesencephalic cat. J Neurophysiol 51: 986–997
Shefchyk SJ, Jordan LM (1985) Motoneuron input-resistance during fictive locomotion produced by stimulation of the mesencephalic locomotor region. J Neurophysiol 54: 1101–1108
Somjen GG, Lothman EW (1974) Extracellular K+ accumulation in the mammalian central nervous system. Ann Rev Physiol 41: 159–179
Sykova E (1981) K+ changes in the extracellular space of the spinal cord and their physiological role. J Exp Biol 95: 93–109
Vyklický L, Sykova E, Kriz N (1975) Slow potentials induced by changes of extracellular potassium concentration in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res 45: 608–611
Wall PD (1958) Excitability changes in afferent fibres and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol (Lond) 142: 1–12
Wallén F, Grafe P, Grillner S (1984) Phasic variations of extracellular potassium during fictive swimming in the lamprey spinal cord in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand 120: 457–463
Wetzel MG, Stuart DG (1976) Ensemble characteristics of cat locomotion and its neural control. Prog Neurobiol 7: 1–98
Willis WD, Núńez R, Rudomin P (1976) Excitability changes of terminal arborizations of single Ia and Ib afferent fibers produced by muscle and cutaneous conditioning volleys. J Neurophysiol 39: 1150–1159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dueñas, S.H., Rudomin, P. Excitability changes of ankle extensor group Ia and Ib fibers during fictive locomotion in the cat. Exp Brain Res 70, 15–25 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271842
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271842