Abstract
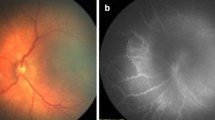
The authors describe a scoring system they have developed for evaluating damage produced in the retinal vascular network of the newborn rat by exposure to oxygen. India ink-injected retinal flat mounts are used. The scoring system provides for division of the retina into three concentric zones with the optic disk as a center point. Each retinal quadrant is then examined for the presence of the following lesions of progressive severity: vaso-obliteration of the capillary network, loss of the periarteriolar capillary-free zone, newly formed capillary tufts. When more than one type of lesion is present in a quadrant, only the most severe lesion is considered. The numerical score corresponding to that lesion is then multiplied by the factor corresponding to the concentric zone in which the lesion lies to give the quadrant score. The total retinal score is represented by the sum of the four quadrant scores. This type of system, if adopted by other investigators, can facilitate precise and systematic description of the results of different experimental protocols.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OIR:
-
oxygen-induced retinopathy
- ROP:
-
retinopathy of prematurity
References
Ashton, N. Some aspects of the comparative pathology of oxygen toxicity in the retina. Brit J Ophthalmol 1968; 52: 505–31.
Phelps, DL, Rosenbaum, AL. The role of Tocopherol in oxygen-induced retinopathy: kitten model. Pediatrics 1977; 59 (suppl): 998–1005.
Gole, GA, Gannon, BJ, Goodger, AM. Oxygen-induced retinopathy: the kitten model reexamined. Aust J Ophthalmol 1982; 10: 223–32.
Ernest, JT, Goldtick, K. Retinal oxygen tension and oxygen reactivity in retinopathy of prematurity in kittens. Invest Ophthal Vis Sci 1984; 25: 1129–34.
Flower, RW, Blake, DA. Retrolental fibroplasia: evidence for a role of the prostaglandin cascade in the pathogenesis of oxygen-induced retinopathy in the newborn beagle. Pediat Res 1981; 15: 1293–1302.
Flower, RW, McLeod, DS, Lutty, GA, Goldberg, B, Wajer, SD. Post-natal retinal vascular development of the puppy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1985; 26: 957–68.
Patz, A, Eastham, A, Higgenbotham, DH, Kleh, T. Oxygen studies in retrolental fibroplasia, II: The production of the microscopic changes of retrolental fibroplasia in experimental animals. Am J Ophthalmol 1953; 36: 1511–22.
Gyllensten, LJ, Hellstrom, BE. Experimental approach to the pathogenesis of retrolental fibroplasia. I. Changes of the eye induced by exposure of newborn mice to concentrated oxygen. Acta Pediat 1954; 43 (suppl): 131–48.
Gerschman, R, Nadig, PW, Snell, AC, Nye, SW. Effect of high oxygen concentrations on eyes of newborn mice. Am J Physiol 1954; 179: 115–18.
Patz, A. Oxygen studies in retrolental fibroplasia, IV: Clinical and experimental observations. Am J Ophthal 1954; 38: 291–308.
Ashton, N, Black, R. Studies in developing retinal vessels, VIII: Effect of oxygen on the vessels of the ratling. Brit J Ophthal 1961; 45: 321–40.
Ricci, B. Effects of hyperbaric, normobaric and hypobaric oxygen supplementation on retinal vessels in newborn rats: a preliminary study. Exp Eye Res 1987; 44: 459–64.
Ricci, B, Calogero, G. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in newborn rats: effects of prolonged normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen supplementation. Pediatrics 1988; 82: 193–98.
Ricci, B, Lepore, D, Iossa, M. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in newborn rats: orthograde axonal transport changes in optic pathways. Exp Eye Res 1988; 47: 579–86.
Henkind, P, De Oliveira, LF. Development of retinal vessels in the rat. Invest Ophthal Vis Sci 1967; 6: 520–30.
Gole, GA. Animal models of retinopathy of prematurity. In: Silverman, WA, Flynn, JT, eds. Contemporary Issues in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine 2: Retinopathy of Prematurity. Boston: Blackwell Scientific Publishers, 1985: 53–95.
Michaelson, IC. Retinal circulation in man and animals. Springfield: Charles C. Thomas, 1954: 39–63.
Committee for the Classification of ROP. An international classification of ROP. Arch Ophthal 1984; 102: 1130–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricci, B., Lepore, D., Zonghi, E. et al. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the newborn rat: a scoring system for the evaluation of retinal vascular changes. Doc Ophthalmol 76, 241–249 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142683
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142683