Abstract
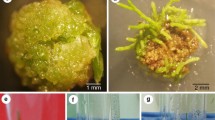
Transient expression of the uidA reporter gene was used in preliminary experiments with two oncogenic and two disarmed Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains in order to test the efficiency of T-DNA transfer to N084 x Populus nigra and N107 x P. nigra clones. The oncogenic strain A281 pKIWI105 produced the highest average number of GUS spots per leaf disc. In order to optimize the production of transgenic plantlets from different P. nigra clones (San Giorgio, Jean Pourtet, N084 x P. nigra and N107 x P. nigra, respectively), two A. tumefaciens strains (GV2260 p35S GUS, A281pKIWI105) and bacterial concentrations (7×108; 1.2×09 bacteria ml-1) were used. Following co-cultivation with A281 pKIWI105, the frequency of leaf discs producing kanamycin-resistant calli was not significantly different between the clones and bacteria concentrations used. Transformed shoots were regenerated from all clones, except for Jean Pourtet. Co-cultivation of leaf discs with GV2260 p35S GUS produced very few calli which died when transferred to selective regeneration medium. In addition, the effects of acetosyringone and leaf wounding were evaluated for the San Giorgio and Jean Pourtet clones, using the same strains. Factors which significantly affected the transformation efficiency of leaf explants were the P. nigra clone, the A. tumefaciens strain, and the presence of acetosyringone. Genetic transformation of calli and regenerated plantlets was confirmed by their ability to grow and root on Woody Plant Medium containing kanamycin, by histochemical β-glucuronidase assays, and Southern blot hybridization analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzyladenine
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase
- IBA:
-
indolebutyric acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NAA:
-
β-naphthaleneacetic acid
- nptII :
-
neomycin phosphotransferase II gene
- uidA :
-
β-glucuronidase gene
- WPM:
-
Woody Plant Medium
References
Atkinson RG & Gardner RC (1993) Regeneration of transgenic tamarillo plants. Plant Cell Rep. 12: 347–351
Brasileiro ACM, Leplé J-C, Muzzin J, Ounnoughi D, Michel M-F & Jouanin L (1991) An alternative approach for gene transfer in trees using wild-type Agrobacterium strains. Plant Mol. Biol. 17: 441–452
Confalonieri M, Balestrazzi A & Bisoffi S (1994) Genetic transformation of Populus nigra by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep. 13: 256–261
De Jong J, Rademaker W & van Wordragen MF (1993) Restoring adventitious shoot formation on chrysanthemum leaf explants following co-cultivation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 32: 263–270
Janssen BJ & Gardner RC (1989) Localized transient expression of GUS in leaf discs following cocultivation with Agrobacterium. Plant Mol. Biol. 14: 61–72
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5: 387–405
Lloyd G & McCown BH (1981) Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot-tip culture. Proc. Int. Plant Prop. 30: 421–427
Mathews H, Bharathan N, Litz RE, Narayanan KR, Rao PS & Bathia CR (1990) The promotion of Agrobacterium mediated transformation in Atropa belladona L. by acetosyringone. J. Plant Physiol. 136: 404–409
McClelland M & Nelson M (1988) The effect of site-specific DNA methylation on restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases — a review. Gene 74: 291–304
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Rogers JC & Rogers SW (1995) Comparison of the effects of N6-methyldeoxyadenosine and N5-methyldeoxycytosine on transcription from nuclear gene promoters in barley. Plant Journal 7: 221–223
Rogers SO & Bendich AJ (1988) Extraction of DNA from plant tissues. Plant Molecular Biology Manual A6: 1–10
Vancanneyt G, Schmidt R, O Connor-Sanchez A, Willmitzer L & Rocha-Sosa M (1990) Construction of an intron — containing marker gene: Splicing of the intron in transgenic plants and its use in monitoring early events in Agrobacterium — mediated plant transformation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 220: 245–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Confalonieri, M., Balestrazzi, A., Bisoffi, S. et al. Factors affecting Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation in several black poplar clones. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 43, 215–222 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039947
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039947