Abstract
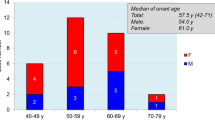
200Lys mutation in the human PRNP coding region has been identified in 45 of the 55 CJ-Daffected families thus far presented to our NIH laboratory. These codon 200lys families have a total of 87 patients, and originate from 7 different countries: Slovakia, Poland, Germany, Tunisia, Greece, Libya, and Chile. Forty-seven patients were neuropathologically verified, and brain tissue from 14 patients transmitted disease to experimental primates.
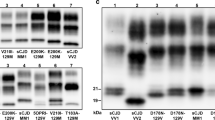
The mutation was found by direct sequencing in 4 patients, and it was detected by restriction endonuclease analysis with BsmA 1 and/or the single nucleotide extension reaction in 36 other patients and 45 of 109 first degree relatives (1 parent, 14 siblings, and 30 children).
The mutation is associated with all known geographical clusters of CJD (Slovakia, Libyan Jews, Chile) in which the annual mortality rate is tens or hundreds of times higher than the world average of 1 per million. All patients originating from the cluster areas carried the mutation, but it was seen in only 1 of 103 unrelated control individuals from the same areas, and in none of 102 controls from other areas, indicating a strong association between the mutation and disease. The penetrance of the mutation was estimated to be 0.56.
Branches of some families migrating from cluster areas to other countries continue to have CJD over several generations, suggesting that CJD in these families is a genetic disorder, in which the 200Lys mutation is responsible for the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ArayaG., GalvezS., CartierL. and GajdusekD.C. (1983): A spatiotemporal clustering of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Chile. - Rev. Chil. Neuropsiquiat. 21: 291–295.
BrownP., CathalaF., RaubertasR.F., GajdusekD.C. and CastaigneP. (1987): The epidemiology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: conclusion of a 15-year investigation in France and review of the world literature. - Neurology 37: 895–904.
Brown P., Goldfarb L.G., McCombie W.R., Nieto A., Trapp S., Squillacote D., Sheremata W., Godec M.S., Gibbs C.J. Jr. and Gajdusek D.C. (1991): Atypical Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in an American family with an insert mutation in the PRNP amyloid precursor gene. - Neurology 42: in press.
Ferrak, V., Kroupová, Z. and Mayer, V. (1981): Are population-genetic mechanisms responsible for clustering of cases of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease? -Brit. Med. J. 282: 521–522.
GàlvezS., MastersC. and GajdusekD.C. (1980): Descriptive epidemiology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Chile. - Arch. Neurol. 37: 11–14.
GoldfarbL. G., BrownP.GoldgaberD., GarrutoR.M., YanagiharaR., AsherD.M. and GajdusekD.C. (1990): Identical mutation in unrelated patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. - Lancet 336: 174–175.
Goldfarb L.G., Brown P., McCombie W.R., Goldgaber D., Swergold G.D., Wills P.R., Cervenáková L., Baron H., Gibbs C.J., Jr. and Gajdusek D.C. (1991): Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with extra octapeptide coding repeats in the PRNP gene: analysis of 3 families with 10, 12, and 13 repeat elements. - Proc. Soc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA): in press.
GoldfarbL. G., HaltiaM., BrownP., NietoA., KovanenJ., McCombieW.R., Trapp, S. and Gajdusek, D.C. (1991): New mutation in scrapie amyloid precursor gene (at codon 178) in Finnish Creutzfeldt-Jakob kindred. - Lancet 337: 425.
GoldfarbL.G., KorczynA.D., BrownP., ChapmanJ. and GajdusekD.C. (1990): Mutation in codon 200 of scrapie amyloid precursor gene linked to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Sephardic Jews of Libyan and non-Libyan origin. - Lancet 336: 637.
GoldfarbL.G., MitrovaE., BrownP., TohB.H. and Gajdusek, D.C. (1990): Mutation in codon 200 of scrapie amyloid protein gene in two clusters of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Slovakia. - Lancet 336: 514.
GoldgaberD., GoldfarbL.G., BrownP., AsherD.M., BrownW.T., LinW.S., TeenerJ.W., FeinstoneS.M., RubensteinR., KascsakR.J., BoellaardJ.W. and GajdusekD.C. (1989): Mutations in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Sträussler's syndrome. - Exper. Neurol. 106:204–206.
HsiaoK., MeinerZ., KahanaE., CassC., KahanaI., AvrahamiD., Scarlato, G., Abramsky0., PrusinerS.B. and GabizonR. (1991): Mutation of the prion protein in Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. - New Engl. J. Med. 324: 1091–1097.
KuppuswamyM.N., HoffmannJ.W., KasperCK., ApitzerS. G., GroceS.L. and BajajS.P. (1991): Single nucleotide primer extension to detect genetic diseases: experimental application to hemophilia B (factor IX) and cystic fibrosis genes. - Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 88: 1143–1147.
MastersC.L., GajdusekD.C. and GibbsC.J.Jr. (1981): The familial occurrence of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Alzheimer's disease. - Brain 104: 535–558.
MastersC.L., HarrisJ.O., GajdusekD.C., GibbsC.J.Jr., BernoulliC. and AsherD.M. (1979): Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: patterns of worldwide occurrence and the significance of familial and sporadic clustering. - Ann. Neurol. 5: 177–188.
MayerV., OrolinD. and MitrovaE. (1977): Cluster of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and presenile dementia. -Lancet ii: 256.
MitrovaE. (1990): Analytical epidemiology and risk factors of CJD. - In: Unconventional Virus Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Court L.A., Dormont D., Brown P., Kingsbury D.T., eds., Commissariat l'Energie Atomique, Dpartement de Protection Sanitaire, Service de Documentation, B.P. 6, 92265 Fontenay-aux-Roses, France, pp. 19–29.
Nieto A., Goldfarb L.G., Brown P., McCombie W.R., Trapp S., Asher D.M. and Gajdusek D.C. (1991): Codon 178 mutation in ethnically diverse Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease families. - Lancet 337:623.
OwenF., PoulterM., LofthouseR., CollingeJ., CrowT.J., RisbyD., BakerH.F., RidleyR.M., HsiaoK. and PrusinerS.B. (1989): Insertion in prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. - Lancet 1: 51–52.
OwenF., PoulterM., ShahT., CollingeJ., LofthouseR., BakerH., RidleyR., McVeyJ. and CrowT.J. (1990): An in-frame insertion in the prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. - Molec. Brain Res. 7: 273–276.
PrusinerS.B., ScottM., FosterD., PanK-M., Groth, D., MirendaC., TorchiaM., YangS.-L., SerbanD., CarlsonG.A., HoppeP.C., WestawayD. and DeArmondS.J. (1990): Transgenic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. - Cell 63: 673–686.
SangerF., NicklenS. and CoulsonA.R. (1977): DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. - Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 74: 5463–5467.
SparkesR.S., SimonM., CohnY.H., FournierR.E.K., LemJ., KlisakI., HeinzmannC., BlattC., LuceroM., MohandasT., DeArmondS.J., WestawayD.A., PrusinerS.B. and WeinerL.P. (1986): Assignment of the human and mouse prion protein genes to homologous chromosomes. - Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 83: 7358–7362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldfarb, L.G., Brown, P., Mitrovà, E. et al. Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease associated with the PRNP codon 200LYS mutation: An analysis of 45 families. Eur J Epidemiol 7, 477–486 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143125
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143125