Summary
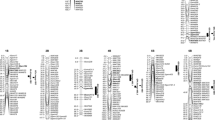
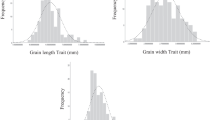
Chromosome 5B of bread wheat is known to carry two major genes giving rise to genetic disorders, Ne1 for hybrid necrosis and Vg for winter variegation. Additionally, in many european winter wheat varieties this chromosome is represented in a translocated form, with 5BL-7BL, 5BL-7BS chromosomes rather than the normal 5B and 7B forms of the standard variety Chinese Spring. Genetic analysis has been carried out to map these genes and the translocation break point, and to investigate their pleiotropic effects or those of linked quantitative trait loci (qtl) for economically important characters. This was facilitated by the development of single chromosome recombinant lines between a normal and translocated karyotype, and growing these in field experiments over two seasons. There was differential segregation in favour of the translocated karyotype in the population of recombinant lines. Linkage analysis revealed that the two morphological markers and the isozyme locus Ibf-B1 were located on the long arm of 5B with a gene order of: breakpoint — Ne1 — Vg — Ibf-B1. Analysis of quantitative characters using these genes as landmarks showed pleiotropic effects of Ne1 or effects of tightly linked qtl on most of the quantitative characters related to grain yield. An additional qtl determining spikelet and grain number/ear appeared to be linked to the centromere. Effects on ear emergence time were associated with both Ne1 and Vg, and these interacted with environments. Similarly, effects on plant height were associated with Ne1 and Vg. In addition, there was a further unlocated locus (loci) for height acting independently of the markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuspira J, Unrau J (1957) Genetic analysis of certain characters in common wheat using whole chromosome substitution lines. Can J Plant Sci 37:300–326
Law CN (1966) The location of genetic factors affecting a quantitative character in wheat. Genetics 53:487–498
Law CN (1967) The location of genetic factors controlling a number of quantitative characters in wheat. Genetics 56:445–461
Law CN, Snape JW and Worland AJ (1987) Aneuploidy in wheat and its uses in genetic analysis. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding: its scientific basis. Chapman and Hall, London New York, pp 71–108
Law CN, Worland AJ (1973) Aneuploidy in wheat and its uses in genetic analysis. Plant Breed Inst Annu Rep 1972:25–65
Liu CJ, Gale MD (1989) Ibf-1 (Iodine-binding factor), a highly variable marker system in the Triticeae. Theor Appl Genet 77:233–240
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincoln SE, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–726
Paterson AH, Damon S, Hewitt JD, Zamir D, Rabinowitch HD, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Tanksley SD (1991) Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations and environments. Genetics 127:181–197
Sax K (1923) The association of size differences with seed-coat pattern and pigmentation in Phaseolus vulgaris. Genetics 8:552–560
Snape JW, Law CN, Parker BB, Worland AJ (1985) Genetic analysis of chromosome 5A of wheat and its influence on important agronomic characters. Theor Appl Genet 71:518–526
Stuber CW, Edwards MD, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. II. Factors influencing yield and its component traits. Crop Sci 27:639–648
Tanksley SD, Media-Filho H, Rick CM (1982) Use of naturally-occurring enzyme variation to detect and map genes controlling quantitative traits in an interspecific backcross of tomato. Heredity 49:11–25
Thoday JM (1961) Location of polygenes. Nature 191:368–370
Thompson JN Jr, Thoday JM (1979) Quantitative genetic analysis. Academic Press, London
Tsunewaki K (1960) Monosomic and conventional analyses in common wheat. III. Lethality. Jpn J Genet 35:71–75
Weller JI, Soller M, Brody T (1988) Linkage analysis of quantitative traits in an interspecific cross of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum x Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium) by means of genetic markers. Genetics 118:329–339
Worland AJ, Law CN (1983) Cytoplasmic variation in wheat. Plant Breed Inst Annu Rep 1982:79–80
Worland AJ, Gale MD, Law CN (1987) Wheat genetics. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding: its scientific basis. Chapman and Hall, London New York, pp 129–171
Worland AJ, Petrovic S, Law CN (1988) Genetic analysis of chromosome 2D of wheat. II. The importance of this chromosome to Yugoslavian varieties. Plant Breed 100:247–259
Zhuckenko AA, Korol AB, Andryuschenko VK (1978) Linkage between loci of quantitative characters and marker loci. Genetika 14:771–778
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, H., Parker, B.B. & Snape, J.W. The location of major genes and associated quantitative trait loci on chromosome arm 5BL of wheat. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 85, 197–204 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222860
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222860