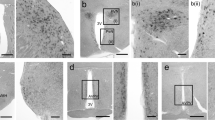
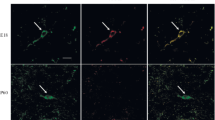
Summary
In situ hybridization was used to study the expression of prepro-neuropeptide Y (NPY), preprosomatostatin (SOM), preprotachykinin (PPT) and preprocholecystokinin (CCK) mRNA in caudate-putamen and frontoparietal cortex of rat brain with unilateral lesion of midbrain dopamine neurons. Neurons expressing NPY and SOM mRNA showed a similar distribution and the expression of both NPY and SOM appears to be regulated by dopamine in a similar fashion. Following a dopamine deafferentation, the numerical density of both NPY and SOM mRNA producing neurons almost doubled in the lesioned caudate-putamen with no change in the average grain density over positive neurons. Hence, in the intact caudate-putamen dopamine appears to suppress expression of these two neuropeptide genes leading to an activation of both NPY and SOM mRNA expression in many non- or low-expressing neurons when the level of dopamine is decreased. In the fronto-parietal cortex, on the other hand, dopamine appears to stimulate NPY and SOM gene expression. Thus, in the absence of dopamine about half of the NPY positive neurons disappeared. However, for SOM the number of positive neurons did not change, but rather most positive neurons appeared to have down-regulated their SOM mRNA expression. No evidence was found for a change in CCK mRNA expression by the dopamine deafferentation, while PPT mRNA expression decreased in the deafferented caudate-putamen. Consequently, dopamine exerts dissimilar effects on the expression of different neuropeptide genes, that in turn do not respond in the same way in different brain regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen YS, Adrian TE, Allen JM, Tatemoto K, Crow TJ, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1983) Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science 221:877–879
Allen J, Novotny J, Martin J, Heinrich G (1987) Molecular structure of mammalian neuropeptide Y: analysis by molecular cloning and computer-aided comparison with crystal structure of avian homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2532–2536
Arentzen R, Baldino F, Davis LG, Higgins GA, Lin Y, Manning RW, Wolfson B (1985) In situ hybridization of putative somatostatin mRNA within hypothalamus of the rat using synthetic oligonucleotide probes. J Cell Biochem 27:415–422
Bannon MJ, Lee J-M, Giraus P, Young A, Affolter HU, Bonner TI (1986) Dopamine antagonist haloperidol decreases substance P, substance K, and preprotachykinin mRNAs in rat striatonigral neurons. J Biol Chem 261:6640–6642
Beal MF, Martin JB (1983) Effects of lesions on somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the rat striatum. Brain Res 266:67–73
Beal MF, Martin JB (1984) Effects of neuroleptic drugs on brain somatostatin-like immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett 47:125–130
Beal MF, Chattha GK, Martin JB (1986a) A comparison of regional somatostatin and neuropeptide Y distribution in rat striatum and brain. Brain Res 377:240–245
Beal MF, Frank RC, Ellison DW, Martin JB (1986b) The effect of neuropeptide Y on striatal catecholamines. Neurosci Lett 71:118–123
Beal MF, Clevens RA, Mazurek MF (1988) Somatostatin and neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity in Parkinson's disease dementia with Alzheimer's changes. Synapse 2:463–467
Benoit R, Ling N, Alford B, Guillemin R (1982) Seven peptides derived from pro-somatostatin in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 107:944–950
Bennett-Clarke C, Romagnano MA, Joseph SA (1980) Distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain: telencephalon and diencephalon. Brain Res 188:473–486
Berod A, Biguet NF, Dumas S, Bloch B, Mallet J (1987) Modulation of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in the central nervous system visualized by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1699–1703
Björklund A, Lindvall O (1984) Catecholaminergic brain stem regulatory systems. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, Vol 2. Elsevier, New York, pp 55–122
Brownstein M, Arimura A, Sato H, Schally AV, Kizer JS (1975) The regional distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain. Endocrinology 96:1456–1461
Brownstein M, Mroz EA, Kizer JS, Palkovitz M, Leeman SE (1976) Regional distribution of substance P in the brain of the rat. Brain Res 116:299–305
Chan-Palay V (1987) Somatostatin immunoreactive neurons in the human hippocampus and cortex shown by immunogold/silver intensification on vibratome sections: coexistence with neuropeptide Y neurons, and effects in Alzheimer-type dementia. J Comp Neurol 260:201–223
Chesselet M-F, Reisine TD (1983) Somatostatin regulates dopamine release in rat striatal slices and cat caudate nuclei. J Neurosci 3:232–236
Chronwall BM, Chase TN, O'Donohue TL (1984) Coexistence of neuropeptide Y and somatostatin in rat and human cortical and rat hypothalamic neurons. Neurosci Lett 52:213–217
Deschenes RJ, Lorenz LJ, Haun RS, Roos BA, Collier KJ, Dixon JE (1984) Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding rat preprocholecysto-kinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:726–730
Dockray GJ (1976) Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin-like peptides in brain. Nature 264:568–570
Epelbaum J, Ruberg M, Moyse E, Javoy-Agid F, Dubois B, Agid Y (1983) Somatostatin and dementia in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 278:376–379
Fitzpatrick-McElligott S, Card JP, Lewis ME, Baldino F (1988) Neuronal localization of prosomatostatin mRNA in the rat brain with in situ hybridization histochemistry. J Comp Neurol 273:558–572
Gaykema RPA, Compaan JC, Nyakas C, Horvath E, Luiten PGM (1989) Long-term effects of cholinergic basal forebrain lesions on neuropeptide Y and somatostatin immunoreactivity in rat neocortex. Brain Res 489:392–396
Gehlert DR, Chronwall BM, Schaffer MP, O'Donohue TL (1987) Localization of neuropeptide Y messenger ribonucleic acid in rat and mouse brain by in situ hybridization. Synapse 1:25–31
Gerfen CR, Young WS (1988) Distribution of striato-nigral and striatopallidal peptidergic neurons in both patch and matrix compartments: and in situ hybridization histochemistry and fluorescent retrograde tracing study. Brain Res 460:161–167
Goodman RH, Aron DC, Roos BA (1983) Rat pre-prosomatostatin. J Biol Chem 258:5570–5573
Grima B, Lamaouroux A, Blanot F, Biquet NF, Mallet J (1985) Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:617–621
Hasegawa M, Usui H, Araki K, Kuwano R, Takahashi Y (1986) Developmental and regional changes of cholecystokinin mRNA in rat brain. FEBS Lett 194:224–226
Haverstick DM, Rubenstein A, Bannon MJ (1989) Striatal tachykinin gene expression regulated by interaction of D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:858–862
Hendry SHC, Jones EG, Bienfeld MC (1983) Cholecystokinin-immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey cerebral cortex make symmetric synapses and have intimate associations with blood vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2400–2404
Hendry SHC, Jones EG, Emson PC (1984a) Morphology, distribution, and synaptic relations of somatostatin- and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey neocortex. J Neurosci 4:2497–2517
Hendry SHC, Jones EG, DeFelipe J, Schmechel D, Brandon C, Emson PC (1984b) Neuropeptide-containing neurons of the cerebral cortex are also GABAregic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:6526–6530
Herrera-Marschitz M, Ungerstedt U (1984) Evidence that striatal efferents relate to different dopamine receptors. Brain Res 323:269–278
Herrera-Marschitz M, Goiny M, Utsumi H, Ungerstedt U (1989) Mesencephalic dopamine innervation of frontoparietal (sensorimotor) cortex of the rat: a microdialysis study. Neurosci Lett 97:266–270
Higuchi H, Yang HY, Sabol SL (1988) Rat neuropeptide Y precursor gene expression. J Biol Chem 263:6288–6295
Hoeffler H, Childers H, Montminy MR, Lechan RM, Goodman RH, Wolfe HJ (1986) In situ hybridization methods for the detection of somatostatin mRNA in tissue sections using antisense RNA probes. Histochem J 18:597–604
Hornykiewicz O (1982) Brain neurotransmitter changes in Parkinson's disease. In: Marsden CD, Fahn S (eds) Movement disorders. Butterworth Scientific, London, pp 41–58
Hökfelt T, Skirboll L, Rehfeld JF, Goldstein M, Markey K, Dann O (1980) A subpopulation of mesencephalic dopamine neurons projecting to limbic areas contains a cholecystokinin-like peptide: evidence from immunohistochemistry combined with retrograde tracing. Neuroscience 5:2093–2124
Hökfelt T, Herrera-Marschitz M, Seroogy K, Ju G, Staines A, Holets V, Schalling M, Ungerstedt U, Post C, Rehfelt JF, Frey P, Fischer J, Dockray G, Hamaoka T, Walsh JH, Goldstein M (1988) Immunohistochemical studies on cholecystokinin (CCK)-immunoreactive neurons in the rat using sequence specific antisera and with specific reference to the caudate nucleus and primary sensory neurons. J Chem Neuroanat 1:11–52
Innis RB, Correa FMA, Uhl GR, Schneider B, Snyder SH (1979) Cholecystokinin octa-peptide-like immunoreactivity: histochemical localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:521–525
Kanazawa I, Ogawa T, Kimura S, Munekata E (1984) Regional distribution of substance P, neurokinin α, and neurokinin β in rat central nervous system. Neurosci Res 2:111–120
Kerkerian L, Bosler O, Pelletier G, Nieoullon A (1986) Striatal neuropeptide Y neurons are under the influence of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway: immunohistochemical evidence. Neurosci Lett 66:106–112
Kerkerian L, Salin P, Nieoullon A (1988) Phrmacological characterization of dopaminergic influence on expression of neuropeptide Y immuno-reactivity by rat striatal neurons. Neuroscience 26:809–817
Kobayashi RM, Brown M, Vale W (1977) Regional distribution of neurotensin and somatostatin in rat brain. Brain Res 126:584–588
Kubota Y, Inagaki S, Kito S, Shimada S, Okayama T, Hatanaka H, Pelletier G, Takagi H, Tohyama M (1988) Neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neurons receive synaptic inputs from dopaminergic terminals in the rat neostriatum. Brain Res 458:389–393
Krause JE, Chirgwin JM, Carter MS, Xu ZS, Hershey AD (1987) Three rat preprotachykinin mRNAs encode the neuropeptides substance P and neurokinin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:881–885
Larhammar D, Ericsson A, Persson H (1987) Structure and expression of the rat neuropeptide Y gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2068–2072
Lindefors N, Brodin E, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Ungerstedt U (1985) Regional distribution and in vivo release of tachykinin-like immunoreactivities in rat brain: evidence for regional differences in relative propotions of tachykinins. Regul Pept 10:217–230
Lindefors N, Brodin E, Tossman U, Segovia J, Ungerstedt U (1989a) Tissue levels and in vivo release of tachykinins and GABA in striatum and substantia nigra of rat brain after unilateral striatal dopamine denervation. Exp Brain Res 74:527–534
Lindefors N, Brene' S, Herrera-Marschitz M, Persson H (1989b) Region specific regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA expression by dopamine neurons in rat brain. Exp Brain Res 77:611–620
Ljungdahl Å, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G (1978) Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat. I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience 3:861–943
Maggio JE (1988) Tachykinins. Ann Rev Neurosci 11:13–28
Marksteiner J, Sperk G (1988) Concomitant increase of somatostatin, neuropeptide Y and glutamate decarboxylase in the frontal cortex of rats with decreased seizure threshold. Neuroscience 26:379–385
Mauborgne A, Javoy-Agid F, Legrand JC, Agid Y, Cesselin F (1983) Decrease of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra and pallidum of parkinsonian brains. Brain Res 268:167–170
Meyer DK, Bienfeld MC, Oertel WH, Brownstein MJ (1982) Origin of the cholecystokinin-containing fibers in the rat caudatoputamen. Science 215:187–188
Minamino N, Masuda H, Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1984) Regional distribution of neuromedin K and neuromedin L in rat brain and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Com 124:731–738
Nakagawa Y, Shiosaka S, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Distribution of neuropeptide Y in the forebrain and diencephalon: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res 361:52–60
Naus CCG, Miller FD, Morrison JH, Bloom F (1988) Immunohisto-chemical and in situ hybridization analysis of the development of the rat somatostatin-containing neocortical neuronal system. J Comp Neurol 269:448–463
Nawa H, Hirose T, Takashima H, Inayama S, Nakanishi S (1983) Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNAs for two types of bovine brain substance P precursor. Nature 306:32–36
Nemeroff CB, Kizer JS, Reynolds GP, Bissette G (1989) Neuropeptides in Altzheimer's disease: a postmortem study. Regul Pept 25:123–130
Oblin A, Zivkovic B, Bartholini G (1984) Involvement of the D-2 dopamine receptor in the neuroleptic-induced decrease in nigral substance P. Eur J Pharmacol 105:175–177
Paxinos S, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Australia
Peters A, Miller M, Kimerer LM (1983) Cholecystokinin-like immunoreactive neurons in rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 8:431–448
Savasta M, Ruberte E, Palacios JM, Mengod G (1989) The colocalization of cholecystokinin and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNAs in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in the rat brain examined by in situ hybridization. Neuroscience 29:363–369
Shults CW, Yajima H, Guller H-G, Chase TN, O'Donohue TL (1985) Demonstration and distribution of kassinin-like material (substance K) in rat central nervous system. J Neurochem 45:552–558
Somogyi P, Hodgson AJ, Smith AD, Nunzi MG, Gorio A, Wu J-Y (1984) Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatinor cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci 4:2590–2603
Sonsalla PK, Gibb JW, Hanson GR (1984) Opposite responces in the striato-nigral substance P system to D1 and D2 receptor activation. Eur J Pharmacol 105:185–187
Sperk G, Widmann R (1984) Somatostatin precursor in the rat striatum: changes after local injection of kainic acid. J Neurochem 45:1441–1447
Studler JM, Javoy-Agid F, Cesselin F, Legrand JC, Agid Y (1982) CCK-8-immunoreactivity distribution in human brain: selective decrease in the substantia nigra from parkinsonian patients. Brain Res 243:176–179
Uhl GR, Sasek CA (1986) Somatostatin mRNA: regional variation in hybridization densities in individual neurons. J Neurosci 6:3258–3264
Ungerstedt U, Arbuthnott GW (1970) Quantitative recording of rotational behaviour in rats after 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res 24:485–493
Vincent SR, Johansson O, Hökfelt T, Meyerson B, Sachs C, Elde RP, Terenius L, Kimmel J (1982) Neuropeptide coexistence in human cortical neurons. Nature 298:65–67
Voigt MM, Uhl GR (1988) Preprocholecystokinin mRNA in rat brain: regional expression includes thalamus. Mol Brain Res 4:247–253
Weiss LT, Chesselet M-F (1989) Regional distribution and regulation of preprosomatostatin messenger RNA in the striatum, as revealed by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Mol Brain Res 5:121–130
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Struble RG, Clark AW, Coyle JT, DeLong MR (1982) Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 215:1237–1239
Young WS, Bonner TI, Brann MR (1986) Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9827–9831
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindefors, N., Brené, S., Herrera-Marschitz, M. et al. Neuropeptide gene expression in brain is differentially regulated by midbrain dopamine neurons. Exp Brain Res 80, 489–500 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227990