Summary
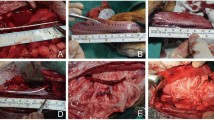
Lyophilized dura mater (Lyodura) and autogenous free peritoneum were compared in the replacement of the partially resected renal pelvis and ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) in the pig. The Lyodura and peritoneum grafts were both progressively resorbed, and replaced by fibroblasts which formed a mature scar lined by transitional epithelium, but without smooth muscle regeneration. Lyodura was found to be superior to free peritoneum with a longer time before resorption of the graft, less intense inflammatory reaction, absence of metaplastic bone formation, less risk of urine leak and greater ease of surgical manipulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquaviva A, Turrisi A and Cannizzaro MA (1980) Part replacement of the ureter wiyh lyophilized dura mater. Experimental research. Chir Ital 32:1152
Davis D (1943) Intubated ureterotomy. A new operaton for ureteral and ureteropelvic stricture. Surg Gyn Obstet 76:513
Faber P, Beef L, Heidenreich J (1978) Treatment of stress incontinence in women with the lyodura sling. Urol Int 33:117
Hinman F Jr (1981) Ureteral reconstitution. In: Bergman H (ed) The ureter, chapt 8, 2nd edn. Harper & Rowe, New York, pp 179–185
Hohenfellner R (1965) Experimentelle und klinische Untersuchungen über die Peritoenallappenplastik der Harnblase. Ann Univ Sarav [Med] 12:108
Hutschenreiter R, Rumpelt HJ, Klippel KF, Hohenfellner R (1978) The free peritoneal transplant as a substitute for the urinary bladder wall. Invest Urol 15:375
Ianetti G, D'Arco F (1977) The use of lyphilized dura in reconstruction of the orbital floor. J Maxillefac Surg 5:58
Kelami A (1971) Lyophilized human dura as a bladder wall substitute: experimental and clinical results. J Urol 105:518
Kelami A (1975) Duraplasty of the bladder — results after two to six years. Eur Urol 1:178
Kelami A, Ludtke-Handjery A, Korb G, Rolle J, Schnell J, Dangiel KH (1970) Alloplastic replacement of the urinary bladder wall with lyophilized human dura. Eur Surg Res 2:195
Lenzi R, Di Cello V, Ponchietti R, Barbagli G (1981) Rupture of the bulb of the urethra: repair effectuated using a patch of human dura mater. J Urol 125:506
MacFarlane MR, Symon L (1979) Lyophilized dura mater: experimental implantation and extended clinical neurosurgical use. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 42:854
Thompson IE (1977) Repair of ureteropelvic junction and ureteral injury with renal capsule flaps. Urol Clin North Am 4: 45
Thompson IE, Kovacsi L, Proterfield J (1963) Reconstruction of the ureteropelvic junction with pedicle grafts of renal capsule. J Urol 89:573
Thüroff JW, Hutschenreiter G, Frohnberg D, Hohenfellner R (1981) Transplantation of a free peritoneal patch in surgery of the renal pelvis and ureter. Eur Urol 7:304
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the University Urological Research Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Royce, P.L., Zimmern, P.E. & deKernion, J.B. Patch grafting the renal pelvis and ureteropelvic junction. Urol. Res. 16, 37–41 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264626
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264626