Abstract
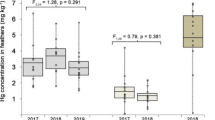
Levels of total mercury were determined in body feathers of 257 seabirds belonging to seven species from the Azores Archipelago, Mid-North Atlantic Ocean. Mercury levels in adult birds showed highly significant inter-specific variations. Median levels were higher in small petrels (Madeiran storm petrel=12.5 μg/g; Bulwer's petrel=22.1 μg/g) than in shearwaters (Little shearwater=2.1 μg/g; Cory's shearwater=6.0 μg/g) and terns (Roseate tern=2.0 μg/g; Common tern=2.3 μg/g). Such inter-specific variability is discussed in relation to biological factors that may influence mercury dynamics in birds. Intra-specific variations in mercury levels were also found. Mercury levels were significantly lower in chicks than in adults of Cory's shearwater, Roseate tern and Common tern. The levels in chick feathers were 60–70% of those in adult feathers. In Cory's shearwater and the terns (Roseate and Common combined), mercury levels decreased significantly with increasing age of chicks. Mercury levels in adult Madeiran storm petrel showed pronounced seasonal variation, being about 50% lower in Spring breeders than in Autumn breeders. Mercury levels are compared with levels reported for seabird populations of the same or related species, from a variety of regions. The use of bird feathers to monitor mercury in the marine environment is briefly discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1975) Atomic absorption methods, mercury in canned fish. Pye Unicam Ltd., Ref. AA/5 June/1975/951
Appelquist H, Asbirk S, Drabaek I (1984) Mercury monitoring: Mercury stability in bird feathers. Mar Pollut Bull 15:22–24
Becker PH, Sperveslage H (1989) Organochlorines and heavy metals in Herring gull (Larus argentatus) eggs and chicks from the same clutch. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 42:721–727
Becker PH (1991) Population and contamination studies in coastal birds: The Common Tern Sterna hirundo. In: Perrins CM, Lebreton JD, Hirons GJM (eds) Bird Population Studies: Relevance to Conservation and Management. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 433–460
Becker PH, Furness RW, Henning D (1993) Mercury dynamics in young Common tern (Sterna hirundo) from a polluted environment. Ecotoxicology 2:33–40
Becker PH, Schuhmann S, Koepff C (1993) Hatching failure in Common terns (Sterna hirundo) in relation to environmental chemicals. Environ Pollut 79:207–213
Bernhard M (1988) Mercury in the Mediterranean. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies No. 98
Braune BM, Gaskin DE (1987a) Mercury levels in Bonaparte's gull (Larus philadelphia) during Autumn moult in the Quoddy Region, New Brunswick, Canada. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 16:539–549
Braune BM (1987b) A mercury budget for the Bonaparte's gull during Autumn moult. Ornis Scand 18:244–250
Bryan GW (1979) Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond (B) 286:483–505
Burger J, Gochfeld M (1991) Lead, mercury, and cadmium in feathers of tropical terns in Puerto Rico and Australia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:311–315
Burger J, Nisbet ICT, Gochfeld M (1992a) Metal levels in regrown feathers: Assessment of contamination on the wintering and breeding grounds in the same individuals. J Toxicol Environ Health 36:327–338
Burger J, Schreiber EAE, Gochfeld M (1992b) Lead, cadmium, selenium and mercury in seabird feathers from the Tropical Mid-Pacific. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:815–822
Burger J (1993) Metals in avian feathers: Bioindicators of environmental pollution. Rev Environ Toxicol 5:203–311
Burger J, Nisbet ICT, Gochfeld M (1994) Heavy metal and selenium levels in feathers of known-aged Common terns (Sterna hirundo). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 26:351–355
Crewther WG, Fraser RDB, Lennox FG, Lindley H (1965) The chemistry of keratins. Adv Prot Chem 20:191–346
Elliott JE, Scheuhammer AM, Leighton FA, Pearce PA (1992) Heavy metal and metallothionein concentrations in Atlantic Canadian seabirds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:63–73
Furness RW, Muirhead SJ, Woodburn M (1986) Using bird feathers to measure mercury in the environment: Relationships between mercury content and moult. Mar Pollut Bull 1:27–30
Furness RW, Lewis SA, Mills JA (1990) Mercury levels in the plumage of Red-billed gulls Larus novaehollandie scopulinus of known sex and age. Environ Pollut 63:33–39
Furness RW, Thompson DR, Becker PH (in press) Spatial and temporal variation in mercury contamination in seabirds in the North Sea. Helgoländer Meeresuntersulhungen
Furness RW (1993) Birds as monitors of pollutants. In: Furness RW, Greenwood JJD (ed) Birds as monitors of environmental change. Chapman Hall, London, pp 86–143
Gochfeld M (1980a) Mercury levels in some seabirds of the Humboldt Current, Peru. Environ Pollut (A) 22:197–205
Gochfeld M (1980b) Tissue distribution of mercury in normal and abnormal young Common terns. Mar Pollut Bull 11:362–366
Goede AA, deBruin M (1984) The use of bird feather parts as a monitor for metal pollution. Environ Pollut (B) 8:281–298
Honda K, Nasu T, Tatsukakawa R (1986) Seasonal changes in mercury accumulation in the Black-eared Kite, Milvus migrans lineatus. Environ Pollut (A) 42:325–334
Honda K, Marcovecchio JE, Kan S, Tatsukawa R, Ogi H (1990) Metal concentrations in pelagic seabirds from the north Pacific Ocean. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:704–711
Lewis SA (1991) Studies of mercury dynamics in birds. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Glasgow
Lewis SA, Furness RW (1991) Mercury accumulation and excretion in laboratory reared Black-headed gull Larus ridibundus chicks. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:316–320
Lewis SA, Becker PH, Furness RW (1993) Mercury levels in eggs, internal tissues and feathers of herring gulls Larus argentatus from the German Wadden Sea. Environ Pollut 80:293–299
Lindqvist O (1991) Mercury in the Swedish environment—Recent research on causes, consequences and corrective methods. Water Air Soil Pollut 55:1–261
Lock JW, Thompson DR, Furness RW, Bartle JA (1992) Metal concentrations in seabirds of the New Zealand region. Environ Pollut 75:289–300
Monteiro LR, Lopes HD (1990) Mercury content of swordfish Xiphias gladius in relation to length, weight, age and sex. Mar Pollut Bull 21:293–296
Monteiro LR, Isidro EJ, Lopes HD (1991) Mercury content in relation to sex, size, age and growth in two scorpionfish (Helicolenus dactylopterus and Pontinus kuhlii) from Azorean waters. Water Air Soil Pollut 56:359–367
Monteiro LR, Porteiro FM, Gonçalves JM (1992) Inter-and intraspecific variation of mercury levels in muscle of cephalopods from the Azores. Arquipélago (Life and Earth Sciences) 10:13–22
Mougin J-L, Jouanin C, Roux F (1988) Les migrations du Puffin cendré Calonectris diomedea. L'Oiseau et RFO 58:303–318
Muirhead SJ, Furness RW (1988) Heavy metal concentrations in tissues of seabirds from Gough Island, South Atlantic Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 19:278–283
Nicholson JK, Osborn D (1983) Kidney lesions in pelagic seabirds with high tissue levels of cadmium and mercury. J Zool Lond 200:99–118
Osborn D, Harris MP, Nicholson JK (1979) Comparative tissue distribution of mercury, cadmium and zinc in three species of pelagic seabirds. Comp Biochem Physiol 64 C:61–67
Renzoni A, Focardi S, Fossi C, Leonzio C, Mayol J (1986) Comparison between concentrations of mercury and other contaminants in eggs and tissues of Cory's shearwater Calonectris diomedea collected on Atlantic and Mediterranean islands. Environ Pollut (A) 40:17–35
Scheuhammer AM (1987) The chronic toxicity of aluminium, cadmium, mercury, and lead in birds: A review. Environ Pollut 46:263–295
Stewart FM, Thompson DR, Furness, RW, Harrison N (in press) Seasonal variation in heavy metal levels in tissues of common guillemots, Uria aalge from Northwest Scotland. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol
Thompson DR, Furness RW (1989) The chemical form of mercury stored in South Atlantic seabirds. Environ Pollut 60:305–317
Thompson DR, Stewart FM, Furness RW (1990) Using seabirds to monitor mercury in the marine environments: The validity of conversion ratios for tissue comparisons. Mar Pollut Bull 21:339–342
Thompson DR, Hamer KC, Furness RW (1991) Mercury accumulation in Great skuas Catharacta skua of known age and sex, and its effect upon breeding and survival. J Appl Ecol 28:672–684
Thompson DR, Furness RW, Walsh PM (1992a) Historical changes in mercury concentrations in the marine ecosystem of the north and northeast Atlantic ocean as indicated by seabird feathers. J Appl Ecol 29:79–84
Thompson DR, Furness RW, Barrett RT (1992b) Mercury concentrations in seabirds from colonies in the Northeast Atlantic. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 23:383–389
Thompson DR, Becker PH, Furness RW (1993a) Long-term changes in mercury concentrations in Herring gulls Larus argentatus and Common terns Sterna hirundo from the German North Sea coast. J Appl Ecol 30:316–329
Thompson DR, Furness RW, Lewis SA (1993b) Spatial and temporal variation in mercury concentrations in some albatrosses and petrels from the subAntarctic. Polar Biol 13:239–244
Walsh PM (1990) The use of seabirds as monitors of heavy metals in the marine environment. In Furness RW & Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy Metals in the Marine Environment. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, FL, pp 183–204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, L.R., Furness, R.W. & del Nevo, A.J. Mercury levels in seabirds from the Azores, Mid-North Atlantic Ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 304–309 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213106
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213106