Summary
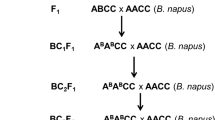
Atrazine resistant Brassica napus × B. oleracea F1 hybrids were backcrossed to both parental species. The backcrosses to B. napus produced seeds in both directions but results were much better when the F1 hybrid was the pollen parent. Backcrosses to B. oleracea failed completely but BC1s were rescued by embryo culture both from a tetraploid hybrid (2n = 4x = 37; A1C1CC) and sesquidiploid hybrids (2n = 3x = 8; A1C1C). Progeny of crosses between the tetraploid hybrid and B. oleracea had between 25 and 28 chromosomes. That of crosses between the sesquidiploid hybrid and B. oleracea had between 21 and 27. A few plants that had chromosome counts outside the expected range may have originated from either diploid parthenogenesis, unreduced gametes or spontaneous chromosome doubling during in vitro culture. Pollen stainability of the BC1s ranged from 0% to 91.5%. All the BC1s to B. oleracea were resistant to atrazine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte R., P.M. Harney & V. Souza Machado, 1987. The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. I. Production of F1 hybrids through embryo rescue. Euphytica 36: 615–624.
Ayotte R., P.M. Harney & V. Souza Machado, 1988. The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. II. Morphology fertility and cytology of the F1 hybrid. Euphytica 37: 189–197.
Calder R.A., 1937. Interpollination of Brassicas New Zeal J Agric 55: 299–308.
Chiang M.S., B.Y. Chiang & W.F. Grant, 1977. Transfer of resistance to race 2 of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Brassica napus to cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). I. Interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea var. capitata. Euphytica 26: 319–336.
Erickson L.R., N.A. Strauss & W.D. Beversdorf, 1983. Restriction patterns reveal origin of chloroplast genomes in Brassica amphidiploids. Theor Appl Genet 65: 201–206.
Honma S. & W.L. Summers, 1976. Interspecific hybridization between Brassica napus L. (Napobrassica group) and B. oleracea L. (Botrytis group). J Amer Soc Hort Sci 101: 299–302.
U., N., 1935. Genome-analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jap J Bot 7: 389–452.
Yarnell S.H., 1956. Cytogenetics of the vegetable crops. II. Crucifers. Bot Rev 22: 81–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayotte, R., Harney, P.M. & Machado, V.S. The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. III. First backcross to parental species. Euphytica 38, 137–142 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040184
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040184