Abstract
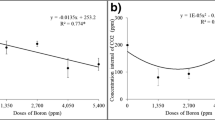
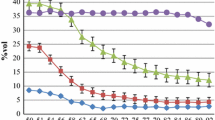
In a greenhouse experiment nine current Australian cultivars of pea were grown to flowering time under five levels of soil boron (0, 10, 20, 30 and 40 mg kg−1) applied to the soil. This study was conducted to identify the genetic range in tolerance to boron within the group and to identify specific responses which may be utilised as selection criteria in a breeding program. Significant differences in response to increasing levels of boron were found between cultivars for dry-weight yield, and boron concentrations were lowest in shoots of the most tolerant cultivars. Of the other parameters measured, emergence was not affected but plant height and the number of nodes were reduced and the severity of symptom expression increased at the higher boron treatments. Symptom expression was the most efficient observation for predicting the response of cultivars, as determined by dry-weight yield and concentration of boron in shoots, and it was found that the correlation coefficients between symptoms and the latter two measurements were r=−0.78 (p<0.01) and r=0.81 (p<0.01), respectively. Early Dun, Dundale, Alma and Maitland were the more tolerant of the cultivars and these happen to be the most widely grown cultivars in southern Australia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers R S and Westcot D W 1976 Water quality for irrigation. Irrigation and drainage paper 29, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nation, Rome Italy. In Toxicity and Deficiency: A Review. U C Gupta, Y M Jame, C A Campbell, A J Leyshon and W Nichlaichuk. Can. J. Soil Sci. 65, 381–409.
Blum A 1988 Plant Breeding for Stress Environments. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Cartwright B, Zarcinas B A and Mayfield A H 1984 Toxic concentrations of boron in a red-brown earth at Gladstone, South Australia. Aust. J. Soil Res. 22, 261–272.
Chauhan R P S and Powar S L 1978 Tolerance of wheat and pea to boron in irrigation water. Plant and Soil 50, 145–149.
Cochran W G and Cox G M 1966 Experimental Designs. Wiley, New York.
Daratech Pty. Ltd. 1988 Field pea (Pisum sativum) variety Dinkum. Plant Varieties J. 1, 19–22.
Eaton F M 1944 Deficiency, toxicity and accumulation of boron in plants. J. Agric. Res. 69, 237–277.
Gupta U C and MacLeod J A 1981 Plant and soil boron as influenced by soil pH and calcium sources on Podzol soils. Soil Sci. 131, 20–25.
Materne M A 1989 Genetic Variability in the Response of Field Pea Varieties to Soil Boron. B. Ag. Sc. (Hons) Thesis, University of Adelaide.
Nable R O, Cartwright B and Lance R C M 1990 Genotypic differences in boron accumulation in barley: Relative susceptibilities to boron deficiency and toxicity. In Genetic Aspects of Plant Nutrition. Eds. N El Bassam, M Dambroth and B C Loughman, pp 361–369. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Nable R O 1988 Resistance to boron toxicity amongst several barley and wheat cultivars: A preliminary examination of the resistance mechanism. Plant and Soil 112, 45–52.
Paull J G, Cartwright B and Rathjen A J 1988 Response of wheat and barley genotypes to toxic concentrations of soil boron. Euphytica 39, 137–144.
Rathjen A J, Cartwright B, Paull J G, Moody D B and Lewis J 1987 Breeding for tolerance of mineral toxicities in Australian cereals with special reference to boron. In Perspectives and Priorities in Plant Production Research. Eds. P G E Searle and B G Davey. pp 111–130. Sydney University Press.
Salinas M R, Cerda A, Romero M. and Caro M 1981 Boron tolerance of pea (Pisum sativum). J. Plant Nutr. 4, 205–215.
Salinas R, Cerda A and Martinez V 1986 The interactive effect of boron and macronutrients (P, K, Ca and Mg) on pod yield and chemical composition of pea (Pisum sativum) Hortic. Sci. 61, 343–347.
Steel R G D and Torrie J H 1960 Principles and Procedures of Statistics. MacGraw-Hill, New York.
Zaricinas B A, Cartwright B and Spouncer L R 1987 Nitric acid digestion and multi-element analysis of plant material by inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 18, 131–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagheri, A., Paull, J.G., Rathjen, A.J. et al. Genetic variation in the response of pea (Pisum sativum L.) to high soil concentrations of boron. Plant Soil 146, 261–269 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012020