Abstract
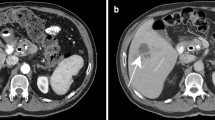
Fungal splenic abscesses are a potentially fatal complication of childhood leukemia, especially during hematologic relapse. Optimal treatment requires splenectomy combined with amphotericin B therapy. Previous reports have suggested that splenectomy should not be performed prior to complete control of the relapse. Three children with relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia developed fever and splenomegaly, two during the re-induction phase of chemotherapy and the third within 1 month after a second remission. Imaging studies revealed non-homogeneity of the spleen. Uneventful splenectomy was performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes before the return of normal hematopoiesis. Our results indicate that splenectomy for treatment of fungal abscesses can be successfully undertaken before complete hematologic remission is accomplished.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodey GP (1966) Fungal infectious complications in acute leukemia. J Chron Dis 19: 667–687
Bodey G, DeJongh D, Isassi A, Freirech EJ (1969) Hypersplenism due to disseminated candidiasis in a patient with acute leukemia. Cancer 24: 417–420
Brereton HD, Ihde D, Levine AS, Young RC (1977) Candida infectious; clinical and pathologic correlations in 168 consecutive autopsy proven cases in cancer patients. (Abstract) Proc Am Ass Can Res 18: 19
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital (1982). N Engl J Med 307: 806–814
Chun CH, Raff MJ, Contreras L, Varghese R, Waterman N, Daffner R, Melo JC (1980) Splenic abscess. Med 59: 50–65
Edwards JE (1980) Clinical aspects of mucormycosis. Ann Int Med 93: 93–108
Gadacz T, Way LW, Dunphy JE (1974) Changing clinical spectrum of splenic abscess. Am J Surg 128: 182–187
Mirsky HS, Cuttner J (1972) Fungal infection in acute leukemia. Cancer 30: 348–352
Myerowitz RL, Pazin GJ, Allen CM (1977) Disseminated candidiasis. Am J Clin Path 68: 29–38
Page CP, Coltman CA, Robertson HD, Nelson EA (1980) Candidal abscess of the spleen in patients with acute leukemia. Surg Gynecol Obstet 151: 604–608
Singer C, Kaplan MH, Armstrong D (1977) Bacteremia and fungemia complicating neoplastic disease. Am J Med 62: 731–742
Stone HH, Kolb LD, Currie CA, Geheber CE, Cuzzell JZ (1974) Candida sepsis: pathogenesis and principles of treatment. Ann Surg 179: 697–711
Wald BR, Ortega JA, Ross L, Wald P, Laug WE, Williams KO (1981) Candidal splenic abscesses complicating acute leukemia of childhood treated by splenectomy. Pediatrics 67: 296–299
Wingard JR, Merz WG, Saral R (1979) Candida tropicalis: a major pathogen in immunocompromised patients. Ann Int Med 91: 539–543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: C. D. Vinocur
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marmon, L.M., Vinocur, C.D., Wimmer, R.S. et al. Fungal splenic abscesses: management in childhood leukemia. Pediatr Surg Int 5, 118–120 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178230
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178230