Abstract
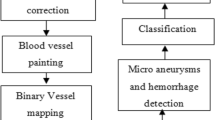
In recent years, heart disease increases the humanity rate transversely the world. So, it is required to extend a model to envisage the heart disease incident as early as feasible with an elevated rate of accuracy. In this study, cardiovascular disease is predicted by a novel method with the retinal image data. In this system, the retinal fundus image data are used to indicate heart disease occurrence. The cardiovascular disease gets detected from the changes in the microvasculature, which is imaged from the retina. The prediction of disease is by considering features like age, gender, smoking status, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and HbA1c that can be extracted using Improved GLCM approach. Then the pointed features can be selected using the ICA algorithm. Risk factors for heart disease occurrence are detected from the microvasculature of ERNN-classified retinal fundus image using MATLAB. The input image is taken from the UCI machine learning repository based on Cleveland datasets. The main objective of the proposed system is to predict the occurrence of heart disease from retinal fundus image with a higher rate of accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaptoge S et al (2019) World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions. Lancet Glob Health 7(10):e1332–e1345
Hervella AS, Rouco J, Novo J, Penedo MG, Ortega M (2020) Deep multi-instance heatmap regression for the detection of retinal vessel crossings and bifurcations in eye fundus images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 186:105201
Herrett E et al (2019) Eligibility and subsequent burden of cardiovascular disease of four strategies for blood pressure-lowering treatment: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet 394(10199):663–671
Naqvi SS, Fatima N, Khan TM, Rehman ZU, Khan MA (2019) Automatic optic disk detection and segmentation by variational active contour estimation in retinal fundus images. SIViP 13(6):1191–1198
Chang J et al (2020) Association of cardiovascular mortality and deep learning-funduscopic atherosclerosis score derived from retinal fundus images. Am J Ophthalmol
Farrah TE, Dhillon B, Keane PA, Webb DJ, Dhaun N (2020) The eye, the kidney cardiovascular disease: old concepts, better tools new horizons. In: Kidney international
Rajan SP (2020) Recognition of cardiovascular diseases through retinal images using optic cup to optic disc ratio. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 30(2):256–263
Ahiante BO, Smith W, Lammertyn L, Schutte AE (2020) Leptin and the retinal microvasculature in young black and white adults: the African-predict study. In: Heart, lung and circulation
Zhang Z, Qiu Y, Yang X, Zhang M (2020) Enhanced character-level deep convolutional neural networks for cardiovascular disease prediction. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 20(3):1–10
Patro SP, Padhy N, Chiranjevi D (2020) Ambient assisted living predictive model for cardiovascular disease prediction using supervised learning. In: Evolutionary intelligence, pp 1–29
Boscari F et al (2020) Performance of the Steno type 1 risk engine for cardiovascular disease prediction in Italian patients with type 1 diabetes. In: Nutrition, metabolism and cardiovascular diseases
Rekha R, Brintha V, Anushree P (2019) Heart disease prediction using retinal fundus image. International conference on artificial intelligence, smart grid and smart city applications. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 765–772
Parameswari C, Ranjani SS (2020) Prediction of atherosclerosis pathology in retinal fundal images with machine learning approaches. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput 1–11
Wong KK, Fortino G, Abbott D (2020) Deep learning-based cardiovascular image diagnosis: a promising challenge. Futur Gener Comput Syst 110:802–811
Lim G, Bellemo V, Xie Y, Lee XQ, Yip MY, Ting DS (2020) Different fundus imaging modalities and technical factors in AI screening for diabetic retinopathy: a review. Eye and Vision 7:1–13
Litjens G et al (2019) State-of-the-art deep learning in cardiovascular image analysis. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging 12(8):1549–1565
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Riedl S, Michl M, Bogunovic´ H (2020) Artificial Intelligence in retinal vascular imaging. In: Retinal vascular disease. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 133–145
Benjamins J, Hendriks T, Knuuti J, Juarez-Orozco L, van der Harst P (2019) A primer in artificial intelligence in cardiovascular medicine. Netherlands Heart J 1–9
Appaji A et al (2019) Retinal vascular tortuosity in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 212:26–32
Amin MS, Chiam YK, Varathan KD (2019) Identification of significant features and data mining techniques in predicting heart disease. Telematics Inform 36:82–93
Mienye ID, Sun Y, Wang Z (2020) An improved ensemble learning approach for the prediction of heart disease risk. Inf Med Unlocked 20:100402
Oh SL et al (2020) Classification of heart sound signals using a novel deep WaveNet model. In: Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, p 105604
Deng Y et al (2020) ST-Net: synthetic ECG tracings for diagnosing various cardiovascular diseases. Biomed Signal Process Control 61:101997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shahina Parveen, M., Hiremath, S. (2023). Cardiovascular Disease Prediction in Retinal Fundus Images Using ERNN Technique. In: Mandal, J.K., De, D. (eds) Frontiers of ICT in Healthcare . Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 519. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5191-6_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5191-6_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5190-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5191-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)