Abstract
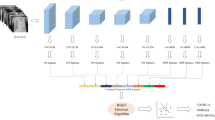
Most attention has been paid to chest Computed Tomography (CT) in this burgeoning crisis because many cases of COVID-19 demonstrate respiratory illness clinically resembling viral pneumonia which persists in prominent visual signatures on high-resolution CT befitting of viruses that damage lungs. However, CT is very expensive, time-consuming, and inaccessible in remote hospitals. As an important complement, this research proposes a novel kNN-regularized Support Vector Machine (kNN-SVM) algorithm for identifying COVID-induced pneumonia from inexpensive and simple frontal chest X-ray (CXR). To compute the deep features, we used transfer learning on the standard VGG16 model. Then the autoencoder algorithm is used for dimensionality reduction. Finally, a novel kNN-regularized Support Vector Machine algorithm is developed and implemented which can successfully classify the three classes: Normal, Pneumonia, and COVID-19 on a benchmark chest X-ray dataset. kNN-SVM combines the properties of two well-known formalisms: k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) and Support Vector Machines (SVMs). Our approach extends the total-margin SVM, which considers the distance of all points from the margin; each point is weighted based on its k nearest neighbors. The intuition is that examples that are mostly surrounded by similar neighbors, i.e., of their own class, are given more priority to minimize the influence of drastic outliers and improve generalization and robustness. Thus, our approach combines the local sensitivity of kNN with the global stability of the total-margin SVM. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed kNN-SVM can detect COVID-19-induced pneumonia from chest X-ray with greater or comparable accuracy relative to human radiologists.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S.E.A.: Reconet: Multi-level preprocessing of chest x-rays for covid-19 detection using convolutional neural networks. MedRxiv (2020)
Al-Waisy, A.S.E.A.: Covid-chexnet: hybrid deep learning framework for identifying covid-19 virus in chest x-rays images. Soft Comput. 1–16 (2020)
Apostolopoulos, I.D., Mpesiana, T.A.: Covid-19: automatic detection from x-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 43(2), 635–640 (2020)
Bassi, P.R., Attux, R.: A deep convolutional neural network for covid-19 detection using chest x-rays. Res. Biomed. Eng. 1–10 (2021)
Belkin, M. et al.: Manifold regularization: a geometric framework for learning from labeled and unlabeled examples. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 2399–2434 (2006)
Bernheim, A.E.A.: Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (covid-19): relationship to duration of infection. Radiology 200463 (2020)
Brunese, L., Mercaldo, F., Reginelli, A., Santone, A.: Explainable deep learning for pulmonary disease and coronavirus covid-19 detection from x-rays. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 196, 105608 (2020)
Cheng, H., Tan, P.N., Jin, R.: Efficient algorithm for localized support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 22(4), 537–549 (2010)
Cohen, J.P., Morrison, P., Dao, L.: Covid-19 image data collection (2020). arXiv:2003.11597. https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset
Cover, T., Hart, P.: Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 13(1), 21–27 (1967)
Crammer, K., Singer, Y., Cristianini, N., Shawe-taylor, J., Williamson, B.: On the algorithmic implementation of multiclass kernel-based vector machines. Mach. Learn. Res. 265–292 (2001)
Das, N.N.E.A.: Automated deep transfer learning-based approach for detection of covid-19 infection in chest x-rays. IRBM (2020)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Hable, R.: Universal consistency of localized versions of regularized kernel methods. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 14(1), 153–186 (2013)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd edn. Springer (2009)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Discriminant adaptive nearest neighbor classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 18(6), 607–616 (1996)
Jaiswal, A.K., Tiwari, P., Rathi, V.K., Qian, J., Pandey, H.M., Albuquerque, V.H.C.: Covidpen: a novel covid-19 detection model using chest x-rays and CT scans. Medrxiv (2020)
Kunapuli, G., Shavlik, J.: Mirror descent for metric learning: a unified approach. In: Proceedings of the ECML ’12, pp. 859–874 (2012)
Ladicky, L., Torr, P.H.S.: Locally linear support vector machines. In: ICML, pp. 985–992 (2011)
Liu, Y.H. et al.: Face recognition using total margin-based adaptive fuzzy support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 18(1), 178–192 (2007)
Lv, D., Qi, W., Li, Y., Sun, L., Wang, Y.: A cascade network for detecting covid-19 using chest x-rays (2020). arXiv:2005.01468
Mei, X., Lee, H.C., Diao, K.y., Huang, M., Lin, B., Liu, C., Xie, Z., Ma, Y., Robson, P.M., Chung, M. et al.: Artificial intelligence–enabled rapid diagnosis of patients with covid-19. Nat. Med. 26(8), 1224–1228 (2020)
Mooney, P.: Kaggle dataset: chest x-ray images (pneumonia) (2017). https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia
Nakayama, H., Yun, Y.: Generating support vector machines using multi-objective optimization and goal programming. In: Jin, Y. (ed.), Multi-Objective Machine Learning, pp. 173–198. Springer (2006)
Ozturk, T., Talo, M., Yildirim, E.A., Baloglu, U.B., Yildirim, O., Acharya, U.R.: Automated detection of covid-19 cases using deep neural networks with x-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103792 (2020)
Panwar, H., Gupta, P., Siddiqui, M.K., Morales-Menendez, R., Singh, V.: Application of deep learning for fast detection of covid-19 in x-rays using ncovnet. Chaos Solitons Fract. 138, 109944 (2020)
Pham, T.D.: Classification of covid-19 chest x-rays with deep learning: new models or fine tuning? Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 9(1), 1–11 (2021)
Rajpurkar, P., Irvin, J., Zhu, K., Yang, B., Mehta, H., Duan, T., Ding, D., Bagul, A., Langlotz, C., Shpanskaya, K., et al.: Chexnet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning (2017). arXiv:1711.05225
Salman, F.M., Abu-Naser, S.S., Alajrami, E., Abu-Nasser, B.S., Alashqar, B.A.: Covid-19 detection using artificial intelligence (2020)
Segata, N., Blanzieri, E., Bottou, L.: Fast and scalable local kernel machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 1883 (2009)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition (2014). arXiv:1409.1556
Suykens, J.A.K., Vandewalle, J.: Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 9(3), 293–300 (1999)
Tsochantaridis, I. et al.: Support vector machine learning for interdependent and structured output spaces. In: In ICML (2004)
Tsochantaridis, I., Joachims, T., Hofmann, T., Altun, Y.: Large margin methods for structured and interdependent output variables. Mach. Learn. Res. 6, 1453–1484 (2005)
Waheed, A., Goyal, M., Gupta, D., Khanna, A., Al-Turjman, F., Pinheiro, P.R.: Covidgan: data augmentation using auxiliary classifier gan for improved covid-19 detection. IEEE Access 8, 91916–91923 (2020)
Wang, Y., Yao, H., Zhao, S.: Auto-encoder based dimensionality reduction. Neurocomputing 184, 232–242 (2016)
Weinberger, K.Q., Saul, L.K.: Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 207–244 (2009). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1577069.1577078
Xu, H., Caramanis, C., Mannor, S.: Robustness and regularization of support vector machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1485–1510 (2009). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1577069.1755834
Xu, L., Schuurmans, D.: Unsupervised and semi-supervised multi-class support vector machines. In: National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. pp. 904–910. AAAI (2005). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1619410.1619478
Yoon, M., Yun, Y., Nakayama, H.: A role of total margin in support vector machines. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 3, pp. 2049–2053 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2003.1223723
Zhang, H.E.A.: Svm-knn: discriminative nearest neighbor classification for visual category recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2. CVPR ’06 (2006)
Zhu, J., Rosset, S., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: 1-norm support vector machines. Technical report, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bahuguna, A., Yadav, D., Senapati, A., Nath Saha, B. (2022). kNN-SVM with Deep Features for COVID-19 Pneumonia Detection from Chest X-ray. In: Rushi Kumar, B., Ponnusamy, S., Giri, D., Thuraisingham, B., Clifton, C.W., Carminati, B. (eds) Mathematics and Computing. ICMC 2022. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 415. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9307-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9307-7_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-9306-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-9307-7
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)