Abstract
After a reduction of the external phosphorus loading to a lake, an internal loading from the sediments may delay the improvement of the water quality. The accepted method to combat internal loading is careful dredging of the upper sediment layers (Cooke et al., 1986), but this method is costly and time consuming. Addition of phosphorus binding agents to the sediments might offer an alternative. In the Netherlands the use of aluminum compounds, the most common phosphorus binding agent, for water quality improvement purposes is not favoured. Therefore a sediment treatment with a solution of iron(III)chloride was tested. Iron was chosen because it is considered to be a natural binder of phosphate. 100 g m−2 of Fe3+ were added to the sediments of the shallow (1.75 m average depth) and eutrophic Lake Groot Vogelenzang (The Netherlands) in October and November 1989. The iron(III)chloride solution was diluted 100 times with lake water and mixed with the surface sediments with a water jet.
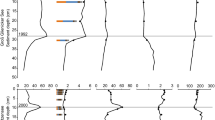
Following the addition the concentrations of total phosphorus (Fig. 1), chlorophyll-a and suspended solids decreased. This improvement of the water quality lasted for three months. After this time the total phosphorus concentration increased again, but remained at a lower level than in spring and summer of 1989. The phosphorus release rate from the sediments as measured from intact sediment cores decreased from 4 to 1.2 mg P m−2 d−1 (n = 5), and the bioavailability of the sediment phosphorus, as measured with bioassays, decreased from 34 to 23% (n = 5) shortly after the treatment. One year after the treatment the release rate was increased to 3 mg P m−2 d−1 (n = 5). Before treatment, the lake was thought to have a residence time of over one year. However, the chloride added to the lake disappeared according to a dilution rate of 0.03 d−1 or a retention time of about 35 days. A high external loading due to rapid flushing with phosphorus-rich water from surrounding lakes possibly prevented a more durable improvement in water quality. Another possibility is that the iron addition has lost its phosphate binding capacity due to reduction or binding with other anions like carbonate or sulphide. Therefore the suitability of the method to reduce internal loading and especially the long term availability of added iron to bind phosphorus needs additional proof.
The treatment of the 18 ha area of Lake Groot Vogelenzang took three weeks. The operational costs were about US$ 125000. This is fast and cheap compared to dredging. Application of the technique is limited to those cases where the sediments are not polluted with micro-pollutants and the water depth need not be increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Peterson & P. R. Newroth, 1986. Lake and reservoir restoration. Butterworths publishers, Boston. 392 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boers, P., Van der Does, J., Quaak, M. et al. Fixation of phosphorus in lake sediments using iron(III)chloride: experiences, expectations. Hydrobiologia 233, 211–212 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016109
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016109