Summary
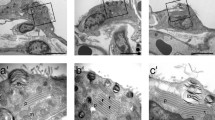
The epithelium covering the respiratory portion in the lung of the slow-worm (Anguis fragilis) has been studied by electron microscopy. The epithelium is composed of two different types of pneumonocytes. The type I pneumonocytes are roughly squamous and their cytoplasmic sheets spread over relatively large areas of the septal walls. These cytoplasmic sheets are attenuated in regions where they overlie septal capillaries; they usually have extensive areas of contact with adjacent cells. The type II pneumonocytes are also squamous but are more compact and possess more organelles. Their osmiophilic inclusion bodies are especially conspicuous. Most of their microvilli are concentrated on the surfaces of cytoplasmic “hillocks”. Deposits of membranous material are present in the air sacs. The morphological evidence suggests that the type II cells of Anguis secrete surface-active material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, J.R.: The histochemical recognition of lipine. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 87, 441–471 (1946)
Finley, T.N., Pratt, S.A., Ladman, A.J., Brewer, L., McKay, M.B.: Morphological and lipid analysis of the alveolar lining material in dog lung. J. Lipid Res. 9, 357–365 (1968)
Gil, J., Reiss, D.K.: Isolation and characterization of lamellar bodies and tubular myelin from rat lung homogenates. J. Cell Biol. 58, 152–171 (1973)
Guibé, J.: L'appareil respiratoire. In: Traité de zoologie (P.P. Grassé, ed.), Vol. 14, pp. 499–520. Paris: Masson 1970
Hirsch, J.G., Fedorko, M.E.: Ultrastructure of human leukocytes after simultaneous fixation with glutaraldehyde and osmium tetroxide and “post-fixation” in uranyl acetate. J. Cell Biol. 38, 615–627 (1968)
Kilburn, K.H.: Functional morphology of the distal lung. Int. Rev. Cytol. 37, 153–270 (1974)
Klaus, M., Reiss, D.K., Tooley, W.H., Piel, C., Clements, J.A.: Alveolar epithelial cell mitochondria as source of the surface-active lung lining. Science 137, 750–751 (1962)
Klika, E.: The electron microscopy of the lung alveolus. Acta Univ. Carol. Med. (Praha) 20, 1–35 (1965)
Kuhn, C.: Cytochemistry of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Amer. J. Path. 53, 809–833 (1968)
Leeson, T.S., Leeson, C.R.: Osmiophilic lamellated bodies and associated material in lung alveolar spaces. J. Cell Biol. 28, 577–581 (1966)
Meban, C.: The pneumonocytes in the lung of Xenopus laevis. J. Anat. (Lond.) 114, 235–244 (1973)
Meban, C.: Ultrastructure of the respiratory epithelium in the lungs of the tortoise, Testudo graeca. Cell Tiss. Res. 181, 267–275 (1977)
Meyrick, B., Reid, L.: The alveolar wall. Brit. J. Dis. Chest 64, 121–140 (1970)
Miller, D.A., Bondurant, S.: Surface characteristics of vertebrate lung extracts. J. appl. Physiol. 16, 1075–1077 (1961)
Nagaishi, C., Okada, Y., Ishiko, S., Daido, S.: Electron microscopic observations of the pulmonary alveoli. Exp. Med. Surg. 22, 81–117 (1964)
Okada, Y., Ishiko, S., Daido, S., Kim, J., Ikeda, S.: Comparative morphology of the lung with special reference to the alveolar epithelial cells. II. Lung of the reptilia. Acta tuberc. jap. 12, 1–10 (1962)
Pattle, R.E., Hopkinson, D.A.W.: Lung lining in bird, reptile and amphibian. Nature (Lond.) 200, 894 (1963)
Policard, A., Collet, A., Pregermain, S.: Recherches au microscope électronique sur les cellules pariétales alvéolaires du poumon des mammifères. Z. Zellforsch. 50, 561–587 (1959)
Schulz, H.: The submicroscopic anatomy and pathology of the lung. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970
Weibel, E.R.: Morphological basis of alveolar capillary gas-exchange. Physiol. Rev. 53, 419–495 (1973)
Wood, S.C., Lenfant, C.J.M.: Respiration: mechanics, control, and gas-exchange. In: Biology of the reptilia (C. Gans, ed.), Vol. 5, pp. 225–274. New York-San Francisco-London: Academic Press 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Eastern Health and Social Services Board, Northern Ireland
I am indebted to Mr. G.R. Dickson and Mr. M.S. Henderson for technical assistance and to Mrs. J. Hamilton for typing the manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meban, C. The respiratory epithelium in the lungs of the slow-worm, Anguis fragilis . Cell Tissue Res. 190, 337–347 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218179
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218179