Abstract
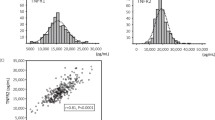
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) has been found to be elevated in patients during hemodialysis and is thought to mediate some of the immune and metabolic dysfunctions in these patients. It has been speculated that infusions of soluble TNF receptor (sTNF-R) may prevent some of the cytotoxic effects of TNF. However, little is still known about preexisting serum TNF-R levels in patients with chronic renal failure, with or without hemodialysis. Therefore we analyzed serum samples of sTNF-R in 26 patients with chronic renal failure (group I), 6I hemodialysis patients (group II), 9 renal transplant recipients with acute renal failure requiring posttransplant dialysis (group III), 13 renal transplant patients with rejection and moderate kidney dysfunction (group IV), and 21 renal transplant recipients with borderline kidney dysfunction and diverse infectious complications (group V). Control groups consisted of 34 blood donors and diseased controls (11 renal transplant recipients with normal kidney function without complications). All patient groups showed significantly higher sTNF-R levels compared to the control groups. In groups I, IV, and V comparable levels were observed. In group I there was a clear correlation between sTNF-R levels and serum creatinine. The highest sTNF-R serum levels were seen in groups II and III, but there was no correlation with creatinine. In the posttransplant cases (group III and diseased controls) there was a decrease in sTNF-R with improvement of kidney function. These data strongly suggest that sTNF-R serum levels are dependent on kidney function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- TNF-R:
-
tumor necrosis factor receptor
- sTNF-R:
-
soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor
- RTX:
-
renal transplantation
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Adolf G, Apfler I (1991) A monoclonal antibody-based enzymeimmunoassay for quantitation of human tumor necrosis factor binding protein I, a soluble fragment of the 60 kD TNF receptor, in biological fluids. J Immunol Meth 143:127–136
Beutler B, Milsakr IW, Cerami AC (1985) Passive immunization against chachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science 229:869–871
Brockhaus M, Schoenfeld HJ, Schlauger EJ, Hunziker W, Lesslauer W, Loetscher H (1990) Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3127–3131
Dinarello C (1992) Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor and their naturally occurring antagonists during hemodialysis. Kidney Int 42 [Suppl 38]:68–77
Engelmann H, Aderka D, Rubinstein M, Rotmann D, Wallach D (1989) A tumor necrosis factor binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem 264:11974–11980
Exley AR, Cohen J (1990) Optimal collection of blood samples for the measurement of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Cytokine 2:353–356
Engelberts I, Möller A, Schoen GJM, van der Linden CJ, Buurman WA (1991) Evaluation of measurement of human TNF in plasma by ELISA. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 10:69
Engelberts I, Stephens S, Francot GJM, van der Linden CJ, Bumman WA (1991) Evidence for different effects of soluble TNF-receptors on various TNF measurements in human biological fluids. Lancet 338:515–516
Herbelin A, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J, Urena P, Descamps-Latscha BI (1990) Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Kidney Int 37:116–125
Hohmann HP, Remy R, Brockhaus M, van Loon APGM (1989) Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem 265:14927–14934
Lonnemann G, van der Meer JWM, Cannon JG, Dinarello CA, Koch KM, Granollereas C, Deschodt G, Shaldon S (1987) Induction of tumor necrosis factor during extracorporal blood purification. N Engl J Med 317:963–964
Lantz M, Malik S, Slevin ML, Olsson I (1990) Infusion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) causes an increase in circulating TNF-binding protein in humans. Cytokine 2:402–406
Leroux-Roels G, Offner F, Philippe J, Vermeulen A (1988) Influence of blood-collecting systems on concentrations of tumor necrosis factor in serum and plasma. Clin Chem 34:2373–2374
Leroux-Roels G, Philippe J, Offner F, Vermeulen A (1990) In-vitro production of cytokines in blood. Lancet 336:1197
Lesslauer W, Tabuchi H, Gentz M, Brockhaus M, Schlauger EJ, Gran G, Piquet H, Pointaire P, Vassali P, Poetscher HR (1991) Recombinant soluble TNF receptor proteins inhibit LTS-induced lethality in mice. Cytokine 3:497 (abstract)
Murch S, MacDonald T (1990) In vitro production of cytokines in serum. Lancet 336:687–688
Peetre CH, Thysell H, Grugg A, Olsson I (1988) A tumor necrosis factor binding protein is present in human biological fluids. Eur J Haematol 41:414–419
Sprang SR (1990) The divergent receptors for TNF. Trends Biochem Sci 15:366–368
Schall TJ, Lewis M, Koller KJ, Lee A, Rice GC, Wong GHW, Gatanaga T, Granger GA, Lentz R, Raab H, Kohr WJ, Goeddel DV (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell 61:361–370
Thoma B, Grell M, Pfitzenmaier K, Scheurich P (1990) Identification of a 60-kD tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor as the major signal transducing component in TNF responses. J Exp Med 172:1019–1023
Tracey KJ (1992) The acute and chronic pathophysiologic effects of TNF: mediation of septic shock and wasting (cachexia). I. In: Beutler B (ed) Tumor necrosis factors, the molecules and their emerging role in medicine. Raven Press, New York, pp 255–273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: G. Halwachs
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halwachs, G., Tiran, A., Reisinger, E.C. et al. Serum levels of the soluble receptor for tumor necrosis factor in patients with renal disease. Clin Investig 72, 473–476 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180527
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180527