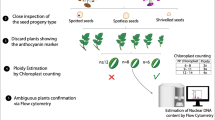
Summary
The frequency of haploid production following the interspecific pollination of eight tetraploid potato cultivars (Solanum tuberosum subsp. tuberosum) with Solanum phureja clone 1.22 was investigated. A total of 185 haploids were produced with an overall haploid frequency of 3.9 haploids/100 fruits. The haploid frequency was affected by the genotype of the maternal parent. Atlantic, ND860-2, Superior, Saginaw Gold, Spartan Pearl, Nooksack and Onaway had frequencies of 6.2, 5.1, 4.7, 3.9, 2.3 and 0.7 haploids/100 fruits, respectively. There were 60 and 57 haploids produced from Atlantic and Saginaw Gold, respectively, and no haploids were extracted from fruits of Lemhi Russet. Isozyme analysis and visual examination were performed independently to compare the efficiency of discriminating hybrids from haploids. Approximately 80% of total hybrids could be identified by electrophoretic analysis, while 77% were distinguished through visual examination. Pgm-2 1, which is unique in the clone 1.22 and absent from all seed parents, was found to be the most useful locus in hybrid identification and 50% of total hybrids could be distinguished by this allele. With similar rationale, Mdh-1 1 allozyme, which was absent in six of the eight parents, identified 37% of total hybrids. A combination of both visual and electrophoretic methods made hybrid identification even more efficient, with an average identification efficiency of 91%. A scheme was proposed to develop a new haploid inducer which would be homozygous for both Pgm-2 1 and embryo spot.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caligari, P.D.S., W. Powell, K. Liddell, M.J. De Maine & G.E.L. Swan, 1988. Methods and strategies for detecting Solanum tuberosum dihaploids in interspecific crosses with S. phureja. Ann. Appl. Biol. 112: 323–328.
Chase, R.W., G. Silva, D.S. Douches & R. Hammerschmidt, 1990. Selecting potato varieties for Michigan. Michigan State University Cooperation Extension Service, Extension Bulletins, E-2222.
Chase, S.S., 1963. Analytical breeding of Solanum tuberosum: A scheme utilizing parthenotes and other diploid stocks. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 5: 359–363.
De Maine, M.J., 1977. A simple technique for the short-term storage of pollen of a dihaploid-inducing diploid potato clone. Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge 89: 511–512.
De Maine, M.J., 1988. Berry and seed production using stored pollen of a Solanum phureja clone. Potato Res. 31: 385–387.
Den Nijs, T.P.M. & S.J. Peloquin, 1977a. 2n gametes in potato species and their function in sexual polyploidization. Euphytica 26: 585–600.
Den Nijs, T.P.M. & S.J. Peloquin, 1977b. Polyploid evolution via 2n gametes. Am. Potato J. 54: 377–386.
Dodds, K.S., 1955. Positional pseudo-alleles in diploid potatoes. Nature 175: 394–395.
Dodds, K.S. & D.H. Long, 1955. The inheritance of colour in diploid potatoes. I. Types of anthocyanidins and their genetic loci. J. Genet. 53: 136–149.
Dodds, K.S. & D.H. Long, 1956. The inheritance of colour in diploid potatoes. II. A three-factor linkage group. J. Genet. 54: 27–41.
Douches, D.S. & K. Ludlam, 1991. Electrophoretic characterization of North American potato cultivars. Am. Potato J. 68: 767–780.
Douches, D.S. & C.F. Quiros, 1987. Use of 4x–2x crosses to determine genecentromere map distances of isozyme loci in Solanum species. Genome 29: 519–527.
Douches, D.S. & C.F. Quiros, 1988a. Additional isozyme loci in tuber-bearing Solanums: Inheritance and linkage relationships. J. Hered. 79: 377–384.
Douches, D.S. & C.F. Quiros, 1988b. Genetic recombination in a diploid synaptic mutant and a Solanum tuberosum X S. chacoense diploid hybrid. Heredity 60: 183–191.
Douches, D.S. & C.F. Quiros, 1988c. Genetic strategies to determine the mode of 2n egg formation in diploid potatoes. Euphytica 38: 247–260.
Frandsen, N.O., 1967. Haploid production in a potato breeding material with intensive back crossing to wild species. Zuchter 37: 120–134.
Frandsen, N.O., 1968. The plastid number as a character in potatoes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 38: 153–167.
Frusciante, L. & S.J. Peloquin, 1987. Haploids extracted from four European potato varieties. p. 211–212. In: G.J. Jellis & D.E. Richardson (Eds.) The Production of New Potato Varieties. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
Gabert, A.C., 1963. Factors affecting the frequency of haploids in the common potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Ph. D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison. Diss. Abstr. 24: 475.
Hermsen, J.G.Th., 1979. Factors controlling interspecific cross-ability and their bearing on the strategy for breaking barriers to intercrossing of tuber-bearing Solanum species. p. 311–318. In: Proc. Conf. Broadening Genet. Base Crops, Wageningen, 1979.
Hermsen, J.G.Th. & J. Verdenius, 1973. Selection from Solanum tuberosum group Phureja of genotypes combining high-frequency haploid induction with homozygosity for embryospot. Euphytica 22: 244–259.
Hougas, R.W. & S.J. Peloquin, 1957. A haploid plant of the potato variety Katahdin. Nature 180: 1209–1210.
Hougas, R.W. & S.J. Peloquin, 1958. The potential of potato haploids in breeding and genetic research. Am. Potato J. 35: 701–707.
Hougas, R.W., S.J. Peloquin & R.W. Ross, 1958. Haploids of the common potato. J. Hered. 49: 103–107.
Hougas, R.W., S.J. Peloquin & A.C. Gabert, 1964. Effect of seed parent and pollinator on frequency of haploids in Solanum tuberosum. Crop Sci. 4: 593–595.
Jongedijk, E., 1985. The pattern of megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis in diploid Solanum species hybrids: Its relevance to the origin of 2n eggs and the induction of apomixis. Euphytica 34: 599–611.
Kotch, G.P. & S.J. Peloquin, 1987. A new source of haploid germplasm for genetic and breeding research. Am. Potato J. 64: 137–141.
Ludlam, K., 1991. Factors influencing the resistance of the potato to common scab. Master Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing.
Martinez-Zapater, J.M. & J.L. Oliver, 1984. Genetic analysis of isozyme loci in tetraploid potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Genet. 110: 669–679.
Montelongo-Escobedo, H. & P.R. Rowe, 1969. Haploid induction in potato: Cytological basis for the pollinator effect. Euphytica 18: 116–123.
Murashige, T. & F. Skoog, 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant 15: 473–497.
Oliver, J.L. & J.M. Martinez-Zapater, 1985. A genetic classification of potato cultivars based on allozyme patterns. Theor. Appl. Genet. 69: 305–311.
Peloquin, S.J., 1982. Meiotic mutants in potato breeding. Stadler Genet. Symp. 14: 99–109.
Peloquin, S.J. & R.W. Hougas, 1959. Decapitation and genetic markers as related to haploidy in Solanum tuberosum. Eur. Potato J. 2: 176–183.
Peloquin, S.J., R.W. Hougas & A.C. Gabert, 1966. Haploidy as a new approach to cytogenetics and breeding of Solanum tuberosum. p. 21–28. In: R. Riley & K.R. Lewis (Eds.) Chromosome Manipulations and Plant Genetics. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh.
Peloquin, S.J., G.L. Yerk, J.E. Werner & E. Darmo, 1989. Potato breeding with haploids and 2n gametes. Genome 31: 1000–1004.
Quiros, C.F., 1981. Starch gel electrophoresis techniques used with alfalfa and other Medicago species. Can. J. Plant Sci. 61: 745–749.
Quiros, C.F., 1982. Tetrasomic segregation for multiple alleles in alfalfa. Genet. 101: 117–127.
Quiros, C.F. & N. McHale, 1985. Genetic analysis of isozyme variants in diploid and tetraploid potatoes. Genet. 111: 131–145.
Roose, M.L. & L.D. Gottlieb, 1976. Genetic and biochemical consequences of polyploidy in Tragopogon. Evol. 30: 818–830.
Ross, H., 1986. Potato breeding-problems and perspectives. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin, p. 132.
Rowe, P.R., 1974. Methods of producing haploids: Parthenogenesis following interspecific hybridization. p. 21–28. In: K.J. Kasha (Ed.) Haploids in Higher Plants: Advances and potential, University of Guelph, Guelph.
Rudhe, R.W. & R.E. Hanneman, 1979. Haploid extraction in the cultivar Russet Burbank. Am. Potato J. 56: 587–589.
Spooner, D.M., D.S. Douches & A. Contreras, 1992. Allozyme variation within Solanum sect. Potato, ser. Etuberosa (Solanaceae). Am. J. Bot. 79: 467–471.
Stuber, C.W., J.F. Wendel, M.M. Goodman & J.S.C. Smith, 1988. Techniques and scoring procedures for starch gel electrophoresis from maize (Zea mays L.). Technical Bull. 286. North Carolina Agricultural Research Service, NCSU, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Vallejos, C.E., 1983. Enzyme activity staining. p. 469–516. In: S.D. Tanksley & T.J. Orton (Eds.) Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding, Vol. A. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Van Breukelen, E.W.M., M.S. Ramanna & J.G.Th. Hermsen, 1977. Parthenogenic monohaploid (2n=x=12) from Solanum tuberosum L. and S. verrucosum Schlechtd. and the production of homozygous potato diploids. Euphytica 26: 263–271.
Waara, S., H. Tegelstrom, A. Wallin & T. Eriksson, 1989. Somatic hybridization between anther-derived dihaploid clones of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and the identification of hybrid plants by isozyme analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 77: 49–56.
Wagenheim, K.H. von, S.J. Peloquin & R.W. Hougas, 1960. Embryological investigations on the formation of haploids in the potato (Solanum tuberosum). Z. Vererbungslehre 91: 391–399.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CA., Douches, D.S. Production of haploids of potato (Solanum tuberosum subsp. tuberosum) and their identification with electrophoretic analysis. Euphytica 70, 113–126 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029648
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029648