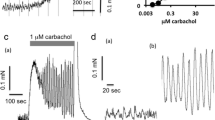
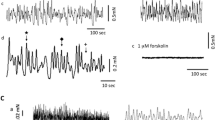
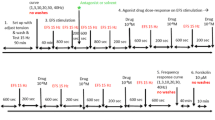
Abstract
Electrical field stimulation of strip preparations of the female rabbit urethral lamina propria induces a frequency-dependent adrenergic contraction or a non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) relaxation, mediated by nitric oxide, depending on the prevailing tension. To study the role of potassium channels in these responses, the effects of inhibitors of voltage-dependent (dendrotoxin I, 4-aminopyridine), low (apamin) and high (iberiotoxin, charybdotoxin) conductance calcium-activated and ATP-sensitive (glibenclamide) potassium channels on the frequency-response relationship were examined. 4-Aminopyridine (1 mM), but none of the other inhibitors, augmented the NANC relaxation. The maximal response was, however, unaffected by 4-aminopyridine. The adrenergic contraction was enhanced by 4-aminopyridine (1 mM), dendrotoxin I(0.1 μM), iberiotoxin (0.1 μM) and charybdotoxin (0.1 μM), but not by apamin (0.1 μM) and glibenclamide (10 μM). Besides reducing the frequency eliciting half maximal contraction, dendrotoxin and charybdotoxin also enhanced the maximal response. None of the inhibitors affected the relaxation induced by the nitric oxide donor 3-morpholinosydnonimine or the contraction elicited by noradrenaline. The results suggest that dendrotoxin-sensitive voltage-dependent and high conductance calcium-activated neuronal potassium channels participate in adrenergic, but not in nitrergic, neurotransmission in the lamina propria of the female rabbit urethra. This offers a possibility to selectively interfere with the adrenergic neuroeffector system with drugs acting on these K-channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkow SG (1953) The corpus spongeosum of the urethra: its possible role in urinary control and stress incontinence in women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 65:346–351
Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Fotuhi M, Hwang PM, Snyder SH (1991). Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal NADPH diaphorase are identical in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7797–7801
Chandy KG, Gutman GA (1995) Voltage-gated potassium channel genes. In:North RA (ed) Handbook of receptors and channels, ligand and voltage-gated ion channels. CRC Press, Boca Raton 1–71
De Man JG, Boeckxstaens GE, Pelckmans PP, De Winter BY, Herman AG, Van Maercke YM (1993) Prejunctional modulation of the nitrergic innervation of the canine ileocolonic junction via potassium channels. Br J Pharmacol 110:559–564
Edwards G, Weston AH (1994) Effect of potassium channel modulating drugs on isolated smooth muscle. In: Szekeres L, Papp GJ (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, III. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 469–531
Ellis JL, Conanan ND (1994) Effects of potassium channel blockers on relaxation to a nitric oxide donor and to nonadrenergic nerve stimulation in guinea pig trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:782–786
Galvan M (1992) Potassium channels in mammalian neurones: their properties and prospects for pharmacological manipulation. In: Weston AH, Hamilton TC (eds) Potassium channel modulators. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 204–236
Garcia ML, Galverez A, Garcia-Calvo M, King VF, Vazquez J, Kaczorowski GJ (1991) Use of toxins to study potassium channels, J Bioenerg Biomembr 23:615–646
Garcia ML, Knaus H-G, Munujos P, Slaughter RS, Kaczorowski GJ (1995) Charybdotoxin and its effects on potassium channels. Am J Physiol 269:01–010
Grissmer S, Nguyen An, Aiyar J. Hanson DC, Mather RJ, Gutman GA, Karmilowicz MJ, Auperin DD, Chandy KG (1994) Pharmacological characterization of five cloned voltage-gated K+ channels, types Kv 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5, and 3.1, stably expressed in mammalian cell lines. Mol Pharmacol 45:1227–1234
Hall A, Stow J, Sorensen R, Dolly JO, Owen D (1994) Blockade by dendrotoxin homologues of voltage-dependent K+ currents in cultured sensory neurones from neonatal rats. Br J Pharmacol 113:959–967
Hope BT, Michael GJ, Knigge KM, Vincent SR (1991) Neuronal NADPH diaphorase is a nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2811–2814
Hopkins WF, Allen ML, Houamed KM, Tempel BI (1994) Properties of voltage-gated K+ currents expressed in Xenopus oocytes by mKvl.l., mKv1.2 and their heteromultimers as revealed by mutagenesis of dendrotoxin-binding site in mKv1.1. Pflügers Arch 428:382–390
Mattiasson A, Andersson K-E, Sjögren C (1985) Contractant and relaxant properties of the female rabbit urethral submucosa. J Urol 133:304–310
Persson K, Alm P, Johansson K, Larsson B, Andersson K-E (1993) Nitric oxide synthase in pig lower urinary tract: immunohistochemistry, NADPH diaphorase histochemistry and functional effects. Br J Pharmacol 110:521–530
Rud T, Andersson K-E, Asmussen M, Hunting A, Ulmsten U (1980) Factors maintaining the intraurethral pressure in women. Invest Urol 17:343–347
Schweitz H, Bidard J-N, Maes P. Lazdunski M (1989a) Charybdotoxin is a new member of the K+ channel family that includes dendrotoxin I and mast cell degranulating peptide. Biochemistry 28:9708–9714
Schweitz H, Stansfeld CE, Bidard J-N, Farni L, Maes P, Lazdunski M (1989b) Charybodotoxin blocks dendrotoxin-sensitive voltage-activated K+ channels. FEBS Lett 250:519–522
Zygmunt PKE, Persson K, Alm P, Larsson B, Andersson K-E (1993) The L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway in the rabbit urethral lamina propria. Acta Physiol Scand 148:431–439
Zygmunt PKE, Zygmunt PM, Högestätt EF, Andersson K-E (1995) NANC neurotransmission in lamina propria of the rabbit urethra: regulation by different subsets of calcium channels. Br J Pharmacol 115:1020–1026
Zygmunt PM, Zygmunt PKE, Högestätt ED, Andersson K-E (1993) Effects of ω-conotoxin on adrenergic, cholinergic and NANC neurotransmission in the rabbit urethra and detrusor. Br J Pharmacol 110:1285–1290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zygmunt, P.K.E., Högestätt, E.D. & Andersson, KE. Effects of potassium channel inhibitors on nitrergic and adrenergic neurotransmission in lamina propria of the female rabbit urethra. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 354, 336–342 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171065
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171065