Summary
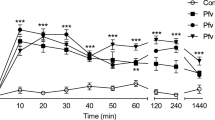
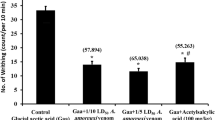
Rat hind-paw swelling was induced dose-dependently by subplantar injection of acidic phospholipase A2 (NNAVPLA2) from Naja naja atra venom. Diphenhydramine and methysergide pretreatment greatly reduced the swelling effect caused by NNAVPLA2. Several doses of compound 48/80 given to deplete the histamine content of rat hind paw, also greatly suppressed NNAVPLA2-induced paw swelling. The paw swelling caused by NNAVPLA2 was reduced following pretreatment with BW 755C, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase/lipoxygenase, or subplantar co-injection with FPL 55712, a SRS-A antagonist, while pretreatment with acetylsalicylic acid had no effect. Captopril significantly potentiated the NNAVPLA2-induced paw swelling. The recovered myeloperoxidase activity was increased within 1 h and still elevated in the rat paw 3 to 6 h after subplantar injection of NNAVPLAZ. In isolated peripheral PMN leukocyte suspension, NNAVPLAZ caused a release of superoxide radical. Subplantar co-injection with superoxide dismutase/catalase significantly inhibited NNAVPLA2-induced paw swelling. NNAVPLA2 did not trigger platelet aggregation either in platelet-rich plasma or in washed platelet suspension. NNAVPLA2-induced hind-paw swelling was also suppressed by the pretreatment with isoprenaline or terbutaline, while this response was not affected by co-injection with BN 52021, a PAF antagonist, into the paw. It is concluded that the hindpaw swelling caused by NNAVPLAZ is mainly due to histamine and serotonin released from mast cells and partly due to the formed kinins and SRS-A in the inflammatory area, and superoxide radical from PMN leukocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Born GVR, Cross MJ (1963) The aggregation of blood platelet. J Physiol 168:178 -195
Boura ALA, Svolmanis AP (1984) Converting enzyme inhibition in the rat by captopril is accompanied by potentiation of carrageenin-induced inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 82:3–8
Chang CC, Chuang ST, Lee CY, Wei JW (1972) Role of cardiotoxin and phospholipase A in the blockade of nerve conduction and depolarization of skeletal muscle induced by cobra venom. Br J Pharmacol 44:752–764
Chiu HIT, Chen IJ, Teng CM (1989) Edema formation and degranulation of mast cells by a basic phospholipase A2 purified from Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus snake venom. Toxicon 27:115–125
Dameau B, Lege L, Oldigs HD, Vogt W (1975) Histamine release, formation of prostaglandin-like activity (SRS-C) and mast cell degranulation by the direct lytic factor (DLF) and phospholipase A of cobra venom. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 287:141–156
Del Maestro RF, Björk J, Arfors KE (1981) Increase in microvascular permeability induced by enzymatically generated free radicals. 1. in vivo study. Microvas Res 22:239–254
DeLuca M, McElory WD (1978) Purification and properties of firefly luciferase. Methods Enzymol 57:3–15
Di Martino MJ, Campbell GK Jr, Wolff CE, Hanna N (1987) The pharmacology of arachidonic acid-induced rat paw edema. Agents Actions 21:303–305
Dobbins DE, Soika CY, Premen AJ, Grega GJ, Dabney JM (1982) Blockade of histamine and bradykinin-induced increases in lymph flow, protein concentration and protein transport by terbutaline in vivo. Microcir 2:127–150
Dri P, Cramer R, Soranzo MR, Comin A, Miotti V, Patriarca P (1982) New approaches to detection of myeloperoxidase deficiency. Blood 60:323–327
Fredholm B (1966) Studies on a mast cell degranulating factor in bee venom. Biochem Pharmacol 15:2037–2043
Greenbaum LM, Freer R, Chang J, Semente G, Yamafuji K (1969) PMN-kinin and kinin metabolizing enzymes in normal and malignant leukocytes. Br J Pharmacol 36:623–634
Hagen PO, Ofstad E, Amundsen E (1969) Experimental acute pancreatitis in dog IV. The relationship between phospholipase A and the histamine releasing and hypotensive effects of pancreatic exudate. Scand J Gastroenterol 4:89–96
Higgs GA, Flower RJ, Vane JR (1979) A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol 28:1959–1961
Hines GC, Moss GF, Cox JSG (1972) Effects of disodium cromoglycate on phospholipase A activity, studies with egg yolk and isolated mast cell systems. Biochem Pharmacol 21:171–179
Markert M, Andrew PC, Babior BM (1984) Measurement of O2 production by human neutrophils: the preparation and assay of NADPH oxidase-containing particles from human neutrophils. Methods Enzymol 105:358–365
Mebs D (1983) Myotoxic and neurotoxic phospholipase A2. In: Hucho F, Ovchinnikov YA (eds) Toxins as tools in neurochemistry. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 337–340
Newby AC (1980) Role of adenosine deaminase ecto-(5′-nucleo-tidase) and ecto-(non-specific phosphatase) in cyanide-induced adenosine monophosphate catabolism in rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem J 186:907–918
O'Brien JR (1962) Platelet aggregation 11. Some results from a new method of study. J Clin Pathol 15:452–455
Ouyang C, Huang TF (1983) Potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from Trimeresurus gramineus snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta 757:332–341
Ouyang C, Shiau SY (1970) Relationship between pharmacological actions and enzymatic activities of the venom of Trimeresurus gramineus. Toxicon 8:183–191
Rosenberg P (1979) Pharmacology of phospholipase A2 from snake venoms. Handb Exp Pharmacol 52:403–447
Rothschild AM, Castania A, Cordeiro RSB (1974) Consumption of kininogen, formation of kinin and activation of arginine ester hydrolase in rat plasma by rat peritoneal fluid cells in the presence of 1-adrenaline. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 285:243–256
Samhoun MN, Piper PJ (1986) Actions of leukotrienes in nonhuman respiratory tissues. In: Piper PJ (ed) The leukotrienes, their biological significance. Raven Press, New York, pp 151–160
Samuelsson B (1983) Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science 220: 568–575
Shore PA, Burkhalter A, Cohn VH Jr (1959) A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 127:182–186
Teng CM, Chen YH, Ouyang C (1984) Biphasic effect on platelet aggregation by phospholipase A purified from Vipera russelli snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta 772:393–402
Teng CM, Kuo YP, Lee LG, Ouyang C (1987) Characterization of the anticoagulants from cobra snake (Naja naja atra) venom. Toxicon 25:201–210
Teng CM, Wang JP, Peng HC, Ouyang C (1989) Edema-producing proteins isolated from Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus snake venom. Toxicon 27:899–905
Undam BJ, Graziano FM, Buckner CK (1985) Studies on \-adrenoceptors of purified mast cell from guinea-pig lung. Eur J Pharmacol 109:413–416
Uvnäs B (1958) The mechanism of histamine liberation. J Pharm Pharmacol 10:1–13
Vishwanath BS, Kini RM, Gowda TV (1987) Characterization of three edema-inducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid aristolochic acid. Toxicon 25:501–515
Wang JP, Teng CM (1989) Role of mast cells and PMN leukocytes in cardiotoxin-induced rat paw edema. Eur J Pharmacol 161:9–18
Wang JP, Teng CM (1990) Comparison of the enzymatic and edemaproducing activities of two venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Eur J Pharmacol 190:347–354
Wang JP, Teng CM (1990a) Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on the cardiotoxin-induced hind-paw oedema in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 42: 842–845
Williams TJ (1979) Prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin I2 and the vascular changes of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 65:517–524
Willoughby DA, Giroud JP (1969) The role of polymorphonuclear leukocyte in acute inflammation in agranulocytic rats. J Pathol 98:53–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to C.-M. Teng at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JP., Teng, CM. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs on rat hind-paw swelling caused by phospholipase A2 from Naja naja atra venom . Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344, 377–381 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183014
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00183014