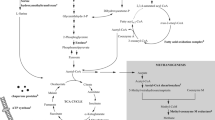
Abstract
The accumulation of solid organic wastes (SOW) has reached critical levels globally and therefore, sustainable management of wastes is the key to minimize the risks to human health, avoid depletion of natural resources, reduce environmental burden and maintain the ecological balance. SOWs mainly include food waste, animal manure, waste activated sludge, yard waste, and agricultural waste. Anaerobic digestion (AD) is one of the most viable and popular technologies for recycling the organic fraction of solid wastes for the production of renewable energy in the form of biogas that can be crucial in meeting the world’s ever-increasing energy demands. Employing sophisticated treatment techniques for the diverse organic fractions present in solid wastes enable proper waste management as well as add value to the economy. Detailed knowledge about the physical properties of these SOWs to determine suitable operating conditions as well as research on the genetic engineering of microbes involved in the AD process are needed to produce biogas efficiently. This chapter summarizes the science underlying the anaerobic digestion process, different feedstock types, the diverse array of microorganisms involved, process variables crucial for AD efficiency, industrial scope of the different reactor modes, and the optimization and pretreatment methods to improve process efficiency.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hajinajaf N, Mehrabadi A, Tavakoli O. Practical strategies to improve harvestable biomass energy yield in microalgal culture: a review. Biomass Bioenergy. 2021;145:105941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105941.
Zhou H, Wen Z. Solid-State anaerobic digestion for waste management and biogas production. In: Steudler S, Werner A, Cheng JJ, editors. Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2019. p. 147–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2019_86.
Mostafazadeh-Fard S, Samani Z, Bandini P. Production of liquid organic fertilizer through anaerobic digestion of grass clippings. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2019;10:771–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0095-7.
Rapport J, Zhang R, Jenkins BM, Williams RB, Schwarzenegger A, Adams LS, Brown MR, Chair B (2008) Current anaerobic digestion technologies used for treatment of municipal organic solid waste.
Ge X, Xu F, Li Y. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass: recent progress and perspectives. Bioresour Technol. 2016;205:239–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.050.
Shi J, Wang Z, Stiverson JA, Yu Z, Li Y. Reactor performance and microbial community dynamics during solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover at mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Bioresour Technol. 2013;136:574–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.073.
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2014) What a waste: a global review of solid waste management cb, Washington, DC.
Ravindran R, Jaiswal AK. A comprehensive review on pre-treatment strategy for lignocellulosic food industry waste: challenges and opportunities. Bioresour Technol. 2016;199:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.106.
Perlack RD, Eaton LM, Turhollow Jr AF, Langholtz MH, Brandt CC, Downing ME, Graham RL, Wright LL, Kavkewitz JM, Shamey AM (2011) US billion-ton update: biomass supply for a bioenergy and bioproducts industry.
Liu S, Li X, Wu S, He J, Pang C, Deng Y, Dong R. Fungal pretreatment by Phanerochaete chrysosporium for enhancement of biogas production from corn stover silage. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;174:1907–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1185-7.
Menardo S, Airoldi G, Balsari P. The effect of particle size and thermal pre-treatment on the methane yield of four agricultural by-products. Bioresour Technol. 2012;104:708–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.061.
Lazarus WF. Economics of anaerobic digesters for processing animal manure. Extension Univ Minnesota; 2015.
Banks CJ, Chesshire M, Heaven S, Arnold R. Anaerobic digestion of source-segregated domestic food waste: performance assessment by mass and energy balance. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:612–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.005.
Mortier N, Velghe F, Verstichel S. Organic recycling of agricultural waste today: composting and anaerobic digestion. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc; 2016.
Yenigün O, Demirel B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: a review. Process Biochem. 2013;48:901–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.04.012.
Melbinger NR, Donnellon J, Zablatzky HR. Toxic effects of ammonia nitrogen in high-rate digestion (with Discussion). J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1971:1658–70.
Albertson OE. Ammonia nitrogen and the anaerobic environment. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1961:978–95.
Appels L, Baeyens J, Degrève J, Dewil R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2008;34:755–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2008.06.002.
Hallaji SM, Kuroshkarim M, Moussavi SP. Enhancing methane production using anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge with combined fruit waste and cheese whey. BMC Biotechnol. 2019;19:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-019-0513-y.
Chow WL, Chong S, Lim JW, Chan YJ, Chong MF, Tiong TJ, Chin JK, Pan G-T. Anaerobic co-digestion of wastewater sludge: a review of potential co-substrates and operating factors for improved methane yield. PRO. 2020;8:39. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010039.
Yao Z, Li W, Kan X, Dai Y, Tong YW, Wang C-H. Anaerobic digestion and gasification hybrid system for potential energy recovery from yard waste and woody biomass. Energy. 2017;124:133–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.035.
Dussadee N, Ramaraj R, Cheunbarn T. Biotechnological application of sustainable biogas production through dry anaerobic digestion of Napier grass. 3 Biotech. 2017;7 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0646-4.
Panigrahi S, Sharma HB, Dubey BK. Overcoming yard waste recalcitrance through four different liquid hot water pretreatment techniques–structural evolution, biogas production and energy balance. Biomass Bioenergy. 2019;127:105268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105268.
Amnuaycheewa P, Hengaroonprasan R, Rattanaporn K, Kirdponpattara S, Cheenkachorn K, Sriariyanun M. Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis and biogas production from rice straw by pretreatment with organic acids. Ind Crop Prod. 2016;87:247–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.069.
Bolado-Rodríguez S, Toquero C, Martín-Juárez J, Travaini R, García-Encina PA. Effect of thermal, acid, alkaline and alkaline-peroxide pretreatments on the biochemical methane potential and kinetics of the anaerobic digestion of wheat straw and sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour Technol. 2016;201:182–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.047.
Mirmohamadsadeghi S, Karimi K, Zamani A, Amiri H, Horváth IS. Enhanced solid-state biogas production from lignocellulosic biomass by organosolv pretreatment. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 2014; https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/350414.
Zhao X, Wang L, Lu X, Zhang S. Pretreatment of corn stover with diluted acetic acid for enhancement of acidogenic fermentation. Bioresour Technol. 2014;158:12–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.122.
Monlau F, Barakat A, Steyer J-P, Carrere H. Comparison of seven types of thermo-chemical pretreatments on the structural features and anaerobic digestion of sunflower stalks. Bioresour Technol. 2012;120:241–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.040.
Tumutegyereize P, Muranga FI, Kawongolo J, Nabugoomu F. Optimization of biogas production from banana peels: effect of particle size on methane yield. Afr J Biotechnol. 2011;10:18243–51.
Stenmarck Å, Jensen C, Quested T, Moates G (2016) Estimates of European food waste levels (FUSION Reducing food waste through social innovation). Stock Sweden.
Bartocci P, Zampilli M, Liberti F, Pistolesi V, Massoli S, Bidini G, Fantozzi F. LCA analysis of food waste co-digestion. Sci Total Environ. 2020;709:136187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136187.
Yong Z, Dong Y, Zhang X, Tan T. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and straw for biogas production. Renew Energy. 2015;78:527–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.01.033.
Zhang Y, Banks CJ. Impact of different particle size distributions on anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2013;33:297–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.01.033.
Safavi SM, Unnthorsson R. Methane yield enhancement via electroporation of organic waste. Waste Manag. 2017;66:61–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.02.032.
Rasapoor M, Ajabshirchi Y, Adl M, Abdi R, Gharibi A. The effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on biogas generation yield from organic fraction of municipal solid waste under medium solids concentration circumstance. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;119:444–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.04.066.
Xu S, Kong X, Liu J, Zhao K, Zhao G, Bahdolla A. Effects of high-pressure extruding pretreatment on MSW upgrading and hydrolysis enhancement. Waste Manag. 2016;58:81–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.07.012.
Amare DE, Ogun MK, Körner I. Anaerobic treatment of deinking sludge: methane production and organic matter degradation. Waste Manag. 2019;85:417–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.12.046.
Zhang Y, Li H. Energy recovery from wastewater treatment plants through sludge anaerobic digestion: effect of low-organic-content sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26:30544–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0184-y.
Giménez JB, Aguado D, Bouzas A, Ferrer J, Seco A. Use of rumen microorganisms to boost the anaerobic biodegradability of microalgae. Algal Res. 2017;24:309–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.04.003.
Klassen V, Blifernez-Klassen O, Wibberg D, Winkler A, Kalinowski J, Posten C, Kruse O. Highly efficient methane generation from untreated microalgae biomass. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017;10:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0871-4.
Kobayashi T, Wu Y-P, Lu Z-J, Xu K-Q. Characterization of anaerobic degradability and kinetics of harvested submerged aquatic weeds used for nutrient phytoremediation. Energies. 2015;8:304–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010304.
Rao MS, Singh SP. Bioenergy conversion studies of organic fraction of MSW: kinetic studies and gas yield–organic loading relationships for process optimisation. Bioresour Technol. 2004;95:173–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.013.
Bi S, Westerholm M, Qiao W, Xiong L, Mahdy A, Yin D, Song Y, Dong R. Metabolic performance of anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under wet, high solid, and dry conditions. Bioresour Technol. 2020;296:122342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122342.
He D, Xiao J, Wang D, Liu X, Fu Q, Li Y, Du M, Yang Q, Liu Y, Wang Q. Digestion liquid based alkaline pretreatment of waste activated sludge promotes methane production from anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2021;199:117198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117198.
Ma S, Wang H, Li L, Gu X, Zhu W. Enhanced biomethane production from corn straw by a novel anaerobic digestion strategy with mechanochemical pretreatment. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2021;146:111099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111099.
Li W, Khalid H, Amin FR, Zhang H, Dai Z, Chen C, Liu G. Biomethane production characteristics, kinetic analysis, and energy potential of different paper wastes in anaerobic digestion. Renew Energy. 2020;157:1081–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.035.
Yue L, Cheng J, Tang S, An X, Hua J, Dong H, Zhou J. Ultrasound and microwave pretreatments promote methane production potential and energy conversion during anaerobic digestion of lipid and food wastes. Energy. 2021;228:120525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120525.
Zinder S. Microbiology of anaerobic conversion of organic wastes to methane: recent developments. Am Soc Microbiol News;(United States). 1984;50(7)
Uçkun Kiran E, Stamatelatou K, Antonopoulou G, Lyberatos G. Production of biogas via anaerobic digestion. Cambridge: Elsevier Ltd.; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100455-5.00010-2.
Ziemiński K. Methane fermentation process as anaerobic digestion of biomass: transformations, stages and microorganisms. Afr J Biotechnol. 2012;11 https://doi.org/10.5897/ajbx11.054.
Ntaikou I, Antonopoulou G, Lyberatos G. Biohydrogen production from biomass and wastes via dark fermentation: a review. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2010;1:21–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-009-9001-2.
Murdoch FK, Murdoch RW, Gürakan GC, Sanin FD. Change of microbial community composition in anaerobic digesters during the degradation of nonylphenol diethoxylate. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2018;135:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.09.002.
Sidhu C, Vikram S, Pinnaka AK. Unraveling the microbial interactions and metabolic potentials in pre-and post-treated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant using metagenomic studies. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:1382. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01382.
Moo-Young M. Comprehensive biotechnology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2019.
Schink B. Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997;61:262–80. https://doi.org/10.1128/.61.2.262-280.1997.
Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Angelidaki I. Influence of environmental conditions on methanogenic compositions in anaerobic biogas reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:331–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.1.331-338.2005.
Demirel B, Scherer P. The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol. 2008;7:173–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9131-1.
Cabezas A, de Araujo JC, Callejas C, Galès A, Hamelin J, Marone A, Sousa DZ, Trably E, Etchebehere C. How to use molecular biology tools for the study of the anaerobic digestion process? Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol. 2015;14:555–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-015-9380-8.
Zhang L, Loh KC, Zhang J. Enhanced biogas production from anaerobic digestion of solid organic wastes: current status and prospects. Bioresour Technol Rep. 2019;5:280–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.07.005.
Cho K, Shin SG, Kim W, Lee J, Lee C, Hwang S. Microbial community shifts in a farm-scale anaerobic digester treating swine waste: correlations between bacteria communities associated with hydrogenotrophic methanogens and environmental conditions. Sci Total Environ. 2017;601:167–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.188.
Lim JW, Ge T, Tong YW. Monitoring of microbial communities in anaerobic digestion sludge for biogas optimisation. Waste Manag. 2018;71:334–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.10.007.
Pham TH, Rabaey K, Aelterman P, Clauwaert P, De Schamphelaire L, Boon N, Verstraete W. Microbial fuel cells in relation to conventional anaerobic digestion technology. Eng Life Sci. 2006;6:285–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200620121.
Goswami R, Chattopadhyay P, Shome A, Banerjee SN, Chakraborty AK, Mathew AK, Chaudhury S. An overview of physico-chemical mechanisms of biogas production by microbial communities: a step towards sustainable waste management. 3 Biotech. 2016;6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0395-9.
Su C, Lei L, Duan Y, Zhang K-Q, Yang J. Culture-independent methods for studying environmental microorganisms: methods, application, and perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;93:993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3800-7.
Riviere D, Desvignes V, Pelletier E, Chaussonnerie S, Guermazi S, Weissenbach J, Li T, Camacho P, Sghir A. Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J. 2009;3:700–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.2.
Shi J, Xu F, Wang Z, Stiverson JA, Yu Z, Li Y. Effects of microbial and non-microbial factors of liquid anaerobic digestion effluent as inoculum on solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour Technol. 2014;157:188–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.089.
Li YF, Shi J, Nelson MC, Chen PH, Graf J, Li Y, Yu Z. Impact of different ratios of feedstock to liquid anaerobic digestion effluent on the performance and microbiome of solid-state anaerobic digesters digesting corn stover. Bioresour Technol. 2016;200:744–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.078.
Li YF, Nelson MC, Chen PH, Graf J, Li Y, Yu Z. Comparison of the microbial communities in solid-state anaerobic digestion (SS-AD) reactors operated at mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:969–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6036-5.
Xu F, Wang ZW, Li Y. Predicting the methane yield of lignocellulosic biomass in mesophilic solid-state anaerobic digestion based on feedstock characteristics and process parameters. Bioresour Technol. 2014;173:168–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.090.
Nayak BS, Levine AD, Cardoso A, Harwood VJ. Microbial population dynamics in laboratory-scale solid waste bioreactors in the presence or absence of biosolids. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;107:1330–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04319.x.
Fdez-Güelfo LA, Álvarez-Gallego C, Sales D, Romero García LI. Dry-thermophilic anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste: methane production modeling. Waste Manag. 2012;32:382–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.11.002.
Weinrich S, Nelles M. Critical comparison of different model structures for the applied simulation of the anaerobic digestion of agricultural energy crops. Bioresour Technol. 2015;178:306–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.138.
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Angelidaki I, Kalyuzhnyi SV, Pavlostathis SG, Rozzi A, Sanders WTM, Siegrist HA, Vavilin VA. The IWA anaerobic digestion model no 1 (ADM1). Water Sci Technol. 2002;45:65–73. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2002.0292.
Liotta F, Chatellier P, Esposito G, Fabbricino M, Frunzo L, Van Hullebusch ED, Lens PNL, Pirozzi F. Modified Anaerobic Digestion Model No.1 for dry and semi-dry anaerobic digestion of solid organic waste. Environ Technol (United Kingdom). 2015;36:870–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.965226.
Bollon J, Le-hyaric R, Benbelkacem H, Buffiere P. Development of a kinetic model for anaerobic dry digestion processes: focus on acetate degradation and moisture content. Biochem Eng J. 2011;56:212–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.06.011.
Abbassi-Guendouz A, Brockmann D, Trably E, Dumas C, Delgenès JP, Steyer JP, Escudié R. Total solids content drives high solid anaerobic digestion via mass transfer limitation. Bioresour Technol. 2012;111:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.174.
Xu F, Wang ZW, Tang L, Li Y. A mass diffusion-based interpretation of the effect of total solids content on solid-state anaerobic digestion of cellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol. 2014;167:178–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.114.
Motte JC, Escudié R, Bernet N, Delgenes JP, Steyer JP, Dumas C. Dynamic effect of total solid content, low substrate/inoculum ratio and particle size on solid-state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol. 2013;144:141–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.057.
Vavilin VA, Lokshina LY, Jokela JPY, Rintala JA. Modeling solid waste decomposition. Bioresour Technol. 2004;94:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.10.034.
Zhang C, Su H, Tan T. Batch and semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of food waste in a dual solid–liquid system. Bioresour Technol. 2013;145:10–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.030.
Mao C, Feng Y, Wang X, Ren G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2015;45:540–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.032.
Bi S, Hong X, Yang H, Yu X, Fang S, Bai Y, Liu J, Gao Y, Yan L, Wang W. Effect of hydraulic retention time on anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure and food waste. Renew Energy. 2020;150:213–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.091.
Gaby JC, Zamanzadeh M, Horn SJ. The effect of temperature and retention time on methane production and microbial community composition in staged anaerobic digesters fed with food waste. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017;10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0989-4.
Mattocks R (1984) Understanding biogas generation (Technical paper No. 4. volunteers in technical Assistance, p. 13). Virginia Volunt Tech Assist, Arlington.
Zhang L, Loh K, Zhang J. Enhanced biogas production from anaerobic digestion of solid organic wastes: current status and prospects. Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering , National University of Singapore , Singapore NUS Environment; 1936. p. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.07.005.
Wang X, Zhang L, Xi B, Sun W, Xia X, Zhu C, He X, Li M, Yang T, Wang P. Biogas production improvement and C/N control by natural clinoptilolite addition into anaerobic co-digestion of Phragmites australis, feces and kitchen waste. Bioresour Technol. 2015;180:192–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.023.
Fricke K, Santen H, Wallmann R, Hüttner A, Dichtl N. Operating problems in anaerobic digestion plants resulting from nitrogen in MSW. Waste Manag. 2007;27:30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.03.003.
Zhou Y, Li C, Nges IA, Liu J. The effects of pre-aeration and inoculation on solid-state anaerobic digestion of rice straw. Bioresour Technol. 2017;224:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.104.
Suksong W, Jehlee A, Singkhala A, Kongjan P, Prasertsan P, Imai T, O-Thong S. Thermophilic solid-state anaerobic digestion of solid waste residues from palm oil mill industry for biogas production. Ind Crop Prod. 2017;95:502–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.11.002.
Choi JH, Jang SK, Kim JH, Park SY, Kim JC, Jeong H, Kim HY, Choi IG. Simultaneous production of glucose, furfural, and ethanol organosolv lignin for total utilization of high recalcitrant biomass by organosolv pretreatment. Renew Energy. 2019;130:952–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.052.
Derman E, Abdulla R, Marbawi H, Sabullah MK. Oil palm empty fruit bunches as a promising feedstock for bioethanol production in Malaysia. Renew Energy. 2018;129:285–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.06.003.
Bauer A, Leonhartsberger C, Bösch P, Amon B, Friedl A, Amon T. Analysis of methane yields from energy crops and agricultural by-products and estimation of energy potential from sustainable crop rotation systems in EU-27. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2010;12:153–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-009-0236-1.
Shahriari H. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste by microwave pretreatment. Unversity of Ottawa. (Ph.D. Dissertation); 2011. https://doi.org/10.20381/ruor-4874.
Vavouraki AI, Angelis EM, Kornaros M. Optimization of thermo-chemical hydrolysis of kitchen wastes. Waste Manag. 2013;33:740–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.07.012.
Sarto S, Hildayati R, Syaichurrozi I. Effect of chemical pretreatment using sulfuric acid on biogas production from water hyacinth and kinetics. Renew Energy. 2019;132:335–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.07.121.
Ariunbaatar J, Panico A, Frunzo L, Esposito G, Lens PNL, Pirozzi F. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of food waste by thermal and ozonation pretreatment methods. J Environ Manag. 2014;146:142–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.07.042.
Shah FA, Mahmood Q, Rashid N, Pervez A, Raja IA, Shah MM. Co-digestion, pretreatment and digester design for enhanced methanogenesis. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2015;42:627–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.053.
Panigrahi S, Dubey BK. A critical review on operating parameters and strategies to improve the biogas yield from anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew Energy. 2019;143:779–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.05.040.
Kiran EU, Stamatelatou K, Antonopoulou G, Lyberatos G. Production of biogas via anaerobic digestion. In: Handbook of biofuels production. Elsevier; 2016. p. 259–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100455-5.00010-2.
Schroyen M, Vervaeren H, Vandepitte H, Van Hulle SWH, Raes K. Effect of enzymatic pretreatment of various lignocellulosic substrates on production of phenolic compounds and biomethane potential. Bioresour Technol. 2015;192:696–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.051.
Schroyen M, Vervaeren H, Van Hulle SWH, Raes K. Impact of enzymatic pretreatment on corn stover degradation and biogas production. Bioresour Technol. 2014;173:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.030.
Ziemiński K, Romanowska I, Kowalska M. Enzymatic pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve biogas production. Waste Manag. 2012;32:1131–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.016.
Zhang Q, He J, Tian M, Mao Z, Tang L, Zhang J, Zhang H. Enhancement of methane production from cassava residues by biological pretreatment using a constructed microbial consortium. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:8899–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.061.
Zhong W, Zhang Z, Luo Y, Sun S, Qiao W, Xiao M. Effect of biological pretreatments in enhancing corn straw biogas production. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:11177–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.077.
Shi J, Sharma-Shivappa RR, Chinn M, Howell N. Effect of microbial pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of cotton stalks for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy. 2009;33:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.04.016.
Ge X, Matsumoto T, Keith L, Li Y. Fungal pretreatment of albizia chips for enhanced biogas production by solid-state anaerobic digestion. Energy Fuel. 2015;29:200–4. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef501922t.
Zhao J, Zheng Y, Li Y. Fungal pretreatment of yard trimmings for enhancement of methane yield from solid-state anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol. 2014;156:176–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.011.
Martinez AT, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Martínez MJ, Del Río JC, Gutierrez A. Enzymatic delignification of plant cell wall: from nature to mill. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2009;20:348–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2009.05.002.
Skiadas IV, Gavala HN, Lu J, Ahring BK. Thermal pre-treatment of primary and secondary sludge at 70 C prior to anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol. 2005;52:161–6. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0512.
Lizasoain J, Trulea A, Gittinger J, Kral I, Piringer G, Schedl A, Nilsen PJ, Potthast A, Gronauer A, Bauer A. Corn stover for biogas production: effect of steam explosion pretreatment on the gas yields and on the biodegradation kinetics of the primary structural compounds. Bioresour Technol. 2017;244:949–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.042.
Carlsson M, Lagerkvist A, Ecke H. Electroporation for enhanced methane yield from municipal solid waste. ORBIT 2008 Mov Org Waste Recycl Towar Resour Manag Biobased Econ. 2008;6:1–8.
Liu CM, Wachemo AC, Yuan HR, Zou DX, Liu YP, Zhang L, Pang YZ, Li XJ. Evaluation of methane yield using acidogenic effluent of NaOH pretreated corn stover in anaerobic digestion. Renew Energy. 2018;116:224–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.07.001.
Capson-Tojo G, Trably E, Rouez M, Crest M, Steyer JP, Delgenès JP, Escudié R. Dry anaerobic digestion of food waste and cardboard at different substrate loads, solid contents and co-digestion proportions. Bioresour Technol. 2017;233:166–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.126.
Fagbohungbe MO, Dodd IC, Herbert BMJ, Li H, Ricketts L, Semple KT. High solid anaerobic digestion: Operational challenges and possibilities. Environ Technol Innov. 2015;4:268–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2015.09.003.
Amani T, Nosrati M, Sreekrishnan TR. Anaerobic digestion from the viewpoint of microbiological, chemical, and operational aspects: a review. Environ Rev. 2010;18:255–78. https://doi.org/10.1139/A10-011.
Wu D, Lü F, Shao L, He P. Effect of cycle digestion time and solid-liquid separation on digestate recirculated one-stage dry anaerobic digestion: use of intact polar lipid analysis for microbes monitoring to enhance process evaluation. Renew Energy. 2017;103:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.11.016.
Fox P, Pohland FG. Anaerobic treatment applications and fundamentals: substrate specificity during phase separation. Water Environ Res. 1994;66:716–24. https://doi.org/10.2175/wer.66.5.8.
Panjičko M, Zupančič GD, Zelić B. Anaerobic biodegradation of raw and pre-treated brewery spent grain utilizing solid state anaerobic digestion. Acta Chim Slov. 2015;62:818–27. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2015.1534.
Nielsen HB, Angelidaki I. Codigestion of manure and industrial organic waste at centralized biogas plants: process imbalances and limitations. Water Sci Technol. 2008;58:1521–8. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2008.507.
Surendra KC, Takara D, Hashimoto AG, Khanal SK. Biogas as a sustainable energy source for developing countries: opportunities and challenges. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2014;31:846–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.12.015.
Korres N, O’Kiely P, Benzie JAH, West JS. Bioenergy production by anaerobic digestion: using agricultural biomass and organic wastes. New York: Routledge; 2013.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Scheme for Promotion of Academic and Research Collaboration (SPARC), MHRD, Govt. of India (Grant No. SPARC/2018-2019/P265/SL). MD thanks the support from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). PP appreciates the support from the Department of Science and Technology (INSPIRE, India for the award of fellowships, DST). AG acknowledges the support from the Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. CRG/2020/002080), Govt. of India. AMV acknowledges start-up funds from the School for Engineering of Matter, Transport and Energy at Arizona State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hajinajaf, N., Das, M., Patra, P., Ghosh, A., Varman, A.M. (2022). Recycling of Multiple Organic Solid Wastes into Biogas via Anaerobic Digestion. In: Fang, Z., Smith Jr., R.L., Xu, L. (eds) Production of Biofuels and Chemicals from Sustainable Recycling of Organic Solid Waste. Biofuels and Biorefineries, vol 11. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6162-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6162-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-6161-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-6162-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)