Abstract
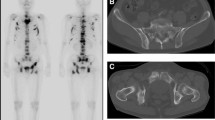
A patient with a muscle hernia in the thigh showed increased muscle uptake of radioactivity during bone imaging using 99mTc-pyrophosphate. The area of excessive accumulation corresponded well to the location and extent of the herniated muscle tissue observed at surgery. Microscopic examination revealed chronic muscle damage, which was assumed to be responsible for the abnormal muscle labelling found in this patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins HL (1971) 99mTechnetium pertechnetate uptake and scanning in the evaluation of thyroid function. Semin Nucl Med 1:345–355
Bellina CR, Bianchi R, Bombardieri S (1978) Quantitative evaluation of 99mTc-pyrophosphate muscle uptake in patients with inflammatory and noninflammatory muscle diseases. J Nucl Med All Sci 22:89–96
Bonte FJ, Parkey RW, Graham KD (1974) A new method for radionuclide imaging of myocardial infarcts. Radiology 110:473–474
Brown M, Swift TR, Spies SM (1976) Radioisotope scanning in inflammatory muscle disease. Neurology 26:517–520
Chaudhuri TK, Chaudhuri TK, Gulesserian HP (1974) Extraosseous noncalcified soft tissue uptake of 99mTc-pyrophosphate. J Nucl Med 15:1054–1056
Crenshaw AH (1971) Hernia of muscles. In: Campbell's operative orthopedics, 5th edn, vol. 2. Mosby, St. Louis, p 1496
Hunt J, Lewis S, Parkey R (1979)The use of technetium-99m-stannous pyrophosphate scintigraphy to identify muscle damage in acute electric burns. J Trauma 19:409–413
Kaye M, Silverton S, Rosenthall L (1975) Technetium-99m-pyrophosphate: studies in vivo and in vitro. J Nucl Med 16:40–45
Lentle BC, Percy JS, Rigal WM (1978) Localization of Tc-99m pyrophosphate in muscle after exercise. J Nucl Med 19:223–224
Mikolajkow A, Chomicki OA (1970) Scanning of the stomach with 99m-Tc. Digestion 3:357–367
Parkey RW, Bonte F, Meyer SL (1974) A new method for radionuclide imaging of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Circulation 50:540–546
Sandritter W, Wartman WB (1973) Muscles. In: Color atlas and textbook of tissue and cellular pathology, 4th edn. Year Book Med Publ, Chicago, pp 201–203
Silberstein EB, Francis MD, Tofe AJ (1975) Distribution of 99m-Tc-Sn diphosphonate and free 99m-Tc-pertechnetate in selected soft and hard tissues. J Nucl Med 16:58–61
Spies SM, Swift TR, Brown M (1975) Increased 99m-Tc-pyrphosphate muscle uptake in a patient with polymyositis: case report. J Nucl Med 16:1125–1127
Suzuki Y, Hisada K, Takeda M (1974) Demonstration of myositis ossificans by 99m-Tc pyrophosphate bone scanning. Radiology 111:663–664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shigeno, C., Fukunaga, M., Yamamoto, I. et al. Accumulation of 99mTc-pyrophosphate in a muscle hernia of the thigh. Eur J Nucl Med 6, 425–428 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266435
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266435