Summary
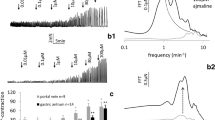
Both bradykinin (BK) and des-Arg9-BK induced relaxations of the isolated longitudinal smooth muscles of the rat duodenum. No contractile effects were observed with both peptides at concentrations up to 1 μmol/l. Des-Arg9-BK was about 1000 times less potent than BK. The novel B2 antagonist HOE 140 (d-Arg-[Hyp3, Thi5, D-Phe7, Oic8]-BK) potently inhibited the BK-induced relaxations, but did not affect the relaxations induced by des-Arg9-BK. Conversely, the B1 receptor antagonist des-Arg9-[Leu8]-BK only inhibited des-Arg9-BK, but did not affect BK-induced relaxations.
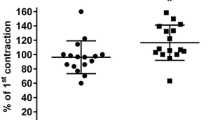
The relaxations induced by BK and by des-Arg9-BK were inhibited by apamin (1 μmol/l) demonstrating that apamin-sensitive K+ channels are involved. In contrast, tetraethylammonium (1 mmol/l) did not inhibit the relaxations. BK-induced relaxations were reduced by about 25% in the presence of indomethacin (10 μmol/l) although the concentration-response curve to BK was not shifted to the left. Prostaglandin E1 caused relaxations with a pD2 value of 9.2.
It is concluded that both BK and des-Arg9-BK can elicit relaxations of the rat duodenum via pharmacologically distinct kinin receptor subtypes, but via similar effector mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altinkurt O, Öztürk Y (1990) Bradykinin receptors in isolated rat duodenum. Peptides 11:39–44
Antonio A (1968) The relaxing effect of bradykinin on intestinal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 32:78–86
Boschcov P, Paiva ACM, Paiva TB, Shimuta SI (1984) Further evidence for the existence of two receptor sites for bradykinin responsible for the biphasic effect in the rat isolated duodenum. Br J Pharmacol 83:591–600
Bramley AM, Samhoun MN, Piper PJ (1990) The role of the epithelium in modulating the responses of guinea-pig trachea induced by bradykinin in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 99:762–766
Coleman RA, Humphrey PPA, Kennedy I, Levy GP, Lumley P (1981) Comparison of the actions of U-46619, a prostaglandin H2-analogue, with those of prostaglandin H2 and thromboxane A2 on some isolated smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol 73:773–778
Cook NS (1988) The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:21–28
Farmer SG, Burch RM, Meeker SA, Wilkins DE (1990) Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol 36:1–8
Ganz MB, Boyarski G, Boron WF (1991) Effects of angiotensin II and vasopressin on intracellular pH of glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol 254:F787-F794
Gill J, Dandona P, Jeremy JY (1990) Indomethacin and ibuprofen inhibit the uptake of 45 Ca2+ by washed human platelets through a thromboxane A2-independent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 187:135–138
Griesbacher T, Lembeck F (1991) Bradykinin antagonists with high potency and long duration of action in vivo. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:R103
Griesbacher T, Lembeck F (1992) Analysis of the antagonistic actions of HOE 140 and other novel bradykinin analogues on the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol 211:393–398
Hall JM, Morton IKM (1991) Bradykinin B2 receptor evoked K+ permeability increase mediates relaxation in the rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol 193:231–238
Hock FJ, Wirth K, Albus U, Linz W, Gerhards HJ, Wiemer G, Henke S, Breipohl G, König W, Schölkens BA (1991) Hoe 140, a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:769–773
Kantor HS, Hampton M (1978) Indomethacin in submicromolar concentrations inhibits cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature 276:841–842
Kume H, Takai A, Tokuno H, Tomita T (1989) Regulation of Ca2+-dependent K+-channel activity in tracheal myocytes by phosphorylation. Nature 341:152–154
Lembeck F, Griesbacher T, Eckhardt M, Henke S, Breipohl G, Knolle J (1991) New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 102:297–304
Liebmann C, Arold C (1978) Effect of bradykinin on prostaglandin synthetase activity in microsomal fractions from rat duodenum and uterus. Acta Biol Med Germ 37:901–903
Liebmann C, Reissmann S, Robberecht P, Arold H (1987) Bradykinin in the rat duodenum: receptor binding and influence on the cyclic AMP system. Biomed Biochim Acta 46:469–478
Paiva ACM, Paiva TB, Pereira CC, Shimuta SI (1989) Selectivity of bradykinin analogues for receptors mediating contraction and relaxation of the rat duodenum. Br J Pharmacol 98:206–210
Pereira CC, Paiva TB (1989) Characterization of the receptors responsible for the biphasic effect of bradykinin in rat duodenum. Braz J Med Biol Res 22:1137–1140
Regoli D, Barabé J (1980) Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev 32:1–46
Regoli D, Barabé J, Park WK (1977) Receptors for bradykinin in rabbit aortae. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 55:855–867
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Rovero P, Dion S, Rhaleb N-E, Barabé J, D'Orléans-Juste P, Ward P (1986) Conversion of kinins and their antagonists into B1 receptor activators and blockers in isolated vessels. Eur J Pharmacol 127:219–224
Saha JK, Sengupta JN, Goyal RK (1991) Effects of bradykinin and bradykinin analogs on the opossum lower esophageal sphincter: characterization of an inhibitory bradykinin receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:265–273
Tsuru H (1988) Heterogeneity of the vascular effects of bradykinin. In: Vanhoutte PM (ed) Vasodilation: vascular smooth muscle, peptides, autonomic nerves, and endothelium. Raven Press, New York, pp 479–482
Wirth K, Hock FJ, Albus U, Linz W, Alpermann HG, Anagnostopoulos H, Henke S, Breipohl G, König W, Knolle J, Schölkens BA (1991) Hoe 140, a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:774–777
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griesbacher, T. Kinin-induced relaxations of the rat duodenum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346, 102–107 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167578
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167578