Abstract
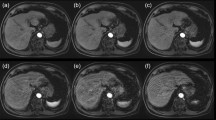
Gadopentetate dimeglumine was administered intravenously to 16 patients undergoing abdominal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. T1-weighted and fat-suppressed T1-weighted images were acquired before and after intravenous administration of 0.1 mmol/kg gadopentetate dimeglumine. The stomach, small bowel, and colon were analyzed regarding the presence and relative intensity of contrast enhancement. Diffuse enhancement of the gastrointestinal tract wall was observed in all patients following contrast material administration. Such enhancement was most conspicuous on fat-suppressed T1-weighted images. Quantitative measurements indicated that the wall of the gastrointestinal tract enhanced approximately 100% with gadopentetate dimeglumine. This study demonstrates that enhancement of the normal gastrointestinal tract occurs routinely when intravenous gadopentetate dimeglumine is administered, and such enhancement should not be considered indicative of gastrointestinal pathology. Furthermore, it suggests the potential utility for using intravenous rather than orally administered contrast agents to provide enhancement of the gastrointestinal tract on MR images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller PJ, Hunter WW Jr, Schmalbrock P. Multisection fatwater imaging with chemical shift selective presaturation. Radiology 1987;164:539–541
Semelka RC, Chew W, Hricak H, Tomei E, Higgins CB. Fatsaturation MR imaging of the upper abdomen. AJR 1990;155:1111–1116
Mitchell DG, Vinitski S, Saponaro S, Tasciyan T, Burk DL Jr, Rifkin MD. Liver and pancreas: improved spin-echo T1 contrast by shorter echo time and fat suppression at 1.5 T. Radiology 1991;178:67–71
Runge VM, Clanton JA, Lukehart CM, Partain CL, James AE Jr. Paramagnetic agents for contrast-enhanced NMR imaging: a review. AJR 1983;141:1209–1215
Runge VM, Stewart RG, Clanton JA, et al. Work in progress: potential oral and intravenous NMR contrast agents. Radiology 1983;147:789–791
Laniado M, Kornmesser W, Hamm B, Clauss W, Weinmann H-J, Felix R. MR imaging of the gastrointestinal tract: value of Gd-DTPA. AJR 1988;150:817–821
Kaminsky S, Laniado M, Gogoll M, et al. Gadopentetate dimeglumine as a bowel contrast agent: safety and efficacy. Radiology 1991;178:503–508
Weinreb JC, Maravilla KR, Redman HC, Nunnally R. Improved MR imaging of the upper abdomen with glucagon and gas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984;8:835–838
Mattrey RF, Hajek PC, Gylys-Morin VM, et al. Perflouro-chemicals as gastrointestinal contrast agents for MR imaging: preliminary studies in rats and humans. AJR 1987;148:1259–1263
Rubin DL, Muller HH, Nino-Murcia M, Sidhu M, Christy V, Young SW. Intraluminal contrast enhancement and MR visualization of the bowel wall: efficacy of PFOB. J Mag Res Imag 1991;1:371–380
Listinsky JJ, Bryant RG. Gastrointestinal contrast agents: a diamagnetic approach. Mag Res Med 1988;8:285–292
Hahn PF, Stark DD, Saini S, Lewis LM, Wittenberg J, Ferrucci JT. Ferrite particles for bowel contrast in MR imaging: design issues and feasibility studies. Radiology 1987;164:37–41
Lonnemark M, Hemmingsson A, Bach-Gansmo T, et al. Effect of superparamagnetic particles as oral contrast medium at magnetic resonance imaging: a phase I clinical study. Acta Radiol 1989;30:193–196
Rinck PA, Smevik O, Nilsen G, et al. Oral magnetic particles in MR imaging of the abdomen and pelvis. Radiology 1991;178:775–779
Goldstein HA, Kashanian FK, Blumetti RF, Holyoak WL, Hugo FP, Blumenfleld DM. Safety assessment of gadopentetate dimeglumine in U.S. clinical trials. Radiology 1990;174:17–23
Van Beers B, Demeure R, Pringot J, et al. Dynamic spin-echo imaging with Gd-DTPA: value in the differentiation of hepatic tumors. AJR 1990;154:515–519
Schmiedl U, Kolbel G, Hess CF, Klose U, Kurtz B. Dynamic sequential MR imaging of focal liver lesions: initial experience in 22 patients at 1.5 T. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1990;14:600–607
Mirowitz SA, Lee JK, Gutierrez E, Brown JJ, Heiken JP, Eilenberg SS. Dynamic gadolinium-enhanced rapid acquisition spin-echo MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 1991;179:371–376
Eilenberg SS, Lee JK, Brown J, Mirowitz SA, Tartar VM. Renal masses: evaluation with gradient-echo Gd-DTPA enhanced dynamic MR imaging. Radiology 1990;176:333–338
Semelka RC, Hricak H, Stevens SK, Finegold R, Tomei E, Carroll PR. Combined gadolinium-enhanced and fat-saturation MR imaging of renal masses. Radiology 1991;178:803–809
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirowitz, S.A. Contrast enhancement of the gastrointestinal tract on MR images using intravenous gadolinium-DTPA. Abdom Imaging 18, 215–219 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198104
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198104