Abstract
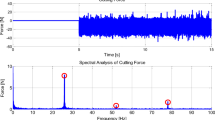
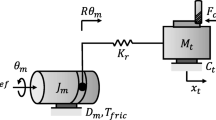
This paper presents numerical results on dampening of cutting force acting on a servo drive positioning system in milling application. In any machining process, accuracy of the servo drive system that governs positioning of the work piece material relatives to the cutting tool are of utmost important. Aside from machine structural vibration and friction, cutting force from the cutting process exerts undesired influence on the servo drive system. Therefore, the servo drive position controller must compensate and damp any acting disturbance force. Disturbance forces are difficult to estimate and physical sensors have various disadvantages such as high cost and reduce reliability. A state observer approach is an attractive alternative to physical sensors. The aim of this work is to estimate and compensate acting disturbance force in milling cutting process simulation via state observer and controller design. The observer was designed based on the principle of conservation of forces utilizing input measurement of relative acceleration of the positioning system. The position cascade P/PI controller and the state observer were designed in MATLAB/SIMULINK environment. The control system performances were measured based on maximum tracking errors for sinusoidal input disturbance signals of single frequency and multi frequency. Numerical results showed reduction of 25.00% and 38.18% in maximum tracking errors signifying the advantages of this control strategy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groover, M.P.: Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems. 6th edn. Wiley Binder (2015)
Kalpakjian, S.: Manufacturing Engineering and Technology. 6th edn. Pearson (2010)
Valentino, J.V., Goldenberg, J.: Introduction to Computer Numerical Control (CNC), 5th edn. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2013)
Nijiri, J.G., Ikua, B.W., Nyakoe, G.N.: Cutting force control for ball end milling of sculptured surfaces using fuzzy logic controller (2012)
Chiew, T.H., Jamaludin, Z., Bani Hashim, A.Y., Leo, K.J., Abdullah, L., Rafan, N.A.: Analysis of tracking performance in machine tools for disturbance forces compensation using sliding mode control and PID controller. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 12, 34–40 (2012)
Altintas, Y., Erkorkmaz, K., Zhu, W.H.: Sliding mode controller design for high speed feed drives. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 49(1), 265–270 (2000)
Heydarzadeh, M.S., Rezaei, S.M., Mardi, N.A., Kamali, E.A.: Motion control of a two-axis linear motor-driven stage in the micro-milling process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 232(1), 65–76 (2018)
Jia, Z.Y., Ma, J.W., Song, D.N., Wang, F.J., Liu, W.: A review of contouring-error reduction method in multi-axis CNC machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 125, 34–54 (2018)
Bao, D.F., Tang, W.C., Dong, L.: Integral sliding mode control for flexible ball screw drives with matched and mismatched uncertainties and disturbances. J. Central South Univ. 24(9), 1992–2000 (2017)
Ozcan, A., Rivière-Lorphèvre, E., Huynh, H.N., Verlinden, O., Filippi, E.: Modelling of pocket milling operation considering cutting forces and CNC control inputs. Procesia CIRP 58, 239–244 (2017)
Rubio, L., Ibeas, A., Luo, X.: P-PI and super twisting sliding mode control schemes comparison for high-precision CNC machining. In: 24th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, ICEE 2016, pp. 1825–1830 (2016)
Hao, W., Zhu, X., Li, X., Turyagyenda, G.: Prediction of cutting force for self-propelled rotary tool using artificial neural networks. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 180(1–3), 23–29 (2006)
Heydarzadeh, M.S., Rezaei, S.M., Azizi, N., Kamali, E.A.: Compensation of friction and force ripples in the estimation of cutting forces by neural networks. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confederation 114, 354–364 (2018)
Kumar, G., Pezhinkattil, R.: A Six Sigma approach for precision machining in milling. In: 12th Global Congress on Manufacturing and Management. Procedia Engineering, vol. 97, pp. 1474–1488 (2014)
Lu, L., Zhang, L., Ji, S., Han, Y., Zhao, J.: An offline predictive feedrate scheduling method for parametric interpolation considering the constraints in trajectory and drive systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 83(9–12), 2143–2157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8112-0
Jamaludin, Z., Brussel, H.V., Swevers, J.: Classical cascade and sliding mode control tracking performances for a XY feed table of a high-speed machine tool. Int. J. Precis. Tech. 1 (1), 65–74 (2007)
Chiew, T.H., et al.: Design and analysis of super twisting sliding mode control for machine tools. Jurnal Teknologi 78(10–3), 25–29 (2016)
İbrahim, K., Nusret, T., Derek, P.A.: Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance. J. Process Control 17(1), 3–16 (2007)
Pritschow, G., Eppler, C., Lehner, W.D.: Ferraris sensor – the key for advanced dynamic drives. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 52(1), 289–292 (2003)
Pritschow, G., Fritz, S., Pruschek, P.: Reconstruction of process forces of direct drives using the Ferraris sensor. In: Proceedings of the VIIth International Conference on Monitoring and Automatic Supervision in Manufacturing AC 2004, Zakopane, pp. 19–21 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend our appreciation to Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan and Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka for the facilities and the research grant provided PJP/2020/FKP/TD/S01724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jamaludin, Z., Hau, P.Y., Heng, C.T., Abdullah, L., Rafan, N.A. (2022). Investigation on Disturbance Force Compensation via State Observer Design and Cascade P/PI Controller Approach. In: Ali Mokhtar, M.N., Jamaludin, Z., Abdul Aziz, M.S., Maslan, M.N., Razak, J.A. (eds) Intelligent Manufacturing and Mechatronics. SympoSIMM 2021. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8954-3_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8954-3_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-8953-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-8954-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)