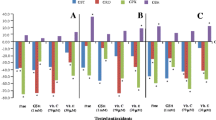
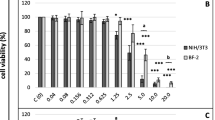
Since chemical modulation of gap junctional intercellular communication has been implicated in several toxicological endpoints, a study to examine the ability of several biological toxins to inhibit this process was undertaken. Eight biological toxins were tested for their ability to inhibit metabolic cooperation, a measure of gap-junctional intercellular communication, in the Chinese V79 cell system. Aplysiatoxin, anhydrodebromoaplysiatoxin and debromoaplysiatoxin showed the strongest ability to inhibit metabolic cooperation while T2-toxin and vomitoxin inhibited metabolic cooperation to a lesser degree. Afatoxin B1, afatoxin B2 and palytoxin were inactive in the Chinese V79 system. Palytoxin, which was extremely cytotoxic, might act as a tumor promoter if it induces compensatory hyperplasia in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-TG:
-
6-thioguanine
- TPA:
-
12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
References
AMSTAD, P., LEVY, A. and CERUTTI, P. (1984). Evidence for membrane-mediated chromosomal damage by aflatoxin B, in human lymphocytes. Carcinogenesis 5:719–723.
BERENBLUM, I. and SHUBIK, P. (1947). A new, quantitative approach to the study of the stages of chemical carcinogenesis in the mouse skin. Br. J. Cancer 1:383–391.
BUSBY, W.F. and WOGAN, G.N. (1981). Tricothecenes. In: Mycotoxins and N-NitrosoCompounds: Environmental Risks (R. C. Shank, ed.), Vol. II, pp. 29–45. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
BOUTWELL, R.K. (1974). The function and mechanism of promoters of carcinogenesis. CRC Crt. Rev. Toxicol. 2:419–443.
CARMICHAEL, W.W., JONES, C.L.A., MAHMOOD, N.A. and THEISS, W.C. (1985). Algal toxins and water-based diseases. CRC Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 15:275–313.
DIX, K.M. (1984). The development of hepatocellular tumours following aflatoxin B1 exposure of the partially hepatectomized mouse. Carcinogenesis 5:385–390.
EAGLE, H. (1959). Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell culture. Science 130:432–437.
ENOMOTO, T. and YAMASAKI, H. (1984). Lack of intercellular communication between chemically transformed and surrounding nontransformed BALB/c 3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 44:5200–5203.
FREI, J.V. (1976). Some mechanisms operative in carcinogenesis: A review. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 12:1–25.
FRIEDMAN, E.A. and STEINBERG, M. (1982). Disrupted communication between latestage premalignant human colon epithelial cells by 12–0-tetradecanoylphorbol-l3-acetate. Cancer Res. 42:5096–5105.
FRIEDEWALD, W.F. and ROUS, P. (1944). The initiating and promoting elements in tumor production. J. Exp. Med. 80:101–126.
FUJIKI, H., SUGANUMA, M., NAKAYASU, M., HOSHINO, H., MOORE, R.E. and SUGIMURA T. (1982). The third class of new tumor promoters, polyacetates (debromoaplysiatoxin and aplysiatoxin), can differentiate biological actions relevant to tumor promoters. Gann 73:495–497.
FUJIKI, H. and Sugimura, T. (1983). New potent tumor promoters: Teleocidin, lyngbyatoxin and aplysiatoxin. Cancer Surveys 2:539–556.
FUJIKI, H., SUGIMURA, T. and MOORE, R.E. (1983). New classes of environmental tumor promoters: Indole alkaloids and polyacetates. Environ. Health Perspect. 50:85–90.
Fujiki, H., Suganuma, M., Tupahira, T., Yoshioka, A., Nakayasu, M., Epndo, Y., Shaudu, K., Takayama, S., Moore, R.E. and Sugimura, T. (1984a). New classes of tumor promoters: Teleocidin, aplysiatoxin, and palytoxin. In: Cellular Interactions by Environmental Tumor Promoters (H. Fujiki, E. Hecker, R.E. Moore, T. Sugimura and I.B. Weinstein, eds.), pp. 37–45. Proceedings 14th International Symposium of the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund, Tokyo, 1983.
FUJIKI, H., SUGANUMA, M., HAKII, H., BARTOLINI, G., MOORE, R.E., TAKAYAMA, S. and SUGIMURA, T. (1984b). A two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis study of lyngbyatoxin A. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 108:174–176.
GAINER, H. St. C. and MURRAY, A.W. (1985). Diacylglycerol inhibits gap junctional communication in cultured epidermal cells: Evidence for a role of protein kinase C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 126:1109–1113.
GILULA, N.B. (1980). Cell to cell communication and development. In: Cell Surface: Mediator of Developmental Processes (S. Subtelny and N. K. Wessells, eds.), pp. 23–42. Academic Press, New York.
GILULA, N.B., REEVES, O.R. and STEINBACH, A. (1972). Metabolic coupling, ionic coupling and cell contacts. Nature 235:262–265.
HAYES, A.W. (1981). Mycotoxin teratogenicity and mutagenicity. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton.
HAYES, M.A., ROBERTS, E. and FARBER, E. (1985). Initiation and selection of resistant hepatocyte nodules in rats given the pyrrolizidine alkaloids lasiocarpine and senecionine. Cancer Res. 45:3726–3734.
Hecker, E., Adolf, W., Hergenhahn, M., Schmidt, R. and Sorg, B. (1984). Irritant diterpene ester promoters of mouse skin: Contributions to etiologies of environmental cancer and to biochemical mechanisms of carcinogenesis. In: Cellular Interactions by Environmental Tumor Promoters (H. Fujiki, E. Hecker, R.E. Moore, T. Sugimura, and I.B. Weinstein, eds.), Proc. 14th International Symposium of the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund, pp. 3–36, Tokyo.
HECKER, E., FUSENIG, N.E., KUNZ, W., MARKS, F. and THIELMANN, H.W. (1982). Carcinogenesis—A comprehensive survey, Vol. 7. Carcinogenesis and Biological Effects of Tumor Promoters, Raven Press, New York.
HECKER, E., and SCHMIDT, R. (1974). Phorbol esters-The irritants and cocarcinogens of Croton tigluim, L. Prog. Chem. Org. Natur. Prod. 31:377–467.
HOLME, J.A. and SODERLUND, E.J. (1985). Species differences in the cytotoxic and genotoxic effect of 2-acetylaminofluorene and its primary metabolites 2-aminofluorene and N-OH-2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis 6:421–425.
Hooper, M.L. (1982). Metabolic cooperation between mammalian cells in culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 651:85–103.
HOOPER, M.S. and SUBAK-SHARPE, J.H. (1981). Metabolic cooperation between cells. In: International Review of Cytology (G.H. Bournem, J.F. Danielli and K.W. Jeon, eds.), Vol. 71, pp. 46–104. Academic Press, London.
HOROWITZ, A.D., FUJIKI, H., WEINSTEIN, I.B., JEFFREY, A., OKIN, E., MOORE, R.G. and SUGIMURA, T. (1983). Comparative effects of aplysiatoxin, debromoaplysiatoxin, and teleocidin on receptor binding and phospholipid metabolism. Cancer Res. 43:1529–1535.
IMAIDA, K., HIROSE, M., OGISO, T., KURATA, Y. and ITO, N. (1982). Quantitative analysis of initiating and promoting activities of five mycotoxins in liver carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Lett. 16:137–143.
JENSEN, R.K., SLEIGHT, S.D., AUST, S.D., GOODMAN, J.I. and TROSKO, J.E. (1983). Hepatic tumor-promoting ability of 3,3′,4,4′,5,5′-hexabromobiphenyl: The interrelationship between toxicity, induction of hepatic microsomal drug metabolizing enzymes and tumor promoting ability. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 71:163–176.
JENSEN, R.K., SLEIGHT, S.D., GOODMAN, J.I., AUST, S.D. and TROSKO, J.E. (1982). Polybrominated biphenyls as promoters in experimental hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis 3:1183–1186.
JONE, C., TROSKO, J.E., AYLSWORTH, C.F., PARKER, L. and CHANG, C.C. (1985). Further characterization of the in vitro assay for inhibitors of metabolic cooperation in the Chinese hamster V79 cell line. Carcinogenesis 6:361–366.
JONE, C.M., TROSKO, J.E., CHANG, C.C., FUJIKI, H. and SUGIMURA, T. (1982). Inhibition of intercellular communication in Chinese hamster V79 cells by teleocidin. Gann 73:874–878.
KALIMI, G.H. and SIRAT, S.M. (1984). The relevance of gap junctions to stage I tumor promotion in mouse epidermis. Carcinogenesis 5: 1671–1677.
KATO, Y. and SCHEUER, P. (1976). The aplysiatoxins: Reactions with acid and oxidants. Pure and Applied Chemistry 489:29–33.
KAVANAGH, T.J., RUBINSTEIN, C., LIU, P.C., CHANG, C.C., TROSKO, J.E. and SLEIGHT, S.D. (1985). Failure to induce mutations in Chinese hamster V79 cells and WB rat liver cells by the polybrominated biphenyls, Firemaster BP-6, 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hex-abromobiphenyl, 3,3′,4,4′,5,5′-hexabromobiphenyl, and 3,3′,4,4′-tetrabromobiphenyl. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 79:91–98.
KOSHAKJI, R.P., WILSON, B.J. and HARBINSON, R.D. (1973). Effect of rubratoxin B on prenatal growth and development in mice. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 5:584–590.
KUCZUK, M.H., BENSON, P.M., HEATH, H. and HAYES, A.W. (1978). Evaluation of the mutagenic potential of mycotoxins using Salmonella typhimurium and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat. Res. 53:11–20.
LANGENBACH, R., FREED, H.J. and HUBERMAN, E. (1978). Liver cell-mediated mutagenesis of mammalian cells by liver carcinogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75:2864–2867.
LIN, J.K., MILLER, J.A. and MILLER, E.C. (1977). 2,3-Dihydro-2-(guan-7-yl)-3-hydroxyaflatoxin B1, a major acid hydrolysis product of aflatoxin B1-DNA or -ribosomal RNA adducts formed in hepatic microsome-mediated reactions in rat liver, in vivo. Cancer Res. 37:4430–4438.
LINSELL, C.A. (1979). Environmental chemical carcinogens and liver cancer. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 5:173–181.
LOEWENSTEIN, W.R. (1968). Communication through cell junctions. Implications for growth control and differentiation. Devel. Biol. 19 (Suppl. 2):151–183.
LOEWENSTEIN, W.R. (1979). Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Cancer Rev. 560:1–65.
LOEWENSTEIN, W.R. (1981). Junctional intercellular communication. The cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol. Rev. 61:829–913.
MCCANN, J., CHOI, E., YAMASAKI, E. and AMES, B.N. (1975). Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in Salmonella/ microsome test: Assay of 300 chemicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72:5135–5139.
MILLER, E.C. and MILLER, J.A. (1981). Mechanism of chemical carcinogenesis. Cancer 47:1055–064.
MOORE, R.E. (1982). Toxins, anticancer agents, and tumor promoters from marine prokaryotes. Pure and App. Chem. 54:1919–1934.
MOORE, R.E. and BARTOLINI, G. (1981). Structure of palytoxin. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 103:2491–2494.
MOORE, R.E., BLACKMAN, A.J., CHEUK, C.E., MYNDERSE, J.S., MATSUMOTO, G.K., CLARDY, J., WOODARD, R.W. and CRAIG, J.C. (1984). Absolute stereochemistries of the aplysiatoxins and oscillatoxin A. J. Orig. Chem. 49:2484–2489.
MORI, H., KAWAO, K., OHBAUASHI, F., KUNIYASU, T., YAMAZAKI, M., HAMASAKI, T. and WILLIAMS, G.M. (1984). Genotoxicity of a variety of mycotoxins in the hepatocyte primary culture/ DNA repair test using rat and mouse hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 44:2918–2923.
MURRAY, A.W. and FITZGERALD, D.J. (1979). Tumor promoters and metabolic cooperation in cocultures of epidermal and 3T3 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 91:395–401.
MYNDERSE, J.S., MOORE, R.E., KASHIWAGI, M. and NORTON, T.R. (1977). Antileukemia activity in the oscillatoriaceae: Isolation of debromoaplysiatoxin from Lyngbya. Science 196:538–539.
PITOT, H.C. and SIRICA, A.E. (1980). The stages of initiation and promotion in hapatocarcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 605:191–215.
POUND, A.W. and MCGUIRE, L.J. (1978). Repeated partial hepatectomy as a promoting stimulus for carcinogenic response of liver to nitrosamines in rats. Br. J. Cancer 37:585–594.
RODRICKS, J.B., HESSELTINE, C.W. and MEHLMAN, M.A., eds. (1977). Mycotoxins in Human and Animal Health. Pathotox Publishers, Park Forest South, IL.
RODGERS, C.G. and HEROUX-METCALF, C. (1983). Cytotoxicity and absence of mutagenic activity of vomitoxin (4-deoxynivalenol) in a hepatocyte-mediated mutation assay with V79 Chinese hamster lung cells. Cancer Lett. 20:29–35.
SAITO, M., HORIUCHI, T., OHTSUBO, K., HATANAKA, Y. and UENO, Y. (1980). Low tumor incidence in rats with long-term feeding of fusaren-X, a cytotoxic tricothecene produced by Fusarium navale. Japan J. Exp. Med. 50:293–302.
SCHOENTAL, R., JOFFE, A.Z. and YAGER, B. (1979). Cardiovascular lesions and various tumors found in rats given T-2 toxin, a trichotecene metabolite of Fusarium. Cancer Res. 39:2179–2189.
STANFORD, G.K., HOOD, R.D. and HAYES, A.W. (1975). Effect of prenatal administration of T-2 toxin to mice. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 10:743–746.
SUBAK-SHARPE, H., BURK, R.R. and PITTS, J.D. (1966). Metabolic cooperation by cell to cell transfer between genetically different mammalian cells in tissues cultures. Heredity 21:342–343.
SUBRAMONIAM, A., PADH, H. and also, J.J. (1985). Factors influencing calcium influx in endotoxin-challenged fibroblasts. Pro. Soc. Expt. Biol. Med. 178:50–59.
Suganuma, M., Fujiki, H., Nakayasu, M., Takira, T. and Sugimura, T. (1983). A new skin tumor promoter, palytoxin. Proc. Japan Cancer Assoc., 42nd Ann. Mtg., p. 49.
SUGANUMA, M., FUJIKI, H., TAHIRA, T., CHEUK, C., MOORE, R.E. and SUGIMURA, T. (1984). Estimation of tumor promoting activity and structure-function relationships of aplysiatoxins. Carcinogenesis 5:315–318.
SUGIMURA, T. (1982). Potent tumor promoters other than phorbol ester and their significance. Gann 73:499–507.
TROSKO, J.E. and CHANG, C.C. (1982). Potential role of intercellular communication in the rat limiting step in carcinogenesis. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 2:5–22.
TROSKO, J.E. and CHANG, C.C. (1983). The role of DNA repair capacity and somatic mutations in carcinogenesis and aging. In: Handbook of the Diseases of Aging: A Pathogenic Perspective (H. T. Blumenthal, ed.), pp. 252–295. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York.
TROSKO, J.E. and CHANG, C.C. (1984). Role of intercellular communication in tumor promotion. In: Mechanisms of Tumor Promotion (T.J. Slaga, ed.), Vol. VI, pp. 119–145. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
TROSKO, J.E., CHANG, C.C. and MEDCALF, A. (1983). Mechanisms of tumor promotion: Potential role of intercellular communication. Cancer Invest. 1:511–526.
TROSKO, J.E., CHANG, C.C., YOTTI, L.P. and CHU, E.H.Y. (1977). Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the recovery of spontaneous and ultraviolet light-induced 6-thioguanine and ouabain-resistant Chinese hamster cells. Cancer Res. 37:188–193.
TROSKO, J.E., JONE, C., AYLSWORTH, C. and CHANG, C.C. (1984). In vitro assay to detect inhibitors of intercellular communication. In: Handbook of Carcinogen Testing (H.A. Milman and E.K. Weisburger, eds.) pp. 420–437. Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ.
TROSKO, J.E., JONE, C. and CHANG, C.C. (1983). The role of tumor promoters on phenotypic alterations affecting intercellular communication and tumorigenesis. In: Cellular Systems for Toxicity Testing (G.M. Williams, V.C. Dunkel and V.A. Ray, eds.), Vol. 407, pp. 316–327. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., New York.
TSUSHIMOTO, G., TROSKO, J.E., CHANG, C.C. and AUST, S.D. (1982). Inhibition of metabolic cooperation in Chinese hamster V79 cells in culture by various polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) congeners. Carcinogenesis 3:181–186.
UEMURA, D., UEDA, K. and HIRATA, Y. (1981). Further studies on palytoxin. II. Structure of palytoxin. Tetrahedron Lett. 22:2781–2784.
UENO, Y. (1980). Tricothecene mycotoxins: Mycology, chemistry, and toxicology. In: Advances in Nutritional Research, Vol. 3 (H. H. Draper, ed.), pp. 301–353. Plenum, New York.
UENO, Y. (1984). Toxicological features of T-2 toxin and related tricothecenes. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 4:S124-S132.
UENO, Y., KUBOTA, K., ITO, T. and NAKAMURA, Y. (1978). Mutagenicity of carcinogenic mycotoxins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cancer Res 38: 536–542.
UMEDA, T.M., TSUTSUI, T. and SAITO, M. (1977). Mutagenicity and inducibility of DNA single-strand breaks and chromosome aberrations by various mycotoxins. Gann 68:619–625.
URAGUCHI, K. and YAMAZAKI, M., eds. (1978). Toxicology, Biochemistry and Pathology of Mycotoxins. Halsted Press, New York.
Van Rensburg, S.J., Marasas, W.F.O., Gelderblom, W.C.A., Thiel, P.G. and Rabie, C.J. (1982). Mycotoxins and Oesophageal Cancer. 5th IUPAC Symposium on Mycotoxins and Physiotoxins, Vienna, Austria, Sept. 1–5, 1982.
WEHNER, F.C., MARASAS, W.F.O. and THIEL, P.G. (1978). Lack of mutagenicity of Salmonella typhimurium of some Fusarium mycotoxins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 35:659–662.
WEINSTEIN, I.B. (1978). Current concept on mechanisms of chemical carcinogens. Bull. N.Y. Acad. Med. 54:366–381.
WOGAN, G. N. (1973). Aflatoxin carcinogenesis. In: Methods in Cancer Research (H. Busch, ed.), Vol. 7, pp. 309–344. Academic Press, New York.
WOGAN, G.N. (1976). Aflatoxins and their relationship to hepatocellular carcinomas. In: Hepatocellular Carcinoma (K. Okeida and R.L. Peters, eds.), pp. 25–41. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
WONG, J.J. and HSIEH, D.P.H. (1976). Mutagenicity of aflatoxins related to their metabolism and carcinogenic potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73:2241–2244.
YAMASAKI, H., ENOMOTO, T., SHIBA, Y., KANNO, Y. and KAKUNGA, T. (1985). Intercellular communication capacity as a possible determinant of transformation sensitivity of BALB/c 3T3 clonal cells. Cancer Res. 45:637–641.
YANCEY, S.B., EDENS, J.E., TROSKO, J.E., CHANG, C.C. and REVEL, J.-P. (1982). Decreased incidence of gap junctions between Chinese hamster V79 cells upon exposure to the tumor promoter 12–0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Exp. Cell Res. 139:329–340.
YOTTI, L.P., CHANG, C.C. and TROSKO, J.E. (1979). Elimination of metabolic cooperation in Chinese hamster cells by a tumor promoter. Science 206:1089–1091.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jone, C., Erickson, L., Trosko, J.E. et al. Effect of biological toxins on gap-junctionai intercellular communication in Chinese hamster V79 cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 3, 1–15 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117821
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117821