Abstract
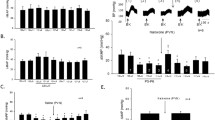
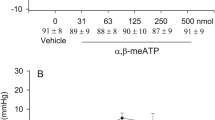
Modulation of somatosympathetic reflexes at the spinal cord and the brainstem was studied by administering opioid receptor agonists into the intrathecal space of the lumbar spinal cord and into the subarachnoid space of the cisterna magna in rats anesthetized with α-chloralose and urethane. Somatocardiac sympathetic A-and C-reflexes were elicited by electrical stimulation of myelinated (A) and unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers of the tibial nerve, respectively. Intrathecal administration of the μ-opioid receptor agonist DAMGO selectively depressed the C-reflex in a dose-dependent manner (minimum effective dose 10 ng), whereas the intrathecal injection of the δ-opioid receptor agonist DPDPE and the κ-opioid receptor agonist U-50,488H only at doses of 10 μg and 100 μg, respectively, led to a significant depression of the C-reflex. Injection of DAMGO into the cisterna magna enhanced both A-and C-reflexes in a dose-dependent manner (minimum effective dose 1 ng). The administration of neither DPDPE nor U-50,488H into the cisterna magna affected A-or C-reflexes. It is concluded that the activation of μ-opioid receptors is mainly or exclusively responsible for suppressing somatosympathetic C-reflexes at the spinal cord and for enhancing them at the brainstem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1992) Depending on the mode of application morphine enhances or depresses somatocardiac sympathetic A-and C-reflexes in anesthetized rats. Neurosci Res 15:281–288
Adler B, Goodman RR, Pasternak GW (1990) Opioid peptide receptors. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T, Kuhar MJ (eds) Neuropeptides in the CNS, part II. (Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, vol 9) Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 359–393
Clarke RW, Ford TW (1987) The contributions of μ-, δ-and κ-opioid receptors to the actions of endogenous opioids on spinal reflexes in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 91:579–589
Czlonkowski A, Millan MJ, Herz A (1987) The selective κ-opioid agonist, U-50,488H, produces antinociception in the rat via a supraspinal action. Eur J Pharmacol 142:183–184
Drower EJ, Stapelfeld A, Rafferty MF, De Costa BR, Rice KC, Hammond DL (1991) Selective antagonism by Naltrindole of the antinociceptive effects of the delta opioid agonist cyclic[d-penicillamine2-d-penicillamine5]enkephalin in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:725–731
Fields HL, Emson PC, Leigh BK, Gilbert RFT, Iversen LL (1980) Multiple opiate receptor sites on primary afferent fibres. Nature 284:351–353
Goldstein A, Naidu A (1989) Multiple opioid receptors: ligand selectivity profiles and binding site signatures. Mol Pharmacol 36:265–272
Ito K, Nakamura H, Sato A, Sato Y (1983) Depressive effect of morphine on the sympathetic reflex elicited by stimulation of unmyelinated hindlimb afferent nerve fibers in anesthetized cats. Neurosci Lett 39:169–173
Kato J, Meguro K, Sato A, Sato Y (1992) The effects of morphine administered into the vertebral artery on the somatosympathetic A-and C-reflexes in anesthetized cats. Neurosci Lett 138:207–210
Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ (1987) Autoradiographic differentiation of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors in the rat forebrain and midbrain. J Neurosci 7:2445–2464
Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ (1988) Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci 11:308–314
Miaskowski C, Levine JD (1992) Antinociception produced by receptor selective opioids: modulation of spinal antinociceptive effects by supraspinal opioids. Brain Res 595:32–38
Miaskowski C, Sutters KA, Taiwo YO, Levine JD (1991) Comparison of the antinociceptive and motor effects of intrathecal opioid agonists in the rat. Brain Res 553:105–109
Millan MJ, Czlonkowski A, Lipkowski A, Herz A (1989) Kappaopioid receptor-mediated antinociception in the rat. II. Supraspinal in addition to spinal sites of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:342–350
Morris BJ, Herz A (1987) Distinct distribution of opioid receptor types in rat lumbar spinal cord. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 336:240–243
Parvini S, Hamann SR, Martin WR (1993) Pharmacologic characteristics of a medullary hyperalgesic center. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:286–293
Porreca F, Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Burks TF (1984) Roles of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:341–348
Przewlocki R, Stala L, Greczek M, Shearman GT, Przewlocka B, Herz A (1983) Analgesic effects of μ-, δ-and κ-opiate agonists and, in particular, dynorphin at the spinal level. Life Sci 33 [Suppl 1]:649–652
Quirion R, Zajac JM, Morgat JL, Roques BP (1983) Autoradiographic distribution of mu and delta opiate receptors in rat brain using highly selective ligands. Life Sci 33 [Suppl 1]:227–230
Sato A, Sato Y, Suzuki A, Swenson RS (1986) The effects of morphine administered intrathecally on the somatosympathetic reflex discharges in anesthetized cats. Neurosci Lett 71:345–350
Sato A, Schmidt RF (1973) Somatosympathetic reflexes: afferent fibers, central pathways, discharge characteristics. Physiol Rev 53:916–947
Schmauss C, Yaksh TL (1984) In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:1–12
Schmidt RF, Weller E (1970) Reflex activity in the cervical and lumbar sympathetic trunk induced by unmyelinated somatic afferents. Brain Res 24:207–218
Yaksh TL, Rudy TA (1976) Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav 17:1031–1036
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, A., Sato, Y. & Schmidt, R.F. Modulation of somatocardiac sympathetic reflexes mediated by opioid receptors at the spinal and brainstem level. Exp Brain Res 105, 1–6 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242176
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242176