Summary
Recent studies suggested that certain erythromycin A (EM-A) derivatives are motilin receptor agonists. As proposed by Itoh they may be called “motilides”. We have investigated the Ca2+-dependence of contractions induced by two potent motilides, ME-34 [de(N-methyl) 8,9-anhydroeryhtromycin A 6,9-hemiacetal] and EM-523 [de(N-methyl)-N-ethyl-8,9-anhydro-erythromycin A 6,9-hemiacetal], in duodenal tissues and compared the results with those previously obtained with motilin.
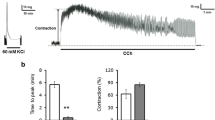
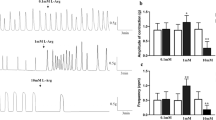
Isometric and isotonic contractile responses of isolated longitudinal muscle sheets from the rabbit duodenum were tested under normal, Ca2+-free and depolarizing conditions. Prior to stimulation with motilides, the maximal response to acetylcholine was recorded and all responses were always expressed as a percentage of this response. Both motilides induced contractions in normally polarized tissue, with an EC50 of 26 ± 5 nM for ME-34 (n = 7), and 27 ± 5 nM for EM-5231 (n = 16) and maximal responses of respectively 88 ± 4% and 80 ± 3%. Like motilin, both compounds induced an ‘extra’-contraction in depolarized tissues. The EM-523 response in 140 mM K+under isotonic conditions was 84 ± 3% (n = 5) at 10−5 M, with an EC50 that was shifted to 65 ± 18 nM. Similar figures were obtained for ME-34. When Ca2+ was added to Ca2+-depleted strips, half-maximal Ca2+ values (in mM) were 1.10 ± 0.11 (n = 9) for EM-523 and 1.13 ± 0.12 (n = 3) for ME-34, as compared with 1.12 ± 0.13 (n = 7) for motilin and 2.8 ± 1.1 (n = 9) for K+. Both ME-34 and EM-523 also induced a transient contraction in Ca+-free solutions under isometric conditions. The response to EM-523 (5 × 10−6 M) was 49 ± 15% (n = 4) after 3 min. A maximal EM-523 -stimulation reduced a subsequent ACh response by 78 ± 7%, whereas EM-523 and ME-34 could not induce a contraction after ACh.
We conclude that motilides depend upon external Ca2+ to a similar extent to motilin. Like motilin, they are also able to mobilize intracellular Ca Z + stores. Our results support the hypothesis that motilides act on motilin receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H, Toda H, Hayashi S, Noguchi M, Suzuki T, Torizuka K, Yajima H, Royama K (1981) Mechanism of the excitatory action of motilin on isolated intestine. Gastroenterology 80:783–788
Bormans V, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G (1986) Motilin receptors in rabbit stomach and small intestine. Regul Pept 15:143–153
Brading AF, Sneddon P (1980) Evidence for multiple sources of calcium for activation of the contractile mechanism of guineapig taenia coli on stimulation with carbachol. Br J Pharmacol 70:229–240
Brittain DC (1987) Update on antibiotics: I. Erythromycin. Med Clin North Am 71:1147–1154
Casteels R, Droogmans G (1981) Exchange characteristics of the noradrenaline-sensitive calcium store in vascular smooth muscle cells of rabbit ear artery. J Physiol (Lond) 317:263–279
Casteels R, Raeymaekers L (1979) The action of acetylcholine and catecholamines on an intracellular calcium store in the smooth musice cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol (Lond) 294:51–68
Depoortere I, Peeters TL, Matthijs G, Cachet T, Hoogmartens J, Vantrappen G (1989) Structure—activity relation of erythromycin-related macrolides in inducing contractions and in dis placing bound motilin in rabbit duodenum. J Gastro-intest Motil 1:150–159
Depoortere I, Peelers TL, Vantrappen G (1990) The erythromycin derivative EM-523 is a potent motilin agonist. Peptides 11:515- 519
Droogmans G, Casteels R (1981) Temperature-dependence of 45Ca fluxes and contraction in vascular smooth muscle cells of rabbit ear artery. Pflügers Arch 391:183–189
Evans DHL, Schild HO (1957) Mechanism of contraction of smooth muscle by drugs. Nature 180:341–342
Himpens B, Matthijs G, Somlyo AP (1989) Desensitization to cytoplasmic Ca2+ and Ca2+ sensitivities of guinea-pig ileum and rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 413:489–503
Itoh Z, Nakayama M, Suzuki T, Arai H, Wakabayashi K (1984) Erythromycin mimics exogenous motilin in gastrointestinal contractile activity in the dog. Am J Physiol 247:G688-G694
Itch Z, Omura S (1987) Motilide, a new family of macrolide compounds mimicing motilin. Dig Dis Sci 32:915
Johansson B, Somlyo AP (1980) Electrophysiology and excitation —contraction coupling. In: Bohr DF, Somlyo AP, Sparks HV (eds) Handbook of physiology, The cardiovascular system, vol II: Vascular smooth muscle. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, pp 301–323
Kitazawa T, Kobayashi S, Horiuti K, Somlyo AV, Somlyo AP (1989) Receptor coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle: role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem 264:5339–5342
Kondo K, Torii T, Omura S, Itoh Z (1988) Erythromycin and its derivatives with motilin-like biological activities inhibit the specific binding of 125I-motilin to duodenal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 150:877–882
Matthijs G, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G (1988) Effect of different calcium modulators on motilin-induced contractions of the rabbit duodenum. Comparison with acetylcholine. Regul Pept 21:321–330
Matthijs G, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G (1989) The role of intracellular calcium stores in motilin induced contractions of the rabbit duodenum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339:332–339
Matthijs G, Himpens B, Peeters TL, Vantrappen G (1990) Effects of substance P on [Ca2+]i and force in intact guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 259:C150-C160
Morgan JP, Morgan KG (1984) Stimulus-specific patterns of intracellular calcium levels in smooth muscle of ferret portal vein. J Physiol (Lond) 351:155–167
Omura S, Tsuzuki K, Sunazuka T, Marui S, Toyoda H, Inatomi N, Itoh Z (1987) Macrolides with gastrointestinal motor stimulating activity. J Med Chem 30:1941–1943
Peeters TL, Bormans, V, Vantrappen G (1988) Comparison of motilin binding to crude homogenates of human and canine gastrointestinal smooth muscle tissue. Regul Pept 23:171–182
Peeters TL, Matthijs G, Depoortere I, Cachet T, Hoogmartens J, Vantrappen G (1989) Erythromycin is a motilin receptor agonist. Am J Physiol 257:G470-G474
Riemer J, Kolling K, Mayer CJ (1977) The effects of motilin on the electrical activity of rabbit circular duodenal muscle. Pflügers Arch 372:243–250
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV (1968) Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 159:129–145
Strunz U, Domschke W, Mitznegg P, Domschke S, Schubert P, Wünsch E, Jaeger E, Demling L (1975) Analysis of the motor effects of 13-norleucine motilin on the rabbit, guinea-pig, rat and human alimentary tract in vitro. Gastroenterology 68:1485–1491
Tomomasa T, Kuroume T, Arai H, Wakabayashi K, Itoh Z (1986) Erythromycin induces migrating motor complex in human gastrointestinal tract. Dig Dis Sci 31:157–161
Vantrappen G, Peeters TL (1989) Motilin. In: Makhlouf GM (ed) Handbook of physiology, Endocrinology of the gastrointestinal system. Waverly Press for The American Physiological Society, Baltimore, Md, pp 545–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to T. L. Peeters at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peeters, T.L., Matthijs, G. & Vantrappen, G. Ca2+ dependence of motilide-induced contractions in rabbit duodenal muscle strips in vitro. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343, 202–208 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168611
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168611